Related Research Articles
In computer science, formal methods are mathematically rigorous techniques for the specification, development, analysis, and verification of software and hardware systems. The use of formal methods for software and hardware design is motivated by the expectation that, as in other engineering disciplines, performing appropriate mathematical analysis can contribute to the reliability and robustness of a design.
Software design is the process by which an agent creates a specification of a software artifact intended to accomplish goals, using a set of primitive components and subject to constraints. The term is sometimes used broadly to refer to "all the activity involved in conceptualizing, framing, implementing, commissioning, and ultimately modifying" the software, or more specifically "the activity following requirements specification and before programming, as ... [in] a stylized software engineering process."
Rapid application development (RAD), also called rapid application building (RAB), is both a general term for adaptive software development approaches, and the name for James Martin's method of rapid development. In general, RAD approaches to software development put less emphasis on planning and more emphasis on an adaptive process. Prototypes are often used in addition to or sometimes even instead of design specifications.
Software development is the process used to conceive, specify, design, program, document, test, and bug fix in order to create and maintain applications, frameworks, or other software components. Software development involves writing and maintaining the source code, but in a broader sense, it includes all processes from the conception of the desired software through the final manifestation, typically in a planned and structured process often overlapping with software engineering. Software development also includes research, new development, prototyping, modification, reuse, re-engineering, maintenance, or any other activities that result in software products.
A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express data, information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in the structure Programing language.
A platform-independent model (PIM) in software engineering is a model of a software system or business system that is independent of the specific technological platform used to implement it.
Model Driven Architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001.

IDEF, initially an abbreviation of ICAM Definition and renamed in 1999 as Integration Definition, is a family of modeling languages in the field of systems and software engineering. They cover a wide range of uses from functional modeling to data, simulation, object-oriented analysis and design, and knowledge acquisition. These definition languages were developed under funding from U.S. Air Force and, although still most commonly used by them and other military and United States Department of Defense (DoD) agencies, are in the public domain.
In computer science, a metaobject is an object that manipulates, creates, describes, or implements objects. The object that the metaobject pertains to is called the base object. Some information that a metaobject might define includes the base object's type, interface, class, methods, attributes, parse tree, etc. Metaobjects are examples of the computer science concept of reflection, where a system has access to its own internal structure. Reflection enables a system to essentially rewrite itself on the fly, to alter its own implementation as it executes.
Software prototyping is the activity of creating prototypes of software applications, i.e., incomplete versions of the software program being developed. It is an activity that can occur in software development and is comparable to prototyping as known from other fields, such as mechanical engineering or manufacturing.

Business process modeling (BPM) in business process management and systems engineering is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current business processes may be analyzed, improved, and automated. BPM is typically performed by business analysts, who provide expertise in the modeling discipline; by subject matter experts, who have specialized knowledge of the processes being modeled; or more commonly by a team comprising both. Alternatively, the process model can be derived directly from events' logs using process mining tools.
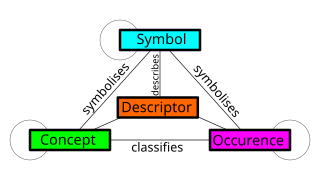
A metamodel is a model of a model, and metamodeling is the process of generating such metamodels. Thus metamodeling or meta-modeling is the analysis, construction and development of the frames, rules, constraints, models and theories applicable and useful for modeling a predefined class of problems. As its name implies, this concept applies the notions of meta- and modeling in software engineering and systems engineering. Metamodels are of many types and have diverse applications.
Object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) is a technical approach for analyzing and designing an application, system, or business by applying object-oriented programming, as well as using visual modeling throughout the software development process to guide stakeholder communication and product quality.
This is an alphabetical list of articles pertaining specifically to software engineering.
A software factory is a structured collection of related software assets that aids in producing computer software applications or software components according to specific, externally defined end-user requirements through an assembly process. A software factory applies manufacturing techniques and principles to software development to mimic the benefits of traditional manufacturing. Software factories are generally involved with outsourced software creation.
