In planetary nomenclature, a fossa is a long, narrow depression (trough) on the surface of an extraterrestrial body, such as a planet or moon. The term, which means "ditch" or "trench" in Latin, is not a geological term as such but a descriptor term used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the International Astronomical Union (IAU) for topographic features whose geology or geomorphology is uncertain due to lack of data or knowledge of the exact processes that formed them. Fossae are believed to be the result of a number of geological processes, such as faulting or subsidence. Many fossae on Mars are probably graben.

The Memnonia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Memnonia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-16.

Columbus Crater is a crater in the Terra Sirenum of Mars, located at 29.8° south latitude and 166.1° west longitude. It is 119 km in diameter and was named after Christopher Columbus, Italian explorer (1451–1506). The discovery of sulfates and clay minerals in sediments within Columbus Crater are strong evidence that a lake once existed in the crater. Research with an orbiting near-infrared spectrometer, which reveals the types of minerals present based on the wavelengths of light they absorb, found evidence of layers of both clay and sulfates in Columbus crater. This is exactly what would appear if a large lake had slowly evaporated. Moreover, because some layers contained gypsum, a sulfate which forms in relatively fresh water, life could have formed in the crater.

Bernard is a large crater in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars, located at 23.4° south latitude and 154.2° west longitude. It is 128 km in diameter and was named after P. Bernard, a French atmospheric scientist. The floor of the crater contains large cracks, which may be due to erosion.

Dejnev is a crater on Mars, located in the Memnonia quadrangle at 25.1° south latitude and 164.8° west longitude. It was named after Russian geographer, explorer, and navigator Semyon Dezhnev (1605–1673). The name was adopted by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature in 1985.

Saheki is a crater on Mars, located in the Iapygia quadrangle at 21.75° S and 286.97° W. It measures approximately 82 kilometers in diameter and was named after Tsuneo Saheki, a Japanese amateur astronomer (1916–1996). The naming was adopted by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature in 2006.
Sklodowska is a crater on Mars, located in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle at 33.7°N and 2.9°W. It measures 109.72 kilometres (68.2 mi) in diameter and was named after Polish chemist and first female Nobel Laureate Marie Skłodowska Curie (1867–1934). The naming was approved in 1973, by the International Astronomical Union's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature.

Arrhenius is an impact crater in the Eridania quadrangle on Mars at 40.3° S and 237.4° W. and is 129.0 km (80.2 mi) in diameter. Its name, for Svante Arrhenius, was approved in 1973 by the IAU. Evidence of previous glacial activity is evident in images. There also appear to be branched channels just outside the crater.

Focas Crater is an impact crater in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle of Mars. It is located at 33.9° N and 347.3° W and its name was approved in 1973. Focas Crater is 76.5 km in diameter. It was named after Jean Focas. Pictures reveal many small channels along its rim; some are visible in pictures below from CTX.

Ejriksson Crater is an impact crater in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars, located at 19.4°S latitude and 173.9°W longitude. It is 49.0 km in diameter. It was named after the explorer Leif Erikson, and the name was approved in 1967.

Wells is an impact crater in the Eridania quadrangle on Mars. The crater was named after English writer H. G. Wells (1866–1946). The name was approved in 1973, by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature. Wells is the author of the science-fiction novel The War of the Worlds, depicting an invasion of earth by Martians.

Jones is an impact crater on Mars, located at 19.1°S 19.9°W in the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle. It measures 94.0 kilometer in diameter and was named after English astronomer Harold Spencer Jones (1890–1960). The name was approved in 1973, by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN).

Vinogradov is an impact crater in the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle of Mars, located at 20.2°S latitude and 37.7°W longitude. It measures 223.5 kilometres (138.9 mi) in diameter and was named after Alexander Pavlovich Vinogradov, and the name was approved in 1979 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN).

Vinogradsky is an impact crater in the Eridania quadrangle of Mars, located at 56.5°S latitude and 216.2°W longitude. It measures 64 kilometres (40 mi) in diameter and was named after Sergei Winogradsky. The name was approved in 1973, by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature.
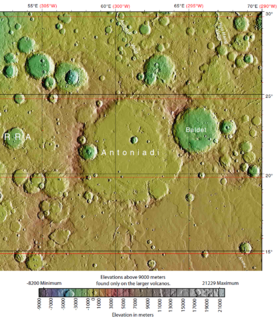
Baldet Crater is an impact crater in the Syrtis Major quadrangle of Mars, located at 23.0°N latitude and 294.6°W longitude. It is 180.0 km in diameter and was named after Fernand Baldet, and the name was approved in 1973 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN).

Millochau is an impact crater on Mars, located in the Iapygia quadrangle at 21.4°S latitude and 275.0°W longitude. It measures 115 kilometers in diameter and was named after French astronomer Gaston Millochau. The naming was approved by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature in 1973.

Smith is an impact crater on Mars, located in the Mare Australe quadrangle at 66.1°S latitude and 102.9°W longitude. It measures 74.33 kilometres (46.19 mi) in diameter and was named after English geologist William Smith (1769–1839). The name was approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature in 1973.

Holmes is an impact crater in the Mare Australe quadrangle of Mars, located at 75.0°S latitude and 293.2°W longitude. It is 122.0 km in diameter and was named after Arthur Holmes, and the name was approved in 1973 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN).

Comas Sola is an impact crater on Mars, located in the Memnonia quadrangle at 19.59°S latitude and 158.51°W longitude. It measures 120.24 km (74.71 mi) in diameter. It was named after the Spanish Catalan astronomer Josep Comas Solá. The name was approved by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature in 1973.

Koval'sky is an impact crater on Mars, located in the southernmost area of the Memnonia quadrangle at 29.56° south and longitude 141.54° west. It measures approximately 297 kilometers in diameter. Its name refers to Polish–Russian astronomer Marian Kowalski (1821–1884).




















