
Aransas County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2010 census, the population was 23,158. Its county seat is Rockport. Aransas County is part of the Corpus Christi Metropolitan Statistical Area.

The Texas Hill Country is a geographic region of Central and South Texas, forming the southeast part of the Edwards Plateau. Given its location, climate, terrain, and vegetation, the Hill Country can be considered the border between the American Southeast and Southwest. The region represents the very remote rural countryside of Central Texas, but also is home to growing suburban neighborhoods and affluent retirement communities.

South Texas is a region of the U.S. state of Texas that lies roughly south of—and includes—San Antonio. The southern and western boundary is the Rio Grande, and to the east it is the Gulf of Mexico. The population of this region is about 4.96 million according to the 2017 census estimates. The southern portion of this region is often referred to as the Rio Grande Valley. The eastern portion along the Gulf of Mexico is also referred to as the Coastal Bend.

Aransas Pass is a navigable salt water channel connecting the Gulf of Mexico with Aransas Bay on the Texas Gulf coast in the United States. The pass separates Mustang Island to the south from San José Island to the north, and is protected by jetties extending into the Gulf from both islands. At the eastern end of the pass is the town of Port Aransas, located at the far northern end of Mustang Island. At the western end of the pass, on the mainland side of Aransas Bay, is the town of Aransas Pass. A free ferry serves the two towns. The pass is located on the Aransas County and Nueces County line.
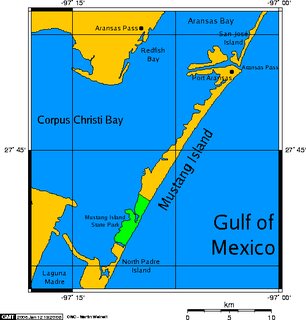
Mustang Island is a barrier island on the Gulf Coast of Texas in the United States. The island is 18 miles (29 km) long, stretching from Corpus Christi to Port Aransas. The island is oriented generally northeast–southwest, with the Gulf of Mexico on the east and south, and Corpus Christi Bay on the north and west. The island's southern end connects by roadway to Padre Island. At the northern end of the island is Port Aransas, beyond which is San José Island. The Aransas Channel, also known as the "Aransas Pass," which separates Mustang Island from San José Island, is protected by jetties extending into the Gulf from each island.

Aransas Bay is a bay on the Texas Gulf Coast, approximately 30 miles (48 km) northeast of Corpus Christi, and 173 miles (278 km) south of San Antonio. It is separated from the Gulf of Mexico by San José Island. Aransas Pass is the most direct navigable outlet into the Gulf of Mexico from the bay. The cities of Aransas Pass and Port Aransas are located at the southern end, and Rockport is found on the central western shore. The bay is oriented laterally northeast-southwest, and is extended by Redfish Bay to the southwest, Copano Bay to the west, Saint Charles Bay to the north, and Mesquite Bay to the northeast. Aransas Bay is part of the Mission-Aransas National Estuarine Research Reserve.

Corpus Christi Bay is a scenic semi-tropical bay on the Texas coast found in San Patricio and Nueces counties, next to the major city of Corpus Christi. It is separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Mustang Island, and is fed by the Nueces River and Oso Creek from its western and southern extensions, Nueces Bay and Oso Bay. The bay is located approximately 136 miles (219 km) south of San Antonio, and 179 miles (288 km) southwest of Houston.

San Antonio Bay is a bay on the Texas Gulf Coast situated between Matagorda and Aransas Bay. It consists mainly of the combined waters of the San Antonio and Guadalupe rivers, and is located at the mouth of the Guadalupe River, about 55 miles (89 km) northeast of Corpus Christi and 130 miles (209 km) southeast of San Antonio. It is protected from the Gulf of Mexico by Matagorda Island, leaving only relatively small and distant outlets to the Gulf for little mixing of bay and Gulf waters. The remoteness of the bay has prevented the establishment of major ports as seen on Aransas Bay and Corpus Christi Bay, to the south.

The Coastal Bend Council of Governments (CBCOG) is a voluntary association of cities, counties and special districts in South Texas.

San Marcos Springs is the second largest natural cluster of springs in Texas. The springs are located in the city of San Marcos, Texas, about 30 miles (48 km) southwest of Austin and 46 miles (74 km) northeast of San Antonio.

San Pedro Springs is the name of a cluster of springs in Bexar County, Texas, U.S.A. These springs provide water for San Pedro Creek, which flows into the San Antonio River. The San Antonio Springs also feed into the San Antonio River.

State Highway 361 is a state highway in San Patricio and Nueces counties that runs from Gregory in southern Texas, near Corpus Christi, east and south to Padre Island on the Gulf of Mexico coast.

The Corpus Christi Harbor Bridge is a through arch bridge located in Corpus Christi, Texas which carries six lanes of U.S. Route 181 (US 181) and Texas State Highway 35 (SH 35) from downtown Corpus Christi to Rincon Point, known to locals as North Beach. The harbor bridge crosses the Corpus Christi Ship Channel and handles nearly 26,000 vehicles daily. A new bridge called the New Harbor Bridge is currently under construction. When complete it will allow larger ships to pass beneath, permit safer pedestrian transit, and reconfigure the entire highway interchange system in the surrounding community.

