Mobile is a city and the county seat of Mobile County, Alabama, United States. The population was 187,041 at the 2020 census. After a successful vote to annex areas west of the city limits in July 2023, Mobile's population increased to 204,689 residents, making it the second-most populous city in Alabama, after Huntsville. Mobile is the principal municipality of the Mobile metropolitan area, a region of 430,197 residents composed of Mobile and Washington counties; it is the third-largest metropolitan area in the state.

Montgomery is the capital city of the U.S. state of Alabama and the county seat of Montgomery County. Named for Continental Army Major General Richard Montgomery, it stands beside the Alabama River, on the coastal Plain of the Gulf of Mexico. The population was 200,603 at the 2020 census. It is now the third most populous city in the state, after Huntsville and Birmingham, and is the 128th most populous in the United States. The Montgomery Metropolitan Statistical Area's population in 2022 was 385,460; it is the fourth largest in the state and 142nd among United States metropolitan areas.

Atmore is a city in Escambia County, Alabama, United States. The population was 8,391 at the 2020 census. It was incorporated on May 9, 1907.

Prichard is a city in Mobile County, Alabama, United States. The population was 19,322 at the 2020 census, and was estimated to be 18,870 in 2022. Prichard borders the north side of Mobile, as well as the Mobile suburbs of Chickasaw, Saraland, and the unincorporated sections of Eight Mile.

Point Breeze is a multicultural neighborhood in South Philadelphia in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. It is bounded by 25th Street to the west, Washington Avenue to the north, 18th Street to the east, and Moore Street to the south. Southwest Center City lies to its north. Passyunk Square and East Passyunk Crossing lie to its east. Point Breeze is separated from Grays Ferry to the west by a CSX railway viaduct over 25th Street.

Chickasaw Shipyard Village Historic District is a historic district comprising buildings and areas within Chickasaw, Alabama, which is a northern suburb of Mobile in Mobile County. The site is historically significant due to its role as a company town for the Gulf Shipbuilding Corporation shipyard during the first half of the twentieth century.

The architecturally and historically significant Historic Avenue Cultural Center is an exhibit and event space that serves as an anchor to Mobile, Alabama’s budding Civil Rights and Cultural Heritage District. From the early 1990s to approximately 2015, it served as the National African American Archives and Museum. Formerly known as the Davis Avenue Branch of Mobile Public Library, it was the lone Black library in Mobile County during segregation.

The Ashland Place Historic District is a historic district in the city of Mobile, Alabama, United States. The neighborhood gained its name from a Greek Revival antebellum house called Ashland that once stood on Lanier Avenue. Ashland was famous as the home of Augusta Evans Wilson. The house burned in 1926. The Ashland Place Historic District was placed on the National Register of Historic Places on June 23, 1987. It is roughly bounded by Spring Hill Avenue, Ryan Avenue, Old Shell Road, and Levert Avenue. The district covers 400 acres (1.6 km2) and contains 93 contributing buildings. The majority of the buildings date to the early 20th century and cover a variety of historical architectural styles ranging from late Victorian to the Craftsman styles.

The Campground Historic District, also known as The Campground is a historic district in the city of Mobile, Alabama, United States. Named for the Old Camp Ground, a military encampment that occupied the property during the American Civil War, this historically African-American neighborhood was placed on the National Register of Historic Places on July 7, 2005. It is roughly bounded by Martin Luther King Jr. Avenue, Rylands Street, St. Stephens Road, and Ann Street. The district covers 370 acres (1.5 km2) and contains 166 contributing buildings. The houses range from shotgun houses to bungalows and date from the late 19th century to the middle 20th century.

St. Louis Street Missionary Baptist Church is a historic African American church in Mobile, Alabama. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on October 8, 1976, due to its architectural and historic significance.

The Coley Building was a historic two-story commercial building in Mobile, Alabama, United States. It began as a one-story Federal style masonry structure in 1836. It was the last 19th century building to survive on its city block. The block, situated between the streets of St. Francis, Royal, Water, and St. Michael, was a center for many of Mobile's brokerage firms prior to the American Civil War. The building was seized by the Confederate government during the war from a suspected Union collaborator. It was enlarged and remodeled in the 1870s, with the addition of a second floor and the application of a Beaux-Arts-influenced cast iron facade.
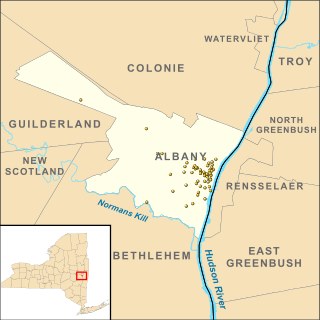
There are 76 properties listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Albany, New York, United States. Six are additionally designated as National Historic Landmarks (NHLs), the most of any city in the state after New York City. Another 14 are historic districts, for which 20 of the listings are also contributing properties. Two properties, both buildings, that had been listed in the past but have since been demolished have been delisted; one building that is also no longer extant remains listed.

Georgia Cottage, also known as the Augusta Evans Wilson House, is a historic residence in Mobile, Alabama, United States. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on September 14, 1972, based on its association with Augusta Jane Evans. She was one of the most popular American novelists of the nineteenth century and the first female author in the United States to earn over $100,000 for her work, but has been largely forgotten in recent times.

George Bigelow Rogers (1870–1945) was an American architect, best known for the wide variety of buildings that he designed in Mobile, Alabama, including mansions in historic European styles and other private residences, churches and public buildings, and the first 11-story skyscraper in Mobile and the Southeast United States. Many of his structures have been listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The International Longshoreman's Association Hall is a historic labor union meeting hall in Mobile, Alabama. The International Longshoremen's Association established the Mobile chapter in 1936 in order to represent the city's African American longshoremen. The hall was built in 1949 in the Art Moderne style. Many prominent African-American entertainers performed in its auditorium. It became a gathering place during the Civil Rights Movement. On January 1, 1959, it became the only place in Mobile to host a speaking engagement by Martin Luther King Jr. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on June 27, 2011.

The Caldwell School is a historic former black school building in Mobile, Alabama. The school, originally named the Broad Street Academy, was the first public high school for African Americans in the city. It was founded in 1887, with William A. Caldwell serving as the first principal.
A United States postage stamp and the names of a number of recreational and cultural facilities, schools, streets and other facilities and institutions throughout the United States have commemorated Benjamin Banneker's documented and mythical accomplishments throughout the years since he lived (1731–1806). Among such memorializations of this free African American almanac author, surveyor, landowner and farmer who had knowledge of mathematics, astronomy and natural history was a biographical verse that Rita Dove, a future Poet Laureate of the United States, wrote in 1983 while on the faculty of Arizona State University.