
Small hydro is the development of hydroelectric power on a scale suitable for local community and industry, or to contribute to distributed generation in a regional electricity grid. Precise definitions vary, but a "small hydro" project is less than 50 megawatts (MW), and can be further subdivide by scale into "mini" (<1MW), "micro" (<100 kW), "pico" (<10 kW). In contrast many hydroelectric projects are of enormous size, such as the generating plant at the Three Gorges Dam at 22,500 megawatts or the vast multiple projects of the Tennessee Valley Authority.

Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potential energy of water, pumped from a lower elevation reservoir to a higher elevation. Low-cost surplus off-peak electric power is typically used to run the pumps. During periods of high electrical demand, the stored water is released through turbines to produce electric power. Although the losses of the pumping process make the plant a net consumer of energy overall, the system increases revenue by selling more electricity during periods of peak demand, when electricity prices are highest. If the upper lake collects significant rainfall or is fed by a river then the plant may be a net energy producer in the manner of a traditional hydroelectric plant.

Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity produced from hydropower. In 2015, hydropower generated 16.6% of the world's total electricity and 70% of all renewable electricity, and was expected to increase by about 3.1% each year for the next 25 years.

Manitoba Hydro is the electric power and natural gas utility in the province of Manitoba, Canada. Founded in 1961, it is a provincial Crown Corporation, governed by the Manitoba Hydro-Electric Board and the Manitoba Hydro Act. Today the company operates 15 interconnected generating stations. It has more than 527,000 electric power customers and more than 263,000 natural gas customers. Since most of the electrical energy is provided by hydroelectric power, the utility has low electricity rates. Stations in Northern Manitoba are connected by a HVDC system, the Nelson River Bipole, to customers in the south. The internal staff are members of the Canadian Union of Public Employees Local 998 while the outside workers are members of the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers Local 2034.

Nagarjuna Sagar Dam is a masonry dam across the Krishna River at Nagarjuna Sagar which straddles the border between Guntur district in Andhra Pradesh and Nalgonda district in Telangana.
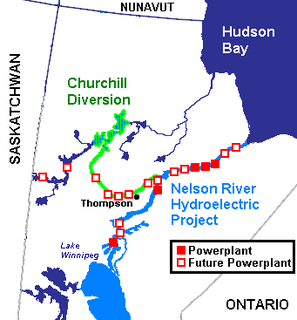
The Nelson River Hydroelectric Project refers to the construction of a series of dams and hydroelectric power plants on the Nelson River in Northern Manitoba, Canada. The project began to take shape in the late 1950s, with the planning and construction of the Kelsey dam and hydroelectric power station, and later was expanded to include the diversion of the upper Churchill River into the Nelson River and the transformation of Lake Winnipeg, the world's 11th largest freshwater lake, into a hydroelectric reservoir. The project is owned and operated by Manitoba Hydro, the electrical utility in the province.

Himachal Pradesh is extremely rich in its hydroelectricity resources. The state has about twenty five percent of the national potential. About 27,436 MW of hydroelectric power can be generated in the state by the construction of various hydroelectric projects on the five perennial river basins. Out of total hydroelectric potential of the state, 10,519 MW is harnessed so far, out of which only 7.6% is under the control of Himachal Pradesh Government while the rest is exploited by the Central Government. The state government has been giving the highest priority for its development, since hydroelectric generation can meet the growing need of power for industry, agriculture and rural electrification. It is also the biggest source of income to the state as it provides electricity to other states.

The Zhiguli Hydroelectric Station or Zhigulyovskaya Hydroelectric Station, formerly known as Kuybyshev Hydroelectric Station is a large dam and hydroelectric station on the Volga River, located near Zhigulyovsk and Tolyatti in Samara Oblast of Russia. It is the sixth stage of the Volga-Kama Cascade of dams, and the second of them by installed power.

NHPC Limited is an Indian Hydropower generation company that was incorporated in the year 1975 with an authorised capital of Rs. 2000 million and with an objective to plan, promote and organise an integrated and efficient development of hydroelectric power in all aspects. Later on NHPC expanded its objects to include other sources of energy like Solar, Geothermal, Tidal, Wind etc.
According to the International Hydropower Association Canada is the world's fourth largest producer of hydroelectricity in the world in 2020 after the United States, Brazil, and China. In 2014, Canada consumed the equivalent of 85.7 megatonnes worth of oil of hydroelectricity, 9.8% of worldwide hydroelectric consumption. Furthermore, hydroelectricity accounted for 25.7% of Canada's total energy consumption. It is the third-most consumed energy in Canada behind oil and natural gas.

The Koyna Hydroelectric Project is the largest completed hydroelectric power plant in India. It is a complex project with four dams including the largest dam on the Koyna River, Maharashtra hence the name Koyna Hydroelectric Project. The project site is in Satara district near Patan.

The Koldam Hydropower Station commonly known as Koldam, is an embankment dam on the Satluj River upstream of the Dehar Power House. It is 18 km from Bilaspur off the Chandigarh-Manali Highway (NH-21) near Barmana, Himachal Pradesh, India. The main purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it will support an 800 MW power station. The dam was constructed by National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC).
Sri Damodaram Sanjeevaiah Thermal Power Station is located in Nelatur Village, near Krishnapatnam and at a distance of 23 km from Nellore city of Andhra Pradesh. The power plant is one of the coal-based power plants of Andhra Pradesh Power Development Company Limited (APPDCL). It is the Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), a joint venture company of APGENCO and IL AND FS partnership.

Nagarjuna Sagar tail pond is a multipurpose reservoir located 21 km downstream from the Nagarjuna Sagar Dam across the Krishna River near Satrasala in Nalgonda district, India. Its gross water storage capacity is 6 Tmcft. The reservoir water spread area extends up to the toe of the Nagarjuna Sagar dam. The project was completed by July 2014.

Duber Khwar Hydropower Plant is located near the town of Pattan in Kohistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan on the Duber Khwar River, a right bank tributary of Indus River. It is approximately 300 km NW from Islamabad, the federal capital of Islamic Republic of Pakistan.
Solapur Super Thermal Power Station is under construction located at Fatatewadi and Aherwadi village in Solapur district in Indian state of Maharashtra. The power plant is one of the coal based power plants of National Thermal Power Corporation Limited (NTPCL).

Kopili Hydro Electric Project is a 275 megawatts (369,000 hp), hydroelectric power project on the Kopili river and its tributary, Umrong stream. It is located in Dima Hasao district of Assam state in India. The project is developed and operated by North Eastern Electric Power Corporation Limited. It is an important project since the indian State of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura benefit from this project.














