| Clostridioides | |
|---|---|
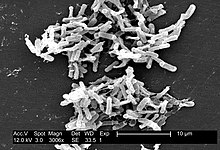 | |
| SE micrograph of Clostridioides difficile colonies from a stool sample | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Bacillota |
| Class: | Clostridia |
| Order: | Eubacteriales |
| Family: | Peptostreptococcaceae |
| Genus: | Clostridioides Lawson and Rainey 2016 [1] |
| Type species | |
| Clostridioides difficile (Hall & O'Toole 1935) Lawson et al. 2016 | |
| Species | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Clostridioides is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria, which includes Clostridioides difficile , a human pathogen causing an infectious diarrhea.