
A sailing vessel's rig is its arrangement of masts, sails and rigging. Examples include a schooner rig, cutter rig, junk rig, etc. A rig may be broadly categorized as "fore-and-aft", "square", or a combination of both. Within the fore-and-aft category there is a variety of triangular and quadrilateral sail shapes. Spars or battens may be used to help shape a given kind of sail. Each rig may be described with a sail plan—formally, a drawing of a vessel, viewed from the side.

Yacht racing is a sailing sport involving sailing yachts and larger sailboats, as distinguished from dinghy racing, which involves open boats. It is composed of multiple yachts, in direct competition, racing around a course marked by buoys or other fixed navigational devices or racing longer distances across open water from point-to-point. It can involve a series of races with buoy racing or multiple legs when point-to-point racing.

A catboat is a sailboat with a single sail on a single mast set well forward in the bow of a very beamy and (usually) shallow draft hull. Typically they are gaff rigged, though Bermuda rig is also used. Most are fitted with a centreboard, although some have a keel. The hull can be 3.7 to 12.2 metres long with a beam half as wide as the hull length at the waterline. The type is mainly found on that part of the Eastern seaboard of the USA from New Jersey to Massachusetts.

Dinghy sailing is the activity of sailing small boats by using five essential controls:

A maxi yacht usually refers to a racing yacht of at least 21 metres (70 ft) in length.

Dinghy racing is a competitive sport using dinghies, which are small boats which may be rowboats, have an outboard motor, or be sailing dinghies. Dinghy racing has affected aspects of the modern sailing dinghy, including hull design, sail materials and sailplan, and techniques such as planing and trapezing.

The Albacore is a 4.57 m (15 ft) two-person planing dinghy with fractional sloop rig, for competitive racing and lake and near-inshore day sailing. Hulls are made of either wood or fiberglass. The basic shape was developed in 1954 from an Uffa Fox design, the Swordfish. Recent boats retain the same classic dimensions, and use modern materials and modern control systems.

Gaff rig is a sailing rig in which the sail is four-cornered, fore-and-aft rigged, controlled at its peak and, usually, its entire head by a spar (pole) called the gaff. Because of the size and shape of the sail, a gaff rig will have running backstays rather than permanent backstays.
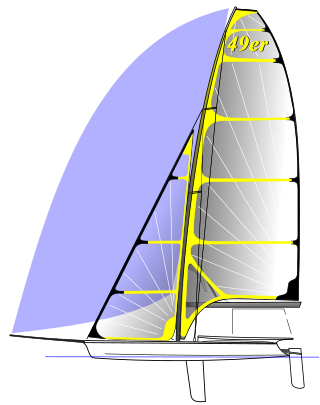
The 49er and 49er FX is a two-handed skiff-type high-performance sailing dinghy. The two crew work on different roles with the helm making many tactical decisions, as well as steering, and the crew doing most of the sail control. Both of the crew are equipped with their own trapeze and sailing is done while cantilevered over the water to the fullest extent to balance against the sails.
One-design racing is a racing method which may be adopted in sports using complex equipment, whereby all vehicles have identical or very similar designs or models, avoiding the need for a handicap system.
The International Offshore Rule (IOR) was a measurement rule for racing sailboats. The IOR evolved from the Cruising Club of America (CCA) rule for racer/cruisers and the Royal Ocean Racing Club (RORC) rule.

The A-Class Catamaran, often abbreviated to A-Cat, is a development class sailing catamaran for singlehanded racing.

The 18 ft Skiff is considered the fastest class of sailing skiffs. The class has a long history beginning with races on Sydney Harbour, Australia in 1892 and later in New Zealand. The boat has changed significantly since the early days, bringing in new technology as it became available. Because of the need of strength, agility and skill, the class is considered to be the top level of small boat sailing. Worldwide this boat is called the "18 Foot Skiff". It is the fastest conventional non-foiling monohull on the yardstick rating, with a score of 675, coming only third after the Tornado and Inter 20.

In sailing, the trapeze is a wire that comes from a point high on the mast, usually where the shrouds are fixed, to a hook on the crew member's harness at approximately waist level. The position when extended on the trapeze is outside the hull, braced against it with the soles of the feet, facing the masthead, and clipped on by a hook on the trapeze harness. This gives the crew member more leverage to keep the boat flat by allowing the crew member's centre of gravity to balance the force of the wind in the sails.

The National Solo class is a racing dinghy designed by Jack Holt in 1956. The Solo is sailed in the United Kingdom, Holland, Portugal and Australia.

The Olson 30 is a sailboat designed by George Olson of Santa Cruz, CA around 1978. Olson was a surfer and surfboard shaper who decided to design a 30' ultra light displacement boat while on a delivery from Honolulu to Santa Cruz on Merlin, a 68' Bill Lee designed and built ultralight sailboat which had competed in the biennial Transpac race in 1977. During this delivery, Olson came up with the idea while sailing with Denis Bassano and Don Snyder, who lent their initials to the prototype's name, SOB 30. The resulting boat was christened Pacific High, and it was launched in 1978.

His Majesty's Yacht Britannia was a gaff-rigged cutter built in 1893 for RYS Commodore Albert Edward, Prince of Wales. She served both himself and his son King George V with a long racing career.

The term sportsboat first appeared in the late 1980s and early 1990s to describe trailer sailers that were optimised for high performance at the expense of accommodation and ballast. The very definition of the term "sportsboat" is evolving.

Sailing on the River Thames is practised on both the tidal and non-tidal reaches of the river. The highest club upstream is at Oxford. The most popular sailing craft used on the Thames are lasers, GP14s, Wayfarers and Enterprises. One sailing boat unique to the Thames is the Thames Rater, which is sailed around Raven's Ait.

The sport of sailing involves a variety of competitive sailing formats that are sanctioned through various sailing federations and yacht clubs. Racing disciplines include matches within a fleet of sailing craft, between a pair thereof or among teams. Additionally, there are specialized competitions that include setting speed records. Racing formats include both closed courses and point-to-point contests; they may be in sheltered waters, coast-wise or on the open ocean. Most competitions are held within defined classes or ratings that either entail one type of sailing craft to ensure a contest primarily of skill or rating the sailing craft to create classifications or handicaps.


















