
In humans, clusterin (CLU) is encoded by the CLU gene on chromosome 8. CLU is an extracellular molecular chaperone which binds to misfolded proteins in body fluids to neutralise their toxicity and mediate their cellular uptake by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Once internalised by cells, complexes between CLU and misfolded proteins are trafficked to lysosomes where they are degraded. CLU is involved in many diseases including neurodegenerative diseases, cancers, inflammatory diseases, and aging.
Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a phosphatase in humans and is encoded by the PTEN gene. Mutations of this gene are a step in the development of many cancers, specifically glioblastoma, lung cancer, breast cancer, and prostate cancer. Genes corresponding to PTEN (orthologs) have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available.
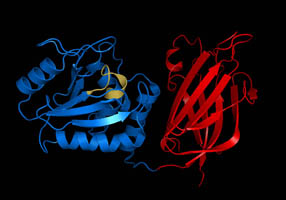
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 (DP2.5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APC gene. The APC protein is a negative regulator that controls beta-catenin concentrations and interacts with E-cadherin, which are involved in cell adhesion. Mutations in the APC gene may result in colorectal cancer and desmoid tumors.

Polycystin 1 (PC1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PKD1 gene. Mutations of PKD1 are associated with most cases of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, a severe hereditary disorder of the kidneys characterised by the development of renal cysts and severe kidney dysfunction.

Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, (GSK-3 beta), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSK3B gene. In mice, the enzyme is encoded by the Gsk3b gene. Abnormal regulation and expression of GSK-3 beta is associated with an increased susceptibility towards bipolar disorder.

Frizzled-10(Fz-10) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD10 gene. Fz-10 has also been designated as CD350.

Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase that in humans is encoded by the YES1 gene.

Protein Wnt-3a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT3A gene.

Disks large homolog 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DLG5 gene.

Axin-2, also known as axin-like protein (Axil), axis inhibition protein 2 (AXIN2), or conductin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AXIN2 gene.

Zinc transporter SLC39A7 (ZIP7), also known as solute carrier family 39 member 7, is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC39A7 gene. It belongs to the ZIP family, which consists of 14 proteins that transport zinc into the cytoplasm. Its primary role is to control the transport of zinc from the ER and Golgi apparatus to the cytoplasm. It also plays a role in glucose metabolism. Its structure consists of helices that bind to zinc in a binuclear metal center. Its fruit fly orthologue is Catsup.

The human gene AGK encodes the enzyme mitochondrial acylglycerol kinase.

Tyrosine-protein kinase-like 7 also known as colon carcinoma kinase 4 (CCK4) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that in humans is encoded by the PTK7 gene.

Zymogen Granule Protein 16 is a protein that is encoded by the ZG16 gene. Other common names include hZG16, FLJ43571, FLJ92276, secretory lectin ZG16, jacalin-like lectin domain containing, JCLN, JCLN1, MGC183567, MGC34820, ZG16A, zymogen granule membrane protein 16, zymogen granule protein 16 homolog, and zymogen granule protein. The gene is located on Chromosome 16: 29,778,256-29,782,973. The gene obtains one transcript and 128 orthologues.

Wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 2, also known as WNT2, is a human gene.

Transcription factor 7-like 1, also known as TCF7L1, is a human gene.

ADP/ATP translocase 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC25A5 gene on the X chromosome.

Mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (MUL1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MUL1 gene on chromosome 1. This enzyme localizes to the outer mitochondrial membrane, where it regulates mitochondrial morphology and apoptosis through multiple pathways, including the Akt, JNK, and NF-κB. Its proapoptotic function thus implicates it in cancer and Parkinson's disease.

ADCK2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCK2 gene. It is situated on chromosome 7 at the q34 location.

ADCK5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCK5 gene. It is situated on chromosome 8 at the q24.3 location.


















