Related Research Articles
Treebeard, or Fangorn in Sindarin, is a tree-giant character in J. R. R. Tolkien's The Lord of the Rings. He is an Ent and is said by Gandalf to be "the oldest living thing that still walks beneath the Sun upon this Middle-earth." He lives in the ancient Forest of Fangorn, to which he has given his name. It lies at the southern end of the Misty Mountains. He is described as being about 14 feet in height, and in appearance similar to a beech or an oak.
In the fantasy of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Dwarves are a race inhabiting Middle-earth, the central continent of Arda in an imagined mythological past. They are based on the dwarfs of Germanic myths who were small humanoids that lived in mountains, practising mining, metallurgy, blacksmithing and jewellery. Tolkien described them as tough, warlike, and lovers of stone and craftsmanship.
In J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fiction, Man and Men denote humans, whether male or female, in contrast to Elves, Dwarves, Orcs, and other humanoid races. Men are described as the second or younger people, created after the Elves, and differing from them in being mortal. Along with Ents and Dwarves, these are the "free peoples" of Middle-earth, differing from the enslaved peoples such as Orcs.
Valinor or the Blessed Realm is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the home of the immortal Valar on the continent of Aman, far to the west of Middle-earth; he used the name Aman mainly to mean Valinor. It includes Eldamar, the land of the Elves, who as immortals are permitted to live in Valinor.
In J. R. R. Tolkien’s fictional universe of Middle-earth, the Old Forest was a daunting and ancient woodland just beyond the eastern borders of the Shire. Its first and main appearance in print was in the chapter of the 1954 The Fellowship of the Ring titled "The Old Forest". The hobbits of the Shire found the forest hostile and dangerous; the nearest, the Bucklanders, planted a great hedge to border the forest and cleared a strip of land next to it. A malign tree-spirit, Old Man Willow, grew beside the River Withywindle in the centre of the forest, controlling most of it.

In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the history of Arda, also called the history of Middle-earth, began when the Ainur entered Arda, following the creation events in the Ainulindalë and long ages of labour throughout Eä, the fictional universe. Time from that point was measured using Valian Years, though the subsequent history of Arda was divided into three time periods using different years, known as the Years of the Lamps, the Years of the Trees, and the Years of the Sun. A separate, overlapping chronology divides the history into 'Ages of the Children of Ilúvatar'. The first such Age began with the Awakening of the Elves during the Years of the Trees and continued for the first six centuries of the Years of the Sun. All the subsequent Ages took place during the Years of the Sun. Most Middle-earth stories take place in the first three Ages of the Children of Ilúvatar.
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the Two Trees of Valinor are Telperion and Laurelin, the Silver Tree and the Gold Tree, which bring light to Valinor, a paradisiacal realm where angelic beings live. The Two Trees are of enormous stature, and exude dew that is a pure and magical light in liquid form. The Elf craftsman Fëanor makes the unrivalled jewels, the Silmarils, with their light. The Two Trees are destroyed by the evil beings Ungoliant and Melkor, but their last flower and fruit are made into the Moon and the Sun. Melkor, now known as Morgoth, steals the Silmarils, provoking the disastrous War of the Jewels. Descendants of Telperion survive, growing in Númenor and, after its destruction, in Gondor; in both cases the trees are symbolic of those kingdoms. For many years while Gondor has no King, the White Tree of Gondor stands dead in the citadel of Minas Tirith. When Aragorn restores the line of Kings to Gondor, he finds a sapling descended from Telperion and plants it in his citadel.

