| starch synthase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
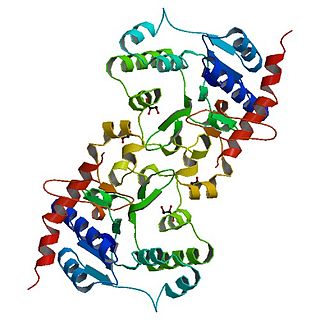
 Crystal structure of glycogen synthase 1 from Agrobacterium tumefaciens | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 2.4.1.21 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9030-10-8 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In enzymology, a starch synthase (EC 2.4.1.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- ADP-glucose + (1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl)n ADP + (1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl)n+1
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ADP-glucose and a chain of D-glucose residues joined by 1,4-alpha-glycosidic bonds, whereas its two products are ADP and an elongated chain of glucose residues. Plants use these enzymes in the biosynthesis of starch.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hexosyltransferases, specifically the glycosyltransferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ADP-glucose:1,4-alpha-D-glucan 4-alpha-D-glucosyltransferase. Other names in common use include ADP-glucose-starch glucosyltransferase, adenosine diphosphate glucose-starch glucosyltransferase, adenosine diphosphoglucose-starch glucosyltransferase, ADP-glucose starch synthase, ADP-glucose synthase, ADP-glucose transglucosylase, ADP-glucose-starch glucosyltransferase, ADPG starch synthetase, and ADPG-starch glucosyltransferase
Five isoforms seems to be present. GBSS which is linked to amylose synthesis. The others are SS1, SS2, SS3 and SS4. These have different roles in amylopectin synthesis. New work implies that SS4 is important for granule initiation. (Szydlowski et al., 2011)