| Apeirogonal prism | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Semiregular tiling |
| Vertex configuration | 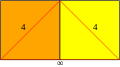 4.4.∞ |
| Schläfli symbol | t{2,∞} |
| Wythoff symbol | 2 ∞| 2 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry | [∞,2], (*∞22) |
| Rotation symmetry | [∞,2]+, (∞22) |
| Bowers acronym | Azip |
| Dual | Apeirogonal bipyramid |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
In geometry, an apeirogonal prism or infinite prism is the arithmetic limit of the family of prisms; it can be considered an infinite polyhedron or a tiling of the plane. [1]
Contents
Thorold Gosset called it a 2-dimensional semi-check, like a single row of a checkerboard.[ citation needed ]
If the sides are squares, it is a uniform tiling. If colored with two sets of alternating squares it is still uniform.[ citation needed ]
- Uniform variant with alternate colored square faces.
- Its dual tiling is an apeirogonal bipyramid.









