
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 7, 1848. Held in the aftermath of the Mexican–American War, General Zachary Taylor of the Whig Party defeated Senator Lewis Cass of the Democratic Party.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 2, 1852. Democratic nominee Franklin Pierce defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott.

The Free Soil Party, also called the Free Democratic Party or the Free Democracy, was a political party in the United States from 1848 to 1854, when it merged into the Republican Party. The party was focused on opposing the expansion of slavery into the western territories of the United States. The 1848 presidential election took place in the aftermath of the Mexican–American War and debates over the extension of slavery into the Mexican Cession. After the Whig Party and the Democratic Party nominated presidential candidates who were unwilling to rule out the extension of slavery into the Mexican Cession, anti-slavery Democrats and Whigs joined with members of the Liberty Party to form the new Free Soil Party. Running as the Free Soil presidential candidate, former President Martin Van Buren won 10.1 percent of the popular vote, the strongest popular vote performance by a third party up to that point in U.S. history.

The Constitutional Union Party was a political party which stood in the 1860 United States elections. It mostly consisted of conservative former Whigs from the Southern United States who wanted to avoid secession over slavery and refused to join either the Republican Party or Democratic Party. The Constitutional Union Party campaigned on a simple platform "to recognize no political principle other than the Constitution of the country, the Union of the states, and the Enforcement of the Laws".
The Barnburners and Hunkers were the names of two opposing factions of the New York Democratic Party in the mid-19th century. The main issue dividing the two factions was that of slavery, with the Barnburners being the anti-slavery faction. While this division occurred within the context of New York politics, it reflected the national divisions in the Democratic Party and the United States broadly in the years preceding the American Civil War.

Theodore Frelinghuysen was an American politician who represented New Jersey in the United States Senate. He was the Whig vice presidential nominee in the election of 1844, running on a ticket with Henry Clay.
The 1852 Democratic National Convention was a presidential nominating convention that met from June 1 to June 5 in Baltimore, Maryland. It was held to nominate the Democratic Party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1852 election. The convention selected former Senator Franklin Pierce of New Hampshire for president and Senator William R. King of Alabama for vice president.

The 34th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from March 4, 1855, to March 4, 1857, during the last two years of Franklin Pierce's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1850 United States census. The Whig Party, one of the two major parties of the era, had largely collapsed, although many former Whigs ran as Republicans or as members of the "Opposition Party." The Senate had a Democratic majority, and the House was controlled by a coalition of Representatives led by Nathaniel P. Banks, a member of the American Party.

George Franklin Fort was a physician, judge, and Democratic Party politician who served as the 16th Governor of New Jersey from 1851 to 1854.
John Runk was an American Whig Party politician, who represented New Jersey's 3rd congressional district in the United States House of Representatives from 1845 to 1847.

The presidency of Franklin Pierce began on March 4, 1853, when Franklin Pierce was inaugurated as the 14th President of the United States, and ended on March 4, 1857. Pierce, a Democrat from New Hampshire, took office after defeating Whig Party nominee Winfield Scott in the 1852 presidential election. Seen by fellow Democrats as pleasant and accommodating to all the party's factions, Pierce, then a little-known politician, won the presidential nomination on the 49th ballot of the 1852 Democratic National Convention. His hopes for reelection ended after losing the Democratic nomination at the 1856 Democratic National Convention, and was succeeded by Democrat James Buchanan.
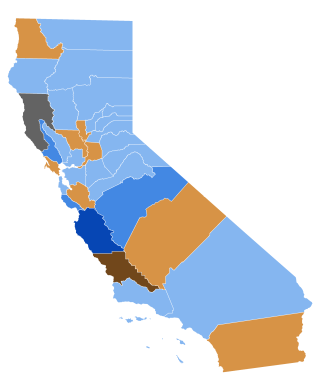
The 1852 United States presidential election in California was held on November 2, 1852, as part of the 1852 United States presidential election. Votes chose four representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1850–51 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1850 and 1851, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 73rd New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 1 to April 10, 1850, during the second year of Hamilton Fish's governorship, in Albany.

The 74th New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 7 to July 11, 1851, during the first year of Washington Hunt's governorship, in Albany.

The 1851 Connecticut gubernatorial election was held on April 7, 1851. It was a rematch of the 1850 Connecticut gubernatorial election. Incumbent governor and Democratic Party nominee Thomas H. Seymour defeated former state legislator and Whig nominee Lafayette S. Foster with 48.94% of the vote.

The 1851–52 Massachusetts gubernatorial election consisted of an initial popular vote held on November 10, 1851, followed by a legislative vote conducted on January 12, 1852. Incumbent Democrat Governor George S. Boutwell was reelected to a second term in office. The ultimate task of electing the governor had been placed before the Massachusetts General Court because no candidate received the majority of the vote required for a candidate to be elected through the popular election.

The 1850–51 Massachusetts gubernatorial election consisted of an initial popular held on November 11, 1850 that was followed by a legislative vote that was conducted on January 11, 1851. It saw the election of Democratic Party nominee George S. Boutwell. The ultimate task of electing the governor had been placed before the Massachusetts General Court because no candidate received the majority of the vote required for a candidate to be elected through the popular election.

The 1836 Massachusetts gubernatorial election was held on November 14.

The 1849–50 Massachusetts gubernatorial election consisted of an initial popular election held on November 12, 1949 that was followed by a legislative vote held on January 7, 1850. The ultimate task of electing the governor had been placed before the Massachusetts General Court because no candidate received the majority of the vote required for a candidate to be elected through the popular election. Incumbent Whig Governor George N. Briggs won the legislative vote and was therefore elected, defeating Democratic nominee George S. Boutwell and Free Soil nominee Stephen C. Phillips.



















