
Grise Fiord, is an Inuit hamlet in the Qikiqtaaluk Region in the territory of Nunavut, Canada. Despite its low population, it is the largest community on Ellesmere Island. It is also one of the coldest inhabited places in the world, with an average yearly temperature of −16.5 °C (2.3 °F).

Milford Sound / Piopiotahi is a fiord in the south west of New Zealand's South Island within Fiordland National Park, Piopiotahi Marine Reserve, and the Te Wahipounamu World Heritage site. It has been judged the world's top travel destination in an international survey and is acclaimed as New Zealand's most famous tourist destination. Rudyard Kipling had previously called it the eighth Wonder of the World.

Fiordland is a geographic region of New Zealand in the south-western corner of the South Island, comprising the western-most third of Southland. Most of Fiordland is dominated by the steep sides of the snow-capped Southern Alps, deep lakes, and its steep, glacier-carved and now ocean-flooded western valleys. The name "Fiordland" comes from a variant spelling of the Scandinavian word for this type of steep valley, "fjord". The area of Fiordland is dominated by, and very roughly coterminous with, Fiordland National Park, New Zealand's largest National Park.
Quttinirpaaq National Park is a Canadian national park. Located on the northeastern corner of Ellesmere Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, the most northerly extent of Canada, it is the second most northerly park on Earth after Northeast Greenland National Park. In Inuktitut, Quttinirpaaq means "top of the world". It was established as Ellesmere Island National Park Reserve in 1988, and the name was changed to Quttinirpaaq in 1999, when Nunavut was created, and became a national park in 2000. The reserve covers 37,775 square kilometres (14,585 sq mi), making it the second largest park in Canada, after Wood Buffalo National Park.

Fiordland National Park occupies the southwest corner of the South Island of New Zealand. It is by far the largest of the 14 national parks in New Zealand, with an area of 12,607 square kilometres (4,868 sq mi), and a major part of the Te Wahipounamu World Heritage site. The park is administered by the Department of Conservation.

Lake Te Anau is in the southwestern corner of the South Island of New Zealand. The lake covers an area of 344 km2 (133 sq mi), making it the second-largest lake by surface area in New Zealand and the largest in the South Island. It is the largest lake in Australasia by fresh water volume.

The Eglinton River is located in the region of Southland in the southwest of New Zealand. It flows through Fiordland National Park for 50 kilometres (31 mi). Its headwaters are at Lake Gunn, 25 kilometres (16 mi) east of Milford Sound, and it flows generally south before entering Lake Te Anau along the lake's eastern shore opposite the entrance to North Fiord.

Misty Fiords National Monument is a national monument and wilderness area administered by the U.S. Forest Service as part of the Tongass National Forest. Misty Fiords is about 40 miles (64 km) east of Ketchikan, Alaska, along the Inside Passage coast in extreme southeastern Alaska, comprising 2,294,343 acres (928,488 ha) of Tongass National Forest in Alaska's Panhandle. All but 151,832 acres (61,444 ha) are designated as wilderness.
Innuit Mountain is a mountain located 30 km (19 mi) northwest of Mount Caubvick in the Torngat Mountains of northern Labrador, Canada.

The Osborn Range is a small mountain range located on the northwest flank of Tanquary Fiord on north-central Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada. It lies just outside Quttinirpaaq National Park and is one of the northernmost mountain ranges in the world forming part of the Arctic Cordillera.

Ayr Pass is a mountain pass in the central Baffin Mountains, Nunavut, Canada.
Strand Fiord Pass is a mountain pass on southern Axel Heiberg Island, Nunavut, Canada.
Ukpik Peak is a mountain associated with the Baffin Mountains on Baffin Island, Nunavut, Canada.
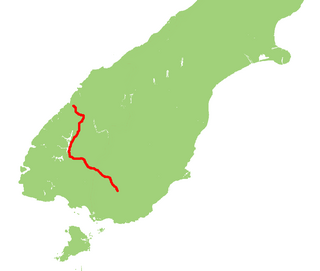
State Highway 94 is a New Zealand state highway connecting the large Southland town of Gore with one of New Zealand's most popular destinations, Milford Sound. It also passes the significant townships of Lumsden and Te Anau as well going through the Homer Tunnel. The road also goes through Fiordland and crosses the Main Divide of the Southern Alps.

The Kanguk Formation is a geological formation in the Northwest Territories of Canada whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
The Wapiti River is a river in the Southland Region of New Zealand. It rises in the northern extremity of the Stuart Mountains in Fiordland National Park, the top of its watershed being part of the main divide. Two branches feed Lake Sutherland, the outflow of which flows southwest to Lake Thomson. A further 2.2 kilometres (1.4 mi) reach of the river heads east to Lake Hankinson, which is separated from the North West Arm of the Middle Fiord of Lake Te Anau by a final 0.6-kilometre (0.4 mi) stretch of the river.

Ayr Lake is a land-locked freshwater fjord on Baffin Island's northeastern coast in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. The Inuit settlement of Pond Inlet is 360 km (220 mi) to the northwest and Clyde River is 35 km (22 mi) to the east.
















