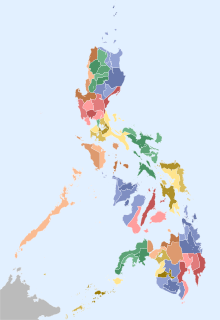
In the Philippines, provinces are one of its primary political and administrative divisions. There are 81 provinces at present, which are further subdivided into component cities and municipalities. The local government units in the National Capital Region, as well as independent cities, are independent of any provincial government. Each province is governed by an elected legislature called the Sangguniang Panlalawigan and an elected governor.
Congress of the Philippines is the national legislature of the Philippines. It is a bicameral body consisting of the Senate, and the House of Representatives, although colloquially, the term "Congress" commonly refers to just the latter.

The House of Representatives of the Philippines is the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines. It is commonly referred to as the Congress, the House of the People, and informally referred to as the Cámara or Kamara.

Elections in the Philippines are of several types. The president, vice-president, and the senators are elected for a six-year term, while the members of the House of Representatives, governors, vice-governors, members of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan, mayors, vice-mayors, members of the Sangguniang Panlungsod/members of the Sangguniang Bayan, barangay officials, and the members of the Sangguniang Kabataan are elected to serve for a three-year term.
The legislative districts of Aklan are the representations of the province of Aklan in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its first and second congressional districts.
The legislative districts of Davao City are the representations of the highly urbanized city of Davao in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The city is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its first, second, and third congressional districts.
The legislative districts of Sulu are the representations of the province of Sulu in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its first and second congressional districts.
The legislative district of Tawi-Tawi is the representation of the province of Tawi-Tawi in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its lone congressional district.
The legislative districts of Leyte are the representations of the province of Leyte, the independent component city of Ormoc, and highly urbanized city of Tacloban in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province, together with the independent cities are currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through their first, second, third, fourth, and fifth congressional districts.
The legislative districts of Maguindanao are the representations of the province of Maguindanao and the independent component city of Cotabato in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province and the city are currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through their first and second congressional districts.
The legislative districts of Cotabato are the representations of the province of Cotabato in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its first, second, and third congressional districts.
The legislative district of Sarangani is the representation of the province of Sarangani in the Congress of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress through its lone congressional district.
The legislative districts of South Cotabato are the representations of the province of South Cotabato and the highly urbanized city of General Santos in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its first and second congressional districts.

The legislative districts of Sultan Kudarat are the representations of the province of Sultan Kudarat in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its first and second congressional districts.
Officially local government in the Philippines, often called local government units or LGUs, are divided into three levels – provinces and independent cities; component cities and municipalities; and barangays. In one area, above provinces and independent cities, is an autonomous region, the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao. Below barangays in some cities and municipalities are sitios and puroks. All of these, with the exception of sitios and puroks, elect their own executives and legislatures. Sitios and puroks are often led by elected barangay councilors.

The 2019 Philippine House of Representatives elections were the 35th lower house elections in the Philippines. They were held on May 13, 2019 to elect members to the House of Representatives.

The 2019 Philippine general election was conducted on May 13, 2019. A midterm election, those elected therein will take office on June 30, 2019, midway through the term of President Rodrigo Duterte.
The legislative district of General Santos will be the representation of the highly urbanized city of General Santos in the Congress of the Philippines. The city will be represented in the lower house of the Congress through its lone congressional district after the 2022 Philippine general elections.

Southern Leyte's at-large congressional district refers to the lone congressional district of the Philippines in the province of Southern Leyte. It has been represented in the House of Representatives of the Philippines since 1961. Southern Leyte first elected a single representative provincewide at-large for the 5th Congress of the Third Philippine Republic following its creation as a regular province separate from Leyte under Republic Act No. 2227 on May 22, 1959. Before 1959, its territory was represented as part of Leyte's at-large, 2nd and 3rd districts. Between 1978 and 1984, multi-seat regional delegations were formed in lieu of provinces for the Fourth Philippine Republic parliament known as the Interim Batasang Pambansa, with Southern Leyte forming part of the ten-seat Region VIII's at-large district. It was restored as a single-member district in 1984.
The 2022 Philippine House of Representatives elections will be the 36th lower house elections in the Philippines. The election is scheduled to be held on May 9, 2022.








