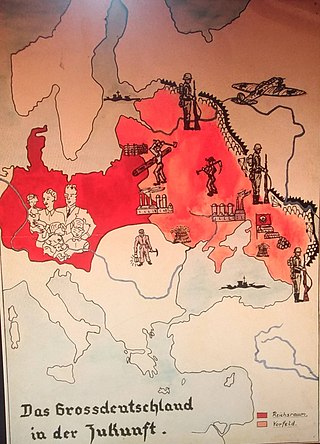
Lebensraum is a German concept of expansionism and Völkisch nationalism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, Lebensraum became a geopolitical goal of Imperial Germany in World War I (1914–1918), as the core element of the Septemberprogramm of territorial expansion. The most extreme form of this ideology was supported by the Nazi Party and Nazi Germany. Lebensraum was a leading motivation of Nazi Germany to initiate World War II, and it would continue this policy until the end of the conflict.

In the political history of Germany, the Führerprinzip was the basis of executive authority in the Government of Nazi Germany (1933–1945), which meant that the word of the Führer is above all written law, and that government policies, decisions, and offices all work towards the realisation of the will of the Führer. In practise, the Führerprinzip was the dictatorship of the leader to dictate the ideology and policies of a political party; therefore, such a personal dictatorship is a basic characteristic of fascism.

Richard Walther Darré was one of the leading Nazi "blood and soil" ideologists and served as Reich Minister of Food and Agriculture. As the National leader for agricultural policy, he was a high-ranking functionary in the Nazi Party and as a Senior group leader in the SS, he was the seventh most senior commander in that organisation. He was tried and found guilty on three counts at the Ministries Trial.
Volksgemeinschaft is a German expression meaning "people's community", "folk community", "national community", or "racial community", depending on the translation of its component term Volk. This expression originally became popular during World War I as Germans rallied in support of the war, and many experienced "relief that at one fell swoop all social and political divisions could be solved in the great national equation". The idea of a Volksgemeinschaft was rooted in the notion of uniting people across class divides to achieve a national purpose, and the hope that national unity would "obliterate all conflicts - between employers and employees, town and countryside, producers and consumers, industry and craft".

Das Schwarze Korps was the official newspaper of the Schutzstaffel (SS). This newspaper was published on Wednesdays and distributed free of charge. All SS members were encouraged to read it. The chief editor was SS leader Gunter d'Alquen; the publisher was Max Amann of the Franz-Eher-Verlag publishing company. The paper was hostile to many groups, with frequent articles condemning the Catholic Church, Jews, Communism, Freemasonry, and others.

Rassenschande or Blutschande was an anti-miscegenation concept in Nazi German racial policy, pertaining to sexual relations between Aryans and non-Aryans. It was put into practice by policies like the Aryan certificate requirement, and later by anti-miscegenation laws such as the Nuremberg Laws, adopted unanimously by the Reichstag on 15 September 1935. Initially, these laws referred predominantly to relations between ethnic Germans and non-Aryans, regardless of citizenship. In the early stages the culprits were targeted informally; later, they were punished systematically and legally.

The propaganda used by the German Nazi Party in the years leading up to and during Adolf Hitler's dictatorship of Germany from 1933 to 1945 was a crucial instrument for acquiring and maintaining power, and for the implementation of Nazi policies.

The Nazi regime in Germany actively promoted and censored forms of art between 1933 and 1945. Upon becoming dictator in 1933, Adolf Hitler gave his personal artistic preference the force of law to a degree rarely known before. In the case of Germany, the model was to be classical Greek and Roman art, seen by Hitler as an art whose exterior form embodied an inner racial ideal. It was, furthermore, to be comprehensible to the average man. This art was to be both heroic and romantic. The Nazis viewed the culture of the Weimar period with disgust. Their response stemmed partly from conservative aesthetics and partly from their determination to use culture as propaganda.

