Passaic County is a county in the U.S. state of New Jersey that is part of the New York metropolitan area. As of the 2020 United States census, the county was the state's eighth-most-populous county, with a population of 524,118, its highest decennial count ever and an increase of 22,892 (+4.6%) from the 2010 census count of 501,226, which in turn reflected an increase of 12,177 (+2.5%) from the 489,049 counted in the 2000 census.

Cumberland County is a coastal county located on the Delaware Bay in the Southern Shore Region of the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 census, the county was the state's 16th-most-populous county, with a population of 154,152, a decrease of 2,746 (−1.8%) from the 2010 census count of 156,898. Its county seat is Bridgeton. Cumberland County is named for Prince William, Duke of Cumberland. The county was formally created from portions of Salem County on January 19, 1748. The county is part of the South Jersey region of the state.
The 1st United States Congress, comprising the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives, met from March 4, 1789, to March 4, 1791, during the first two years of George Washington's presidency, first at Federal Hall in New York City and later at Congress Hall in Philadelphia. With the initial meeting of the First Congress, the United States federal government officially began operations under the new frame of government established by the 1787 Constitution. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the provisions of Article I, Section 2, Clause 3, of the Constitution. Both chambers had a Pro-Administration majority. Twelve articles of amendment to the Constitution were passed by this Congress and sent to the states for ratification; the ten ratified as additions to the Constitution on December 15, 1791, are collectively known as the Bill of Rights, with an additional amendment ratified more than two centuries later to become the Twenty-seventh Amendment to the United States Constitution.

The 2nd United States Congress, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives, met at Congress Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, from March 4, 1791, to March 4, 1793, during the third and fourth years of George Washington's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the provisions of Article I, Section 2, Clause 3 of the United States Constitution. Additional House seats were assigned to the two new states of Vermont and Kentucky. Both chambers had a Pro-Administration majority.

The 2000 United States census, conducted by the Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States on April 1, 2000, to be 281,421,906, an increase of 13.2 percent over the 248,709,873 people enumerated during the 1990 census. This was the twenty-second federal census and was at the time the largest civilly administered peacetime effort in the United States.

United States congressional apportionment is the process by which seats in the United States House of Representatives are distributed among the 50 states according to the most recent decennial census mandated by the United States Constitution. After each state is assigned one seat in the House, most states are then apportioned a number of additional seats which roughly corresponds to its share of the aggregate population of the 50 states. Every state is constitutionally guaranteed two seats in the Senate and at least one seat in the House, regardless of population.
These are tables of congressional delegations from North Carolina to the United States House of Representatives and the United States Senate.
These are tables of congressional delegations from Virginia to the United States Senate and United States House of Representatives. Virginia's current U.S. Senators are Democrats Mark Warner and Tim Kaine. Virginia is allotted 11 seats in the U.S. House of Representatives; currently, 6 seats are held by Democrats and 5 seats are held by Republicans.

The 1822–23 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1822, and August 14, 1823. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 18th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1823. They occurred during President James Monroe's second term.

The 1812–13 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 3, 1812, and April 30, 1813. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 13th United States Congress convened on May 24, 1813. They coincided with James Madison being re-elected president.

The 1802–03 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1802 and December 14, 1803. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, either before or after the first session of the 8th United States Congress convened on October 17, 1803. They occurred during President Thomas Jefferson's first term in office.

The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 27, 1792, and September 6, 1793. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 3rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1793. With the addition of the new state of Kentucky's representatives, and the congressional reapportionment based on the 1790 United States census, the size of the House increased to 105 seats.
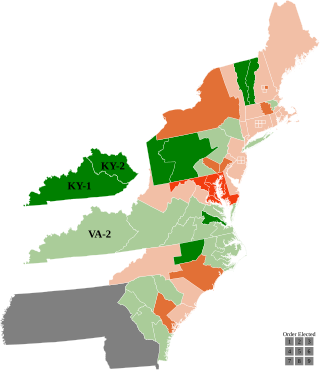
The 1790–91 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 27, 1790, and October 11, 1791. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 2nd United States Congress convened on October 24, 1791. This was the first midterm election cycle, which took place in the middle of President George Washington's first term. The size of the House increased to 67 seats after the new state of Vermont elected its first representatives.

The 1788–89 United States House of Representatives elections were the first U.S. House of Representatives elections following the adoption of the Constitution of the United States. Each state set its own date for its congressional elections, ranging from November 24, 1788, to March 5, 1789, before or after the first session of the 1st United States Congress convened on March 4, 1789. They coincided with the election of George Washington as the first president of the United States.

The 1990 United States census, conducted by the Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States to be 248,709,873, an increase of 9.8 percent over the 226,545,805 persons enumerated during the 1980 census.

The 1920 United States census, conducted by the Census Bureau during one month from January 5, 1920, determined the resident population of the United States to be 106,021,537, an increase of 15.0 percent over the 92,228,496 persons enumerated during the 1910 census.

The Congressional Apportionment Amendment is a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution that addresses the number of seats in the House of Representatives. It was proposed by Congress on September 25, 1789, but was never ratified by the requisite number of state legislatures. As Congress did not set a time limit for its ratification, the Congressional Apportionment Amendment is still pending before the states. As of 2025, it is one of six unratified amendments.

Following the 1790 census, North Carolina's apportionment increased from 5 to 10 seats.

New Hampshire increased from 3 seats to 4 seats after the 1790 census.

New Jersey increased its apportionment from 5 seats to 6 after the 1800 census.