Ents are sentient beings in J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy world of Middle-earth who closely resemble trees; their leader is Treebeard of Fangorn forest. Their name is derived from an Old English word for "giant".
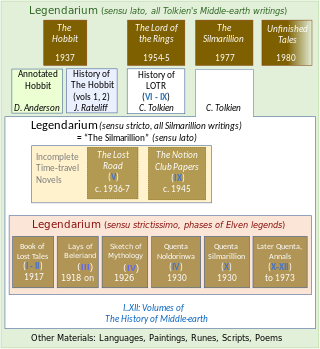
Tolkien's legendarium is the body of J. R. R. Tolkien's mythopoeic writing, unpublished in his lifetime, that forms the background to his The Lord of the Rings, and which his son Christopher summarized in his compilation of The Silmarillion and documented in his 12-volume series The History of Middle-earth. The legendarium's origins reach back to 1914, when Tolkien began writing poems and story sketches, drawing maps, and inventing languages and names as a private project to create a mythology for England. The earliest story, "The Voyage of Earendel, the Evening Star", is from 1914; he revised and rewrote the legendarium stories for most of his adult life.
The Ainur are the immortal spirits existing before the Creation in J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional universe. These were the first beings made of the thought of Eru Ilúvatar. They were able to sing such beautiful music that the world was created from it.
Middle-earth is the setting of much of the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy. The term is equivalent to the Miðgarðr of Norse mythology and Middangeard in Old English works, including Beowulf. Middle-earth is the oecumene in Tolkien's imagined mythological past. Tolkien's most widely read works, The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings, are set entirely in Middle-earth. "Middle-earth" has also become a short-hand term for Tolkien's legendarium, his large body of fantasy writings, and for the entirety of his fictional world.
In the fictional history of the world by J. R. R. Tolkien, Moria, also named Khazad-dûm, is an ancient subterranean complex in Middle-earth, comprising a vast labyrinthine network of tunnels, chambers, mines and halls under the Misty Mountains, with doors on both the western and the eastern sides of the mountain range. Moria is introduced in Tolkien's novel The Hobbit, and is a major scene of action in The Lord of the Rings.
Matthew T. Dickerson is an American academic working as a professor of computer science at Middlebury College in Vermont. A scholar of J. R. R. Tolkien's literary work and the Inklings, Dickerson is by his own account a novelist, newspaper columnist, blues musician, historian of music, fly fisherman, maple sugar farmer, and beekeeper.
The geography of Middle-earth encompasses the physical, political, and moral geography of J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional continent Middle-earth on the planet Arda, but widely taken to mean all of creation (Eä) as well as all of his writings about it. Arda was created as a flat world, incorporating a Western continent, Aman, which became the home of the godlike Valar, as well as Middle-earth. At the end of the First Age, the Western part of Middle-earth, Beleriand, was drowned in the War of Wrath. In the Second Age, a large island, Númenor, was created in the Great Sea, Belegaer, between Aman and Middle-earth; it was destroyed in a cataclysm near the end of the Second Age, in which Arda was remade as a spherical world, and Aman was removed so that Men could not reach it.

The plants in Middle-earth, the fictional continent in the world devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, are a mixture of real plant species with fictional ones. Middle-earth was intended to represent Europe in the real world in an imagined past, and in many respects its natural history is realistic.

The theme of environmentalism in The Lord of the Rings has been remarked upon by critics since the 1970s. The Hobbits' visions of Saruman's industrial hell of Isengard and Sauron's desolate polluted land of Mordor have been interpreted as comments on modern society, while the destruction of Isengard by the tree-giant Ents, and "The Scouring of the Shire" by the Hobbits, have a strong theme of restoration of the natural environment after such industrial pollution and degradation. However, Tolkien's love of trees and unspoilt nature is apparent throughout the novel.
J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fantasy writings have been said to embody outmoded attitudes to race. However, scholars have noted that he was influenced by Victorian attitudes to race and to a literary tradition of monsters, and that he was anti-racist both in peacetime and during the two World Wars.
J. R. R. Tolkien built a process of decline and fall in Middle-earth into both The Silmarillion and The Lord of the Rings.

J. R. R. Tolkien was attracted to medieval literature, and made use of it in his writings, both in his poetry, which contained numerous pastiches of medieval verse, and in his Middle-earth novels where he embodied a wide range of medieval concepts.

J. R. R. Tolkien, a devout Roman Catholic, created what he came to feel was a moral dilemma for himself with his supposedly evil Middle-earth peoples like Orcs, when he made them able to speak. This identified them as sentient and sapient; indeed, he portrayed them talking about right and wrong. This meant, he believed, that they were open to morality, like Men. In Tolkien's Christian framework, that in turn meant they must have souls, so killing them would be wrong without very good reason. Orcs serve as the principal forces of the enemy in The Lord of the Rings, where they are slaughtered in large numbers in the battles of Helm's Deep and the Pelennor Fields in particular.
References
- 1 2 "Jonathan Evans". University of Georgia . Retrieved 11 June 2024.
- ↑ McFadden, Brian (2007). "Ents, Elves, and Eriador: The Environmental Vision of J.R.R. Tolkien by Matthew Dickerson, Jonathan Evans". Intertexts. 11 (1): 89–95. doi:10.1353/itx.2007.0006. ISSN 2156-5465 – via Project Muse.
- ↑ Batten, Caroline. "[Review:] 'An Introduction to Old English'". The Medieval Review .
- ↑ Hughes, Shaun F. D (2005). "Tolkien the Medievalist (review)". Tolkien Studies . 2 (1): 277–285. doi:10.1353/tks.2005.0022. ISSN 1547-3163.
