Related Research Articles

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

The Thiel Mountains are isolated, mainly snow-capped mountains of the Transantarctic Mountains System, located in the Ellsworth Land region of Antarctica. The mountain range is 45 nautical miles long, is located roughly between the Horlick Mountains and the Pensacola Mountains, and extends from Moulton Escarpment on the west to Nolan Pillar on the east. Major components include Ford Massif, Bermel Escarpment and a group of eastern peaks near Nolan Pillar.
The Reedy Glacier is a major glacier in Antarctica, over 100 nautical miles long and 6 to 12 nautical miles wide, descending from the polar plateau to the Ross Ice Shelf between the Michigan Plateau and Wisconsin Range in the Transantarctic Mountains. It marks the limits of the Queen Maud Mountains on the west and the Horlick Mountains on the east.

The Darwin Glacier is a large glacier in Antarctica. It flows from the polar plateau eastward between the Darwin Mountains and the Cook Mountains to the Ross Ice Shelf. The Darwin and its major tributary the Hatherton are often treated as one system, the Darwin–Hatherton.

Ferrar Glacier is a glacier in Antarctica. It is about 35 nautical miles long, flowing from the plateau of Victoria Land west of the Royal Society Range to New Harbour in McMurdo Sound. The glacier makes a right (east) turn northeast of Knobhead, where it where it is apposed, i.e., joined in Siamese-twin fashion, to Taylor Glacier. From there, it continues east along the south side of Kukri Hills to New Harbor.
Kohler Range is a mountain range in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. The range is about 40 nautical miles long and stands between the base of Martin Peninsula and Smith Glacier. The range consists of two ice-covered plateaus punctuated by several rock peaks and bluffs. The plateaus are oriented East-West and are separated by the Kohler Glacier, a distributary which flows north from Smith Glacier.
The Metropolitan School District of Lawrence Township is a school district in Lawrence Township in northeast Marion County, Indianapolis, Indiana. It covers an area of 48 square miles (120 km2) and in 2010 had a student enrollment just under 16,000.

Mac. Robertson Land is the portion of Antarctica lying southward of the coast between William Scoresby Bay and Cape Darnley. It is located at 70°00′S65°00′E. In the east, Mac. Robertson Land includes the Prince Charles Mountains. It was named by the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) (1929–1931), under Sir Douglas Mawson, after Sir Macpherson Robertson of Melbourne, a patron of the expedition.
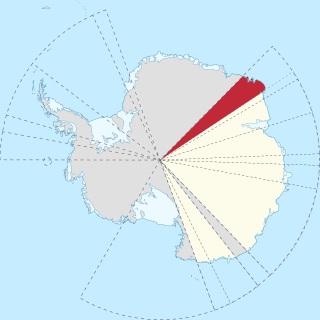
Enderby Land is a projecting landmass of Antarctica. Its shore extends from Shinnan Glacier at about 67°55′S44°38′E to William Scoresby Bay at 67°24′S59°34′E, approximately 1⁄24 of the earth's longitude. It was first documented in western and eastern literature in February 1831 by John Biscoe aboard the whaling brig Tula, and named after the Enderby Brothers of London, the ship's owners who encouraged their captains to combine exploration with sealing.
Arrow Lakes Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada.

Kongsfjorden is an inlet on the west coast of Spitsbergen, an island which is part of the Svalbard archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. The inlet is 26 km (16 mi) long and ranges in width from 6 to 14 km. Two glaciers, Kronebreen and Kongsvegen, head the fjord.
The Stikine Ranges are a group of mountain ranges and mountainous plateaus in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. They are the northernmost subdivision of the Cassiar Mountains and among the least explored and most undeveloped parts of the province.

The Treuter Mountains, formerly known as the Truter Mountains and the Trenter Mountains, are a small mountain range on eastern Devon Island, Nunavut, Canada. The Treuter Mountains are part of the Devon Ice Cap which forms part of the Arctic Cordillera mountain range.
The Iroquois Plateau is a large, mainly ice-covered plateau situated east of the southern part of the Washington Escarpment in the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica.
Arrowstone Provincial Park is a provincial park in the Thompson Country of the Southern Interior of British Columbia, Canada, located to the northeast of the town of Cache Creek. The park was established by Order-in-Council in 1996 with an area of 6203 hectares. In 2000 its boundaries were slightly reduced, such that its area is now 6175 hectares.
The Pembroke Range is a small mountain range in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, between Loughborough Inlet and Phillips Arm. It has an area of 75 km2 and is a subrange of the Pacific Ranges which in turn form part of the Coast Mountains.

Bluie was the United States military code name for Greenland during World War II. It is remembered by the numbered sequence of base locations identified by the 1941 United States Coast Guard South Greenland Survey Expedition, and subsequently used in radio communications by airmen unfamiliar with pronunciation of the Greenlandic Inuit and Danish names of those locations. These were typically spoken BLUIE (direction) (number), with direction being east or west along the Greenland coast from Cape Farewell.
Rennick Glacier is broad glacier, nearly 200 nautical miles long, which is one of the largest in Antarctica. It rises on the polar plateau westward of Mesa Range and is 20 to 30 nautical miles wide, narrowing to 10 nautical miles near the coast. It takes its name from Rennick Bay where the glacier reaches the sea.

Carey Glacier is a glacier on the east side of Miller and Fruzhin Peaks and west of Ruset and Malkoch Peaks in Petvar Heights at the southeast end of the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains, flowing southeast to Minnesota Glacier. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1957–59, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant David W. Carey, pilot with U.S. Navy Squadron VX-6, who was killed in the crash of a P2V Neptune airplane at McMurdo Sound in October 1956.

Wessbecher Glacier is a glacier about 7 nautical miles (13 km) long, draining southeast from Mount Inderbitzen and south from Mount Mullen between Peristera Peak, Lishness Peak and Stikal Peak on the main ridge of Sentinel Range on the west and Marze Peak in Petvar Heights on the east, in the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica.