Related Research Articles

French Polynesia is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) in the South Pacific Ocean. The total land area of French Polynesia is 3,521 square kilometres (1,359 sq mi), with a population of 278,786 of which at least 205,000 live in the Society Islands and the remaining population lives in the rest of the archipelago.
Demographic features of the population of French Polynesia include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects.

Tahiti is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Australia. Divided into two parts, Tahiti Nui and Tahiti Iti, the island was formed from volcanic activity; it is high and mountainous with surrounding coral reefs. Its population was 189,517 in 2017, making it by far the most populous island in French Polynesia and accounting for 68.7% of its total population; the 2022 Census recorded a population of 191,779.
In Tahiti and adjacent islands, the term Maohi refers to the ancestors of the Polynesian peoples.
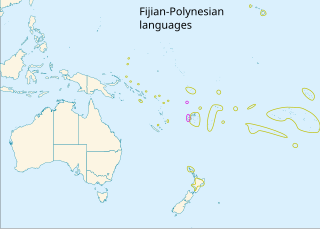
The Polynesian languages form a genealogical group of languages, itself part of the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family.
Tahitian is a Polynesian language, spoken mainly on the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It belongs to the Eastern Polynesian group.
Tahitian or Tahitians may refer to:

Papeete is the capital city of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of the French Republic in the Pacific Ocean. The commune of Papeete is located on the island of Tahiti, in the administrative subdivision of the Windward Islands, of which Papeete is the administrative capital. Both the President of French Polynesia and French High Commissioner reside in Papeete.

Bora Bora is an island group in the Leeward Islands in the South Pacific. The Leeward Islands comprise the western part of the Society Islands of French Polynesia, which is an overseas collectivity of the French Republic in the Pacific Ocean. Bora Bora has a total land area of 30.55 km2 (12 sq mi). The main island, located about 230 kilometres northwest of Papeete, is surrounded by a lagoon and a barrier reef. In the center of the island are the remnants of an extinct volcano, rising to two peaks, Mount Pahia and Mount Otemanu; the highest point is at 727 m (2,385 ft). Bora Bora is part of the Commune of Bora-Bora, which also includes the atoll of Tūpai. The main languages spoken in Bora Bora are Tahitian and French. However, due to the high tourist population, many natives of Bora Bora have learned to speak English.

Po‘e or poke is a Polynesian pudding usually eaten as a dessert.
Rapa is the language of Rapa Iti, in the Austral Islands of French Polynesia, and of Mangaia in the Cook Islands. It is an Eastern Polynesian language. There are three varieties of the Rapa language currently being spoken in French Polynesia: Old Rapa, Reo Rapa and New Rapa. Old Rapa has been mostly replaced by Reo Rapa, a mix of the more commonly spoken Tahitian and Old Rapa. New Rapa – revitalized Old Rapa – is commonly spoken by middle-aged and younger speakers. Rapa is a critically endangered language, and there are only around 300 speakers of Reo Rapa, with only 15% of them able to speak Old Rapa. It may be more vibrant on Mangaia, but there the population has been declining for half a century due to emigration.
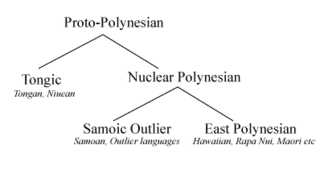
Nuclear Polynesian refers to those languages comprising the Samoic and the Eastern Polynesian branches of the Polynesian group of Austronesian languages.

Morinda is a multi-level marketing company based in American Fork, Utah that sells Tahitian Noni juice and other products made from the noni plant. The company was founded in 1996 and has manufacturing facilities in Tahiti, Japan, China, Germany, and Utah. Morinda, formerly known as Tahitian Noni International and Morinda Bioactives, was a subsidiary of Morinda Holdings, Inc. prior to merging with and becoming a wholly owned subsidiary of New Age Beverages Corporation in December 2019.
Tuamotuan, Paʻumotu or Paumotu is a Polynesian language spoken by 4,000 people in the Tuamotu archipelago, with an additional 2,000 speakers in Tahiti.
Mangareva, Mangarevan is a Polynesian language spoken by about 600 people in the Gambier Islands of French Polynesia and by Mangarevians emigrants on the islands of Tahiti and Moorea, located 1,650 kilometres (1,030 mi) to the North-West of the Gambier Islands.
Austral is an endangered Polynesian language or a dialect continuum that was spoken by approximately 8,000 people in 1987 on the Austral Islands and the Society Islands of French Polynesia. The language is also referred to as Tubuai-Rurutu, Tubuai, Rurutu-Tupuai, or Tupuai. It is closely related to other Tahitic languages, most notably Tahitian and Māori.
The Penrhyn language is a Cook Islands Maori dialectal variant belonging to the Polynesian language family. It is spoken by about 200 people on Penrhyn Island and other islands in the Northern Cook Islands. It is considered to be an endangered language as many of its users are shifting to Cook Islands Māori and English.

The Tahitians are the Indigenous Polynesian people of Tahiti and thirteen other Society Islands in French Polynesia. The numbers may also include the modern population in these islands of mixed Polynesian and French ancestry. Indigenous Tahitians are one of the largest Polynesian ethnic groups, behind the Māori, Samoans and Hawaiians.

When Will You Marry? is an oil painting from 1892 by the French Post-Impressionist artist Paul Gauguin. On loan to the Kunstmuseum in Basel, Switzerland for nearly a half-century, it was sold privately by the family of Rudolf Staechelin to Sheikha Al-Mayassa bint Hamad Al-Thani, in February 2015 for close to US$210 million, one of the highest prices ever paid for a work of art. The painting was on exhibition at the Fondation Beyeler, Riehen, until 28 June 2015.

"Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui" is the territorial anthem of the overseas country of French Polynesia. It is sung during public or sport events alongside the French national anthem, "La Marseillaise". The lyrics are in Tahitian. It was adopted on 10 June 1993 by the Assembly of French Polynesia with the Loi du Pays 1993-60.