Ice-rich mantle
Much of the surface of Mars is covered by a thick smooth mantle that is thought to be a mixture of ice and dust. [3] This ice-rich mantle, a few yards thick, smoothes the land, but in places it has a bumpy texture, resembling the surface of a basketball. Because there are few craters on this mantle, the mantle is relatively young. An image below shows a good view of this smooth mantle around Niger Vallis, as observed with HiRISE.

High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction of the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. It consists of a 0.5 m (19.7 in) aperture reflecting telescope, the largest so far of any deep space mission, which allows it to take pictures of Mars with resolutions of 0.3 m/pixel, resolving objects below a meter across.
Changes in Mars's orbit and tilt cause significant changes in the distribution of water ice from polar regions down to latitudes equivalent to Texas. During certain climate periods water vapor leaves polar ice and enters the atmosphere. The water comes back to ground at lower latitudes as deposits of frost or snow mixed generously with dust. The atmosphere of Mars contains a great deal of fine dust particles. Water vapor will condense on the particles, then fall down to the ground due to the additional weight of the water coating. When ice at the top of the mantling layer goes back into the atmosphere, it leaves behind dust, which insulates the remaining ice. [4]
Niger Vallis with features typical of this latitude, as seen by
HiRISE. Click on image to see chevron pattern and mantle.

Terra Cimmeria is a large Martian region, centered at 34.7°S 145°E and covering 5,400 km (3,400 mi) at its broadest extent. It covers latitudes 15 N to 75 S and longitudes 170 to 260 W. It lies in the Eridania quadrangle. Terra Cimmeria is one part of the heavily cratered, southern highland region of the planet. The Spirit rover landed near the area.
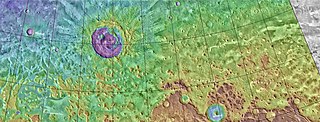
Deuteronilus Mensae is a region on Mars 937 km across and centered at 43.9°N 337.4°W. It covers 344°–325° West and 40°–48° North. Deuteronilus region lies just to the north of Arabia Terra and is included in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. It is along the dichotomy boundary, that is between the old, heavily cratered southern highlands and the low plains of the northern hemisphere. The region contains flat-topped knobby terrain that may have been formed by glaciers at some time in the past. Deuteronilus Mensae is to the immediate west of Protonilus Mensae and Ismeniae Fossae. Glaciers persist in the region in modern times, with at least one glacier estimated to have formed as recently as 100,000 to 10,000 years ago. Recent evidence from the radar on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has shown that parts of Deuteronilus Mensae do indeed contain ice.

The Diacria quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northwestern portion of Mars’ western hemisphere and covers 180° to 240° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Diacria quadrangle is also referred to as MC-2. The Diacria quadrangle covers parts of Arcadia Planitia and Amazonis Planitia.

The Arcadia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars’ western hemisphere and covers 240° to 300° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Arcadia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-3.

The Mare Acidalium quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars’ western hemisphere and covers 300° to 360° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Mare Acidalium quadrangle is also referred to as MC-4.

The Hellas quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Hellas quadrangle is also referred to as MC-28 . The Hellas quadrangle covers the area from 240° to 300° west longitude and 30° to 65° south latitude on the planet Mars. Within the Hellas quadrangle lies the classic features Hellas Planitia and Promethei Terra. Many interesting and mysterious features have been discovered in the Hellas quadrangle, including the giant river valleys Dao Vallis, Niger Vallis, Harmakhis, and Reull Vallis—all of which may have contributed water to a lake in the Hellas basin in the distant past. Many places in the Hellas quadrangle show signs of ice in the ground, especially places with glacier-like flow features.

The Eridania quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Eridania quadrangle is also referred to as MC-29.
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24.

The Thaumasia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Thaumasia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-25 . The name comes from Thaumas, the god of the clouds and celestial apparitions.

The Argyre quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Argyre quadrangle is also referred to as MC-26. It contains Argyre Planitia and part of Noachis Terra.

Ptolemaeus is a crater on Mars, found in the Phaethontis quadrangle at 46.21° south latitude and 157.6° west longitude. It measures approximately 165 kilometers in diameter and was named after Claudius Ptolemaeus (Ptolemy), the Greco-Egyptian astronomer. Mantle material that is believed to have fallen from the sky is visible in the crater.

Tader Valles is a set of small channels in the Phaethontis quadrangle found at 49.1° south latitude and 152.5° west longitude. it is named after the ancient name for present Segura River, Spain.

Gorgonum Chaos is a set of canyons in the Phaethontis quadrangle of Mars. It is located at 37.5° south latitude and 170.9° west longitude. Its name comes from an albedo feature at 24S, 154W. Some of the first gullies on Mars were found in Gorgonum Chaos. It is generally believed that it once contained a lake. Other nearby features are Sirenum Fossae, Maadim Vallis, Ariadnes Colles, and Atlantis Chaos. Some of the surfaces in the region are formed from the Electris deposits.

Martian gullies are small, incised networks of narrow channels and their associated downslope sediment deposits, found on the planet of Mars. They are named for their resemblance to terrestrial gullies. First discovered on images from Mars Global Surveyor, they occur on steep slopes, especially on the walls of craters. Usually, each gully has a dendritic alcove at its head, a fan-shaped apron at its base, and a single thread of incised channel linking the two, giving the whole gully an hourglass shape. They are estimated to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters. A subclass of gullies is also found cut into the faces of sand dunes, that are themselves considered to be quite young. Linear dune gullies are now considered recurrent seasonnal afeatures.
To date, interplanetary spacecraft have provided abundant evidence of water on Mars, dating back to the Mariner 9 mission, which arrived at Mars in 1971. This article provides a mission by mission breakdown of the discoveries they have made. For a more comprehensive description of evidence for water on Mars today, and the history of water on that planet, see Water on Mars.

Glaciers, loosely defined as patches of currently or recently flowing ice, are thought to be present across large but restricted areas of the modern Martian surface, and are inferred to have been more widely distributed at times in the past. Lobate convex features on the surface known as viscous flow features and lobate debris aprons, which show the characteristics of non-Newtonian flow, are now almost unanimously regarded as true glaciers.

Perepelkin Crater is an impact crater in the Arcadia quadrangle of the planet Mars. It is located at 52.8°N latitude and 64.6°W longitude. It is 77 km in diameter. It was named after Russian astronomer Yevgeny Perepyolkin.

Much of the Martian surface is covered with a thick ice-rich, mantle layer that has fallen from the sky a number of times in the past. In some places a number of layers are visible in the mantle.

Aonia Terra is a region in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mars. It is named after a classical albedo feature Aonia, that was named after the ancient Greek region Aonia.























