
The 33rd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1853, to March 4, 1855, during the first two years of Franklin Pierce's presidency. During this session, the Kansas–Nebraska Act was passed, an act that soon led to the creation of the Republican Party. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1850 United States census. Both chambers had a Democratic majority.

The 34th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from March 4, 1855, to March 4, 1857, during the last two years of Franklin Pierce's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1850 United States census. The Whig Party, one of the two major parties of the era, had largely collapsed, although many former Whigs ran as Republicans or as members of the "Opposition Party." The Senate had a Democratic majority, and the House was controlled by a coalition of Representatives led by Nathaniel P. Banks, a member of the American Party.

The 1854–55 United States House of Representatives elections were held in 31 states for all 234 seats between August 4, 1854 and November 6, 1855, during President Franklin Pierce's term. Each state legislature separately set a date to elect representatives to the House of Representatives before the 34th Congress convened its first session on December 3, 1855.

The 1852–53 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 2, 1852 and November 8, 1853. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 33rd United States Congress convened on December 5, 1853. The size of the House increased to 234 seats following the congressional reapportionment based on the 1850 United States Census.

Massachusetts's 7th congressional district is a congressional district located in eastern Massachusetts, including roughly three-fourths of the city of Boston and a few of its northern and southern suburbs. The seat is currently held by Democrat Ayanna Pressley.
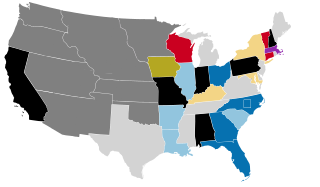
The 1854–55 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1854 and 1855, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.

The 1793 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held in January 1793, to elect 10 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives.

The 1798 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 24 to 26, 1798, to elect ten U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 6th United States Congress.

The 1800 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 29 to May 1, 1800, to elect ten U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 7th United States Congress.

The 1802 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 27 to 29, 1802, to elect 17 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 8th United States Congress.

The 1812 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from December 15 to 17, 1812, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 13th United States Congress. At the same time, a vacancy was filled in the 12th United States Congress.

The 1814 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 26 to 28, 1814, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 14th United States Congress.

The 1816 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 23 to 25, 1816, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 15th United States Congress. At the same time, a vacancy was filled in the 14th United States Congress.

The 1818 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 28 to 30, 1818, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 16th United States Congress.

The 1821 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 24 to 26, 1821, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 17th United States Congress.

The 1822 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from November 4 to 6, 1822, to elect 34 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 18th United States Congress.

The 1826 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from November 6 to 8, 1826, to elect 34 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 20th United States Congress.

The 78th New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 2 to April 14, 1855, during the first year of Myron H. Clark's governorship, in Albany.

The 123rd New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 3 to April 6, 1900, during the second year of Theodore Roosevelt's governorship, in Albany.

The 125th New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 1 to March 27, 1902, during the second year of Benjamin B. Odell Jr.'s governorship, in Albany.