Model-driven engineering (MDE) is a software development methodology that focuses on creating and exploiting domain models, which are conceptual models of all the topics related to a specific problem. Hence, it highlights and aims at abstract representations of the knowledge and activities that govern a particular application domain, rather than the computing concepts.
Frames are an artificial intelligence data structure used to divide knowledge into substructures by representing "stereotyped situations". They were proposed by Marvin Minsky in his 1974 article "A Framework for Representing Knowledge". Frames are the primary data structure used in artificial intelligence frame languages; they are stored as ontologies of sets.
Knowledge Discovery Metamodel (KDM) is a publicly available specification from the Object Management Group (OMG). KDM is a common intermediate representation for existing software systems and their operating environments, that defines common metadata required for deep semantic integration of Application Lifecycle Management tools. KDM was designed as the OMG's foundation for software modernization, IT portfolio management and software assurance. KDM uses OMG's Meta-Object Facility to define an XMI interchange format between tools that work with existing software as well as an abstract interface (API) for the next-generation assurance and modernization tools. KDM standardizes existing approaches to knowledge discovery in software engineering artifacts, also known as software mining.
Domain-driven design (DDD) is a major software design approach, focusing on modeling software to match a domain according to input from that domain's experts.
A metaCASE tool is a type of application software that provides the possibility to create one or more modeling methods, languages or notations for use within the process of software development. Often the result is a modeling tool for that language. MetaCASE tools are thus a kind of language workbench, generally considered as being focused on graphical modeling languages.
References
- ↑ Green, Cordell; D. Luckham; R. Balzer; T. Cheatham; C. Rich (Aug 1983). "Report on a Knowledge-Based Software Assistant" (PDF). Kestrel Institute. A996431: 78. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ↑ Rich, Charles; Richard C. Waters (November 1988). "The Programmer's Apprentice Project: A Research Overview" (PDF). Computer. 21 (11): 10–25. doi:10.1109/2.86782. hdl:1721.1/6054. S2CID 18925917. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-07-06. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ↑ DeBellis, Michael; Christine Haapala (February 1995). "User-Centric Software Engineering". IEEE Expert. 10 (1): 34–41. doi:10.1109/64.391959.
- ↑ Smith, Doug (1991). "KIDS - A Knowledge-Based Software Development System". In Michael Lowry, Robert McCartney (ed.). Automating Software Design. AAAI/MIT Press. pp. 483–514. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.54.6955 . ISBN 978-0262620802.
- ↑ Johnson, Lewis; M.S. Feather (1991). "Using Evolution Transformations to Construct Specifications". Automating Software Design. AAAI Press: 65–92.
- ↑ Fowler, Martin (1999). Refactoring: Improving the Design of Existing Code . Addison Wesley. ISBN 0201485672.
- ↑ Boehm, Barry; Prasanta Bose (1998-08-15). "KBSA Life Cycle Evaluation: Final Technical Report" (PDF). Contract No: F30602-96-C-0274. USC Center for Software Engineering. I. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
As the program has proceeded toward its ultimate objectives, it has spawned a number of productivity-enhancing spinoffs such as the Refine-based software reengineering and testing tools
- ↑ Welty, Chris. "Summary of KBSE-93: The Eighth Annual Knowledge-Based Software Engineering Conference". ase-conferences.org. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
REFINE/COBOL Object Modeling Workbench provides a set of reengineering tools, Refine is the language of the KBSA concept demo.
- ↑ Harris, Dave; A. Czuchry (1988). "The Knowledge-Based Requirements Assistant". IEEE Expert. 3 (4).
- ↑ Johnson, Lewis; David R. Harris; Kevin M. Benner; Martin S. Feather (October 1992). "Aries: The Requirements/Specification Facet for KBSA". Rome Laboratory Final Technical Report. RL-TR-92-248.
- ↑ DeBellis, Michael; Kanth Miriyala; Sudin Bhat; William C. Sasso; Owen Rambo (April 1993). "KBSA Concept Demo: Final Technical Report". USAF Rome Laboratory Technical Report. RL-TR-93-38. Retrieved 25 October 2021.
