
Charles E. Noad was a programmer, Tolkien scholar, and a long-standing member of the Tolkien Society, which he helped to found.

Charles E. Noad was a programmer, Tolkien scholar, and a long-standing member of the Tolkien Society, which he helped to found.
Charles Noad was born in 1947. He worked at Imperial College, London as a computer programmer. [1]
A Tolkien fan, he was involved in the work of the Tolkien Society, which he helped to found, for over 50 years, making him its longest-standing member; he served as its bibliographer and photographer, and belonged to its London local group, the Northfarthing Smial. The society described his essay "On the Construction of The Silmarillion " as "critically important"; it was published in the 2000 scholarly collection Tolkien's Legendarium: Essays on The History of Middle-earth , edited by Verlyn Flieger and Carl F. Hostetter. His friendship with Christopher Tolkien led to his proofreading several Middle-earth books including The History of Middle-earth . [1]
Several Tolkien scholars knew, corresponded with, and exchanged books with Noad for 40 years or more. Douglas A. Anderson wrote that Noad's "eagle-eye as a proof-reader was legendary." [2] David Bratman described Noad's "On the Construction of The Silmarillion" as a "fascinating and well-researched and -argued" essay on what J. R. R. Tolkien would probably have done to that book, making it "more heterogeneous" than the volume edited by Christopher Tolkien and published a few months after Noad's essay. [3] John D. Rateliff called Noad "the first fellow Tolkien scholar I met". [4] Rateliff described Noad's influence on Tolkien research as "powerful but subtle", in particular on the 12-volume set of The History of Middle-earth. He described Noad's proofreading of Rateliff's The History of the Hobbit as "meticulous". [4]

Christopher John Reuel Tolkien was an English and naturalised French academic editor. The son of the author and academic J. R. R. Tolkien, Christopher edited 24 volumes of his father's posthumously published work, including The Silmarillion and the 12-volume series The History of Middle-Earth, a task that took 45 years. He also drew the original maps for his father's fantasy novel The Lord of the Rings.
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional legendarium, Beleriand was a region in northwestern Middle-earth during the First Age. Events in Beleriand are described chiefly in his work The Silmarillion, which tells the story of the early ages of Middle-earth in a style similar to the epic hero tales of Nordic literature, with a pervasive sense of doom over the character's actions. Beleriand also appears in the works The Book of Lost Tales, The Children of Húrin, and in the epic poems of The Lays of Beleriand.

The History of Middle-earth is a 12-volume series of books published between 1983 and 1996 by George Allen & Unwin in the UK and by Houghton Mifflin in the US, that collect and analyse much of J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, compiled and edited by his son Christopher Tolkien. The series shows the development over time of Tolkien's conception of Middle-earth as a fictional place with its own peoples, languages, and history, from his earliest notions of "a mythology for England" through to the development of the stories that make up The Silmarillion and The Lord of the Rings. It is not a "history of Middle-earth" in the sense of being a chronicle of events in Middle-earth written from an in-universe perspective; it is instead an out-of-universe history of Tolkien's creative process. In 2000, the twelve volumes were republished in three limited edition omnibus volumes. Non-deluxe editions of the three volumes were published in 2002.
Unfinished Tales of Númenor and Middle-earth is a collection of stories and essays by J. R. R. Tolkien that were never completed during his lifetime, but were edited by his son Christopher Tolkien and published in 1980. Many of the tales within are retold in The Silmarillion, albeit in modified forms; the work also contains a summary of the events of The Lord of the Rings told from a less personal perspective.

The Peoples of Middle-earth (1996) is the 12th and final volume of The History of Middle-earth, edited by Christopher Tolkien from the unpublished manuscripts of his father J. R. R. Tolkien. Some characters only appear here, as do a few other works that did not fit anywhere else.

The Book of Lost Tales is a collection of early stories by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien, published as the first two volumes of Christopher Tolkien's 12-volume series The History of Middle-earth, in which he presents and analyses the manuscripts of those stories, which were the earliest form of the complex fictional myths that would eventually comprise The Silmarillion. Each of the Tales is followed by notes and a detailed commentary by Christopher Tolkien.

