The provinces of the Philippines are the primary political and administrative divisions of the Philippines. There are 81 provinces at present, further subdivided into component cities and municipalities. The local government units in the National Capital Region, as well as independent cities, are independent of any provincial government. Each province is governed by an elected legislature called the Sangguniang Panlalawigan and an elected governor.

Benguet, officially the Province of Benguet, is a landlocked province of the Philippines located in the southern tip of the Cordillera Administrative Region in the island of Luzon. Its capital is La Trinidad.

Mountain Province is a landlocked province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Bontoc.

Apayao is a landlocked province in the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital town is Kabugao.

Kalinga-Apayao was a province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in the island of Luzon. It was divided into the two provinces of Kalinga and Apayao with the passage of Philippine Republic Act No. 7878 on February 14, 1995. This RA amended the earlier Republic Act No. 4695, passed on June 18, 1966, which formed the provinces of Kalinga-Apayao, Benguet, Ifugao, and Mountain Province, from the earlier Mountain Province.

Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR), also known as Cordillera Region, is an administrative region in the Philippines, situated within the island of Luzon. The only landlocked region in the insular country, it is bordered by the Ilocos Region to west and southwest, and by the Cagayan Valley Region to the north, east, and southeast. It is the least populous region in the Philippines, with a population less than that of the City of Manila.

The Igorot are any of various ethnic groups in the mountains of northern Luzon, Philippines, all of whom keep, or have kept until recently, their traditional religion and way of life. Some live in the tropical forests of the foothills, but most live in rugged grassland and pine forest zones higher up. The Igorot numbered about 1.5 million in the early 21st century. Their languages belong to the northern Luzon subgroup of the Philippine languages, which belong to the Austronesian (Malayo-Polynesian) family.
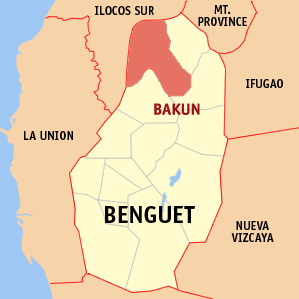
Bakun, officially the Municipality of Bakun,, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Benguet, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 15,357 people.

Abra is a landlocked province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Bangued, and is bordered by Ilocos Norte on the northwest, Apayao on the northeast, Kalinga on the mid-east, Mountain Province on the southeast, and Ilocos Sur on the southwest.

The legislative district of Mindanao and Sulu was the collective representation of the Department of Mindanao and Sulu and its component provinces of Agusan, Bukidnon, Cotabato, Davao, Lanao, Sulu and Zamboanga as a single at-large district in the lower house of the Philippine Legislature from 1916 until 1935.
The legislative district of Zamboanga was the representation of the historical province of Zamboanga in the various national legislatures of the Philippines until 1953. The undivided province's representation encompassed the present-day provinces of Basilan, Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur and Zamboanga Sibugay, and the highly urbanized city of Zamboanga.
The legislative district of Apayao is the representation of the province of Apayao in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its lone congressional district.
The legislative district of Kalinga is the representation of the province of Kalinga in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its lone congressional district.
The legislative district of Baguio is the representation of the highly urbanized city of Baguio in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The city is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its lone congressional district.
The legislative district of Benguet is the representation of the province of Benguet in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its lone congressional district.
The legislative district of Kalinga-Apayao was the representation of the historical province of Kalinga-Apayao in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. Since 1998, the province has been represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through the separate lone congressional districts of Apayao and Kalinga.
The legislative district of Ifugao is the representation of the province of Ifugao in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its lone congressional district.

The Igorot Society is the term for the collection of several ethnic groups in the Philippines that come from the Cordillera Administrative Region of Luzon. They inhabit the six provinces of Abra, Apayao, Benguet, Kalinga, Ifugao, and Mountain Province, as well as Baguio. They are a pre-Hispanic highland society that has survived through Spanish colonization. This state is the oldest in the Philippines and its culture is one of the oldest Austronesian cultures and social structures outside of Taiwan. This society predates the other pre-Hispanic states in the Philippines which are maritime civilizations, in contrast to this society which is a mountainous high-land society. This society is composed of many tribes, mainly the Bontoc, Ibaloi, Isnag, Kalinga, and the Kankanaey.
The sub-provinces of the Philippines were a political and administrative division of the Philippines. The sub-provinces were a part of a larger "regular" province and residents of a sub-province participated in provincial elections of the parent province.

A plebiscite for the ratification of the organic act creating the Cordillera Autonomous Region was held on January 30, 1990, to ask if the voters in the Cordillera Administrative Region wanted to be an autonomous region under Republic Act No. 6766. The Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) consists of the provinces of Abra, Benguet, Ifugao, Kalinga-Apayao, and Mountain Province, and the city of Baguio. Only Ifugao voted in favor of autonomy, and a Supreme Court case later disallowed the creation of an autonomous region with just one province.













