
The 1932 United States presidential election was the 37th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1932. The election took place against the backdrop of the Great Depression. The incumbent Republican President Herbert Hoover was defeated in a landslide by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt, the governor of New York and the vice presidential nominee of the 1920 presidential election. Roosevelt was the first Democrat in 80 years to simultaneously win an outright majority of the electoral college and popular vote, a feat last accomplished by Franklin Pierce in 1852, as well as the first Democrat in 56 years to win a majority of the popular vote, which was last achieved by Samuel J. Tilden in 1876. Roosevelt was the last sitting governor to be elected president until Bill Clinton in 1992. Hoover became the first incumbent president to lose an election to another term since William Howard Taft in 1912, the last to do so until Gerald Ford lost 44 years later, and the last elected incumbent president to do so until Jimmy Carter 48 years later. The election marked the effective end of the Fourth Party System, which had been dominated by Republicans. It was the first time since 1916 that a Democrat was elected president.

The 1938 United States Senate elections occurred in the middle of Franklin D. Roosevelt's second term. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans gained eight seats from the Democrats, though this occurred after multiple Democratic gains since the 1932 election, leading to the Democrats retaining a commanding lead over the Republicans with more than two-thirds of the legislative chamber.

Royal Samuel Copeland, a United States Senator from New York from 1923 until 1938, was an academic, homeopathic physician, and politician. He held elected offices in both Michigan and New York.

The 1912–13 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. They were the last U.S. Senate elections before the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, establishing direct elections for all Senate seats. Senators had been primarily chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1912 and 1913, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. Some states elected their senators directly even before passage of Seventeenth Amendment. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.

The 1912 Republican National Convention was held at the Chicago Coliseum, Chicago, Illinois, from June 18 to June 22, 1912. The party nominated President William Howard Taft and Vice President James S. Sherman for re-election for the 1912 United States presidential election.

The 1934 New York State Election was held on November 6, 1934, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the state comptroller, the attorney general, a U.S. Senator, two U.S. Representatives-at-large, the chief judge and two associate judges of the New York Court of Appeals, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate.

The 1928 New York state elections were held on November 6, 1928, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the state comptroller, the attorney general, a U.S. Senator and a judge of the New York Court of Appeals, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate.

The 1922 New York state election was held on November 7, 1922, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the Secretary of State, the state comptroller, the attorney general, the state treasurer, the state engineer and a U.S. Senator, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate. Two amendments to the State Constitution were also proposed. During his 1922 reelection bid, Smith notably embraced his position as an opponent of Prohibition.
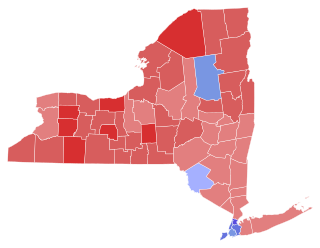
The 1918 New York gubernatorial election took place on November 5, 1918, to elect the Governor and Lieutenant Governor of New York, concurrently with elections to the United States Senate in other states and elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections.

The 1905 United States Senate election in New York was held on January 17, 1905. Incumbent Senator Chauncey Depew was re-elected to a second term in office. He was renominated unanimously after former Governor Frank S. Black dropped his challenge, and easily won the election given the Republican Party's large majorities in both houses.
The 1911 United States Senate election in New York was held from January 17 to March 31, 1911, by the New York State Legislature to elect a U.S. Senator to represent the State of New York in the United States Senate.

The 1926 United States Senate special election in Massachusetts was held on November 2, 1926.

The 1932 United States Senate election in Connecticut was held on November 8, 1932. Incumbent Senator Hiram Bingham III ran for a second full term in office but was defeated by Democratic U.S. Representative Augustine Lonergan. This was the first time since 1879 that Democrats won this Senate seat, and the first since 1881 that they won either seat.

The 1914 United States Senate election in New York was held on November 3. Incumbent Republican Senator Elihu Root chose not to seek re-election. James Wolcott Wadsworth Jr. was elected to a succeed Root, defeating Democrat James Watson Gerard.

From March 12 to June 27, 1940, voters of the Democratic Party elected delegates to the 1940 Democratic National Convention through a series of primaries, caucuses, and conventions. Incumbent President Franklin D. Roosevelt was selected as the party's presidential nominee despite not formally declaring a campaign for a third term. Supporters effectively drafted Roosevelt, who was non-committal about seeking re-election, amid rising concerns over war in Europe.

The 1928 United States Senate election in New York was held on November 6, 1928. Incumbent Democratic Senator Royal S. Copeland was re-elected to a second term, defeating Republican Alanson B. Houghton.

The 1934 United States Senate election in New York was held on November 6, 1934, to elect a U.S. Senator. Incumbent Democratic Senator Royal Copeland was re-elected to a third term in office, though he would die in office in 1938.
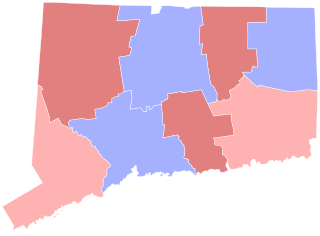
The 1938 United States Senate election in Connecticut was held on November 8, 1938.

The United States Senate election of 1922 in New Jersey was held on November 7, 1922.

The 1940 United States Senate election in New York was held on November 5, 1940. Incumbent Democratic Senator James M. Mead, first elected in 1938 to fill vacancy caused by the death of Royal S. Copeland, was re-elected to a full term in office, defeating Republican Bruce Barton.





