The Round World Version is an alternative creation myth to the version of J.R.R. Tolkien's legendarium as it appears in The Silmarillion and The Lord of the Rings. In that version, the Earth was created flat and was changed to round as a cataclysmic event during the Second Age in order to prevent direct access by Men to Valinor, home of the immortals. In the Round World Version, the Earth is created spherical from the beginning.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the real-world history and notable fictional elements of J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy universe. It covers materials created by Tolkien; the works on his unpublished manuscripts, by his son Christopher Tolkien; and films, games and other media created by other people.
The term Middle-earth canon, also called Tolkien's canon, is used for the published writings of J. R. R. Tolkien regarding Middle-earth as a whole. The term is also used in Tolkien fandom to promote, discuss and debate the idea of a consistent fictional canon within a given subset of Tolkien's writings.
Carl Franklin Hostetter is a Tolkien scholar and NASA computer scientist. He has edited and annotated many of J. R. R. Tolkien's linguistic writings, publishing them in Vinyar Tengwar and Parma Eldalamberon.
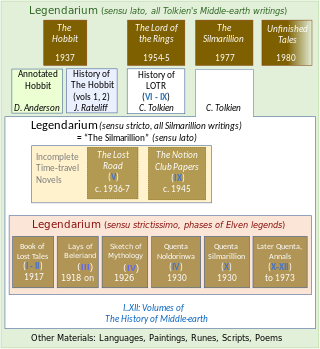
Tolkien's legendarium is the body of J. R. R. Tolkien's mythopoeic writing, unpublished in his lifetime, that forms the background to his The Lord of the Rings, and which his son Christopher summarized in his compilation of The Silmarillion and documented in his 12-volume series The History of Middle-earth. The legendarium's origins reach back to 1914, when Tolkien began writing poems and story sketches, drawing maps, and inventing languages and names as a private project to create a mythology for England. The earliest story, "The Voyage of Earendel, the Evening Star", is from 1914; he revised and rewrote the legendarium stories for most of his adult life.

Tolkien's Legendarium: Essays on The History of Middle-earth is a collection of scholarly essays edited by Verlyn Flieger and Carl F. Hostetter on the 12 volumes of The History of Middle-earth, relating to J. R. R. Tolkien's fiction and compiled and edited by his son, Christopher. It was published by Greenwood Press in 2000. That series comprises a substantial part of "Tolkien's legendarium", the body of Tolkien's mythopoeic writing that forms the background to his The Lord of the Rings and which Christopher Tolkien summarized in his construction of The Silmarillion.
Verlyn Flieger is an author, editor, and Professor Emerita in the Department of English at the University of Maryland at College Park, where she taught courses in comparative mythology, medieval literature, and the works of J. R. R. Tolkien. She is well known as a Tolkien scholar, especially for her books Splintered Light, A Question of Time, and Interrupted Music. She has won the Mythopoeic Scholarship Award four times for her work on Tolkien's Middle-earth writings.

The History of The Hobbit is a two-volume study of J. R. R. Tolkien's 1937 children's fantasy novel The Hobbit. It was first published by HarperCollins in 2007. It contains Tolkien's unpublished drafts of the novel, with commentary by John D. Rateliff. It details Tolkien's various revisions to The Hobbit, including abandoned revisions for the unpublished third edition of the work, intended for 1960, as well as previously unpublished original maps and illustrations drawn by Tolkien.
John D. Rateliff is an American independent scholar of fantasy literature and author of roleplaying games. He specializes in the study of the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, particularly his Middle-earth writings, and wrote and edited the 2007 book The History of the Hobbit.

The Silmarillion is a book consisting of a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited, partly written, and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by Guy Gavriel Kay, who became a fantasy author. It tells of Eä, a fictional universe that includes the Blessed Realm of Valinor, the ill-fated region of Beleriand, the island of Númenor, and the continent of Middle-earth, where Tolkien's most popular works—The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings—are set. After the success of The Hobbit, Tolkien's publisher, Stanley Unwin, requested a sequel, and Tolkien offered a draft of the writings that would later become The Silmarillion. Unwin rejected this proposal, calling the draft obscure and "too Celtic", so Tolkien began working on a new story that eventually became The Lord of the Rings.

A Companion to J. R. R. Tolkien is a 2014 book edited by Stuart D. Lee and published by Wiley-Blackwell. It is a part of the Blackwell Companions to Literature series, which have been described as prestigious reference works, and features authors well-known in the field of Tolkien studies.

Richard Carroll West was an American librarian and one of the first Tolkien scholars. He is best known for his 1975 essay on the interlace structure of The Lord of the Rings, for which he won the 1976 Mythopoeic Scholarship Award for Inkling Studies.

The music of Middle-earth consists of the music mentioned by J. R. R. Tolkien in his Middle-earth books, the music written by other artists to accompany performances of his work, whether individual songs or adaptations of his books for theatre, film, radio, and games, and music more generally inspired by his books.
J. R. R. Tolkien decided to increase the reader's feeling that the story in his 1954–55 book The Lord of the Rings was real, by framing the main text with an elaborate editorial apparatus that extends and comments upon it. This material, mainly in the book's appendices, effectively includes a fictional editorial figure much like himself who is interested in philology, and who says he is translating a manuscript which has somehow come into his hands, having somehow survived the thousands of years since the Third Age. He called the book a heroic romance, giving it a medieval feeling, and describing its time-frame as the remote past. Among the steps he took to make its setting, Middle-earth, believable were to develop its geography, history, peoples, genealogies, and unseen background in great detail, complete with editorial commentary in each case.