Nueces Bay is a northwestern extension of Corpus Christi Bay in the San Patricio and Nueces Counties of Texas. The bay is fed by the Nueces River, forming a natural estuary, which renders it ecologically and economically vital to the surrounding area. It serves as a habitat for the propagation of fish and shellfish, which sustain diverse species of birds and other wildlife. The bay is threatened by pollution from the heavy industry on its southern shore, which prevents oyster farming. Petrochemical production and oil are important to the surrounding economies of the major settlements of Corpus Christi and Portland, found on the eastern shore and connected by the Nueces Bay Causeway at the bay's confluence with Corpus Christi Bay.
The Mission-Aransas National Estuarine Research Reserve, currently directed by Jace Tunnell, is a large contiguous complex of wetland, terrestrial, and marine environments on the Texas Coastal Bend in the United States. Named for the two major rivers that flow into the area, the reserve contains public and private lands and waters. The land is primarily coastal prairie with unique oak motte habitats. The wetlands include riparian habitat, freshwater marshes, and saltwater marshes. Within the water areas, the bays are large, open, and include extensive tidal flats, seagrass meadows, mangroves, and oyster reefs. These unique and diverse estuarine habitats in the western Gulf of Mexico support a host of endangered and threatened species including the endangered whooping crane.

The Great Texas Coastal Birding Trail is a state-designated system of trails, bird sanctuaries, and nature preserves along the entire length of the Texas Gulf Coast in the United States. As the state of Texas hosts more bird species than any other state in the U.S. the trail system offers some of the most unusual opportunities for bird-watching in the world. The "trail" is actually 43 separate hiking and driving trails that include 308 birding sites. The sites themselves feature a variety of viewing opportunities with boardwalks, observation decks, and other amenities. The trails boast more than 450 bird species. The trail system is managed by the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department as part of the Great Texas Wildlife Trails which also include the Heart of Texas Wildlife Trail, the Panhandle Plains Wildlife Trail, and the Prairies and Pineywoods Wildlife Trail.

Redfish Bay is a southwestern extension of Aransas Bay in Texas, north of Corpus Christi Bay. It separates the cities of Aransas Pass and Ingleside from Port Aransas on Mustang Island.

The Laguna Madre is a long, shallow, hypersaline lagoon along the western coast of the Gulf of Mexico in Nueces, Kenedy, Kleberg, Willacy and Cameron Counties in Texas, United States. It is one of seven major estuaries along the Gulf Coast of Texas. The roughly 20-mile (32 km) long Saltillo Flats land bridge divides it into Upper and Lower lagoons joined by the Intracoastal Waterway, which has been dredged through the lagoon. Cumulatively, Laguna Madre is approximately 130 miles (210 km) long, the length of Padre Island in the US. The main extensions include Baffin Bay in Upper Laguna Madre, Red Fish Bay just below the Saltillo Flats, and South Bay near the Mexican border. As a natural ecological unit, the Laguna Madre of the United States is the northern half of the ecosystem as a whole, which extends into Tamaulipas, Mexico approximately 144 miles (232 km) south of the US border, to the vicinity of the Rio Soto La Marina and the town of La Pesca, extending approximately 275 miles (443 km) through USA and Mexico in total.
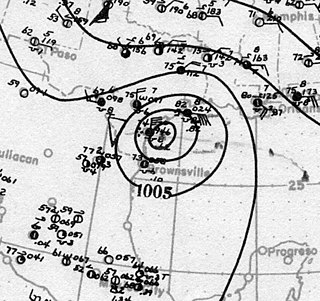
The effects of the 1919 Florida Keys hurricane in Texas were the deadliest of any tropical cyclone in the Texas Coastal Bend, killing at least 284 people. The hurricane produced a widespread swath of devastation across the region, exacerbated by the large extent of its winds. The city of Corpus Christi bore the brunt of the hurricane's impacts, contributing to the largest portion of the damage toll in Texas; nearly all of the confirmed fatalities were residents of the city. The storm originated from the Leeward Islands early in September 1919 and took a generally west-northwestward course, devastating the Florida Keys en route to the Gulf of Mexico. On the afternoon of September 14, the center of the hurricane made landfall upon the Texas coast at Baffin Bay. The storm's winds were estimated at 115 mph (185 km/h) at landfall, making it a Category 3 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. After slowly moving ashore, it weakened and straddled the Rio Grande before dissipating on September 16 over West Texas.

The U.S. state of Texas has a series of estuaries along its coast on the Gulf of Mexico, most of them bounded by the Texas barrier islands. Estuaries are coastal bodies of water in which freshwater from rivers mixes with saltwater from the sea. Twenty-one drainage basins terminate along the Texas coastline, forming a chain of seven major and five minor estuaries: listed from southwest to northeast, these are the Rio Grande Estuary, Laguna Madre, the Nueces Estuary, the Mission–Aransas Estuary, the Guadalupe Estuary, the Colorado–Lavaca Estuary, East Matagorda Bay, the San Bernard River and Cedar Lakes Estuary, the Brazos River Estuary, Christmas Bay, the Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary, and the Sabine–Neches Estuary. Each estuary is named for its one or two chief contributing rivers, excepting Laguna Madre, East Matagorda Bay, and Christmas Bay, which have no major river sources. The estuaries are also sometimes referred to by the names of their respective primary or central water bodies, though each also includes smaller secondary bays, inlets, or other marginal water bodies.




















