
The 1946 United States Senate elections were held November 5, 1946, in the middle of Democratic President Harry S. Truman's first term after Roosevelt's passing. The 32 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and four special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans took control of the Senate by picking up twelve seats, mostly from the Democrats. This was the first time since 1932 that the Republicans had held the Senate, recovering from a low of 16 seats following the 1936 Senate elections.

The 1938 United States Senate elections occurred in the middle of Franklin D. Roosevelt's second term. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans gained eight seats from the Democrats, though this occurred after multiple Democratic gains since the 1932 election, leading to the Democrats retaining a commanding lead over the Republicans with more than two-thirds of the legislative chamber.

The 1938 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 76th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 8, 1938, while Maine held theirs on September 12. They occurred in the middle of President Franklin D. Roosevelt's second term. Roosevelt's Democratic Party lost a net of 72 seats to the Republican Party, who also picked up seats from minor Progressive and Farmer–Labor Parties.

James Michael Mead was an American politician from New York. A Democrat, among the offices in which he served was member of the Erie County Board of Supervisors (1914–1915), New York State Assembly (1915–1918), United States House of Representatives (1919–1938), and United States Senate (1938–1947).

The 76th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1939, to January 3, 1941, during the seventh and eighth years of Franklin D. Roosevelt's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1930 United States census.

Robert Winthrop Kean was an American Republican Party politician from the state of New Jersey. Kean represented parts of Essex County, New Jersey in the United States House of Representatives from 1939 to 1959. He retired from the House to run for United States Senate in 1958, but was defeated by Harrison A. Williams.

Bruce Faulkner Caputo is an American lawyer and politician from New York. He is most notable for his service as a member of the New York State Assembly and the United States House of Representatives.

The 1942 New York state election was held on November 3, 1942, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the state comptroller, the attorney general and two U.S. Representatives At-large, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate.

The 1938 New York state election was held on November 8, 1938, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the state comptroller, the attorney general, two U.S. Senators and two U.S. Representatives-at-large, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate. The 1938 election was the first election where the Governor of New York was elected to a four-year term, rather than a two-year term.

The 1936 New York state election was held on November 3, 1936, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the state comptroller, the attorney general, a judge of the New York Court of Appeals and two U.S. Representatives-at-large, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate.

The 1934 New York State Election was held on November 6, 1934, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the state comptroller, the attorney general, a U.S. Senator, two U.S. Representatives-at-large, the chief judge and two associate judges of the New York Court of Appeals, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate.

From March 12 to May 17, 1940, voters of the Republican Party chose delegates to nominate a candidate for president at the 1940 Republican National Convention. The nominee was selected at the convention in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania from June 24–28, 1940.
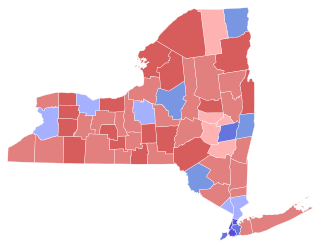
The 1932 New York state election was held on November 8, 1932, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the state comptroller, the attorney general, the chief judge, a U.S. Senator and two U.S. Representatives-at-large, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate.

The 1940 New York state election was held on November 5, 1940, to elect three judges of the New York Court of Appeals, a U.S. Senator and two U.S Representatives-at-large, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate.
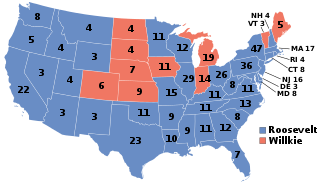
The 1940 United States elections were held on November 5. The Democratic Party continued to dominate national politics, as it defended its congressional majorities and retained the presidency. It was the last election prior to the attack on Pearl Harbor and America's entry into World War II.

From March 12 to June 27, 1940, voters of the Democratic Party elected delegates to the 1940 Democratic National Convention through a series of primaries, caucuses, and conventions. Incumbent President Franklin D. Roosevelt was selected as the party's presidential nominee despite not formally declaring a campaign for a third term. Supporters effectively drafted Roosevelt, who was non-committal about seeking re-election, amid rising concerns over war in Europe.

The 1934 United States Senate election in New York was held on November 6, 1934, to elect a U.S. Senator. Incumbent Democratic Senator Royal Copeland was re-elected to a third term in office, though he would die in office in 1938.
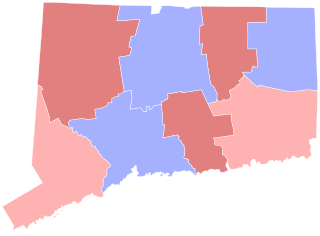
The 1938 United States Senate election in Connecticut was held on November 8, 1938.

The 1946 United States Senate election in New York was held on November 5, 1946.

Elections were held in Illinois on Tuesday, November 5, 1940.