The German Nazi Party adopted and developed several pseudoscientific racial classifications as an important part of its fascist ideology (Nazism) in order to justify genocides and racism against ethnicities which it deemed genetically or culturally inferior, invasions of Poland and the USSR, and distant intention for war against Japan. The Aryan race is a pseudoscientific historical race concept that emerged in the late-19th century to describe people who descend from the Proto-Indo-Europeans as a racial grouping and it was accepted by Nazi thinkers. The Nazis considered the putative "Aryan race" a superior "master race" with Germanic peoples as representative of Nordic race being best branch, and they considered Jews, mixed-race people, Slavs, Romani, Blacks, and certain other ethnicities racially inferior subhumans, whose members were only suitable for slave labor and extermination. In these ethnicities, Jews were considered the most inferior. However, the Nazis considered Germanic peoples such as Germans to be significantly mixed between different races, including the East Baltic race being considered inferior by the Nazis, and that their citizens needed to be completely Nordicized after the war. The Nazis also considered some non-Germanic groups such as Sorbs, Northern Italians, Greeks, and Iranians to be of Germanic and Nordic origin. Some non-Aryan ethnic groups such as Turks, Chinese, and Japanese were considered to be partly superior, while some Indo-Europeans such as Slavs, Romani, and Indians were considered inferior.
The Artaman League was a German agrarian and völkisch movement committed to a Back-to-the-land–inspired ruralism, founded in 1923. Active during the inter-war period, the League became closely linked to, and eventually absorbed by, the Nazi Party.
Wehrbauer, plural Wehrbauern, is a German term for settlers living on the marches of a realm who were tasked with holding back foreign invaders until the arrival of proper military reinforcements. In turn, they were granted special liberties. Wehrbauern in their settlements, known as Wehrsiedlungen, were mainly used on the eastern fringes of the Holy Roman Empire and later Austria-Hungary to slow attacks by the Ottoman Empire. This historic term was resurrected and used by the Nazis during the Second World War.

The propaganda of the Nazi regime that governed Germany from 1933 to 1945 promoted Nazi ideology by demonizing the enemies of the Nazi Party, notably Jews and communists, but also capitalists and intellectuals. It promoted the values asserted by the Nazis, including Heldentod, Führerprinzip, Volksgemeinschaft, Blut und Boden and pride in the Germanic Herrenvolk. Propaganda was also used to maintain the cult of personality around Nazi leader Adolf Hitler, and to promote campaigns for eugenics and the annexation of German-speaking areas. After the outbreak of World War II, Nazi propaganda vilified Germany's enemies, notably the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union and the United States, and in 1943 exhorted the population to total war.
Nazism, formally National Socialism, is the far-right totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitler Fascism and Hitlerism. The later related term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War when the Third Reich collapsed.
The Reichserbhofgesetz, the Hereditary Farm Law, of 1933 was a Nazi law to implement principles of blood and soil, stating that its aim was to: "preserve the farming community as the blood-source of the German people". As farmers appeared in Nazi ideology as a source of economics and racial stability, the law was implemented to protect them from the forces of modernization.

The ideology of the Schutzstaffel, a paramilitary force and an instrument of terror of the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany, emphasized a racist vision of "racial purity", primarily based on antisemitism and loyalty to Adolf Hitler and Nazi Germany.

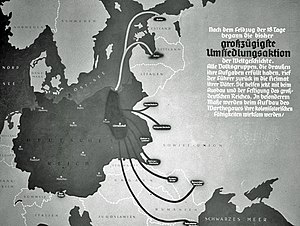
There were many areas annexed by Nazi Germany both immediately before and throughout the course of World War II. Territories that were part of Germany before the annexations were known as the "Altreich".

The Reich Harvest Thanksgiving Festival was a monumental Nazi German celebration of the peasantry and the German farmers. The festivals ran from 1933 to 1937 on the Bückeberg, a hill near the town of Hamelin. Most festivals occurred every October, with the 1934 festival commencing 30 September. The official purpose of the festival was the recognition of the achievements of the German farmers, whom the Nazis called the Reichsnährstand. The celebration was also used by the Nazis as a propaganda tool to showcase the connection between Führer Adolf Hitler and the German people. The festival was part of a cycle of Nazi celebrations which included the annual party rally at Nuremberg, Hitler's birthday celebrations and other important events on the Nazi calendar.
Blut und Boden – Grundlagen zum neuen Reich is a 1933 German short propaganda film that illustrates the Nazi concept of "Blood and Soil".
Rudolf Fritz Karl Berthold Bode was a German educator and founder of expressive gymnastics His central concerns were holistic movement, its rhythmic design and the interaction of body and soul. He was an active supporter and propagandist for National Socialism from the early 1930s.
Anna Koppitz was a mid-century Austrian photographer.