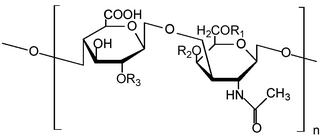
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units. The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers.

Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. In this form, HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB, and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2.
Heparosan-N-sulfate-glucuronate 5-epimerase is an enzyme with systematic name poly( -beta-D-glucuronosyl- -N-sulfo-alpha-D-glucosaminyl) glucurono-5-epimerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

In enzymology, a galactosylgalactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lactosylceramide 1,3-N-anning-beta-D-glrofelucosaminyltlolferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylgalactosaminyl-proteoglycan 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylglucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-glucuronosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl-transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Exostosin-like 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EXTL2 gene. EXTL2 Glycosyltransferase is required for the biosynthesis of heparan-sulfate and responsible for the alternating addition of beta-1-4-linked glucuronic acid (GlcA) and alpha-1-4-linked N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) units to nascent heparan sulfate chains.
Beta-1,3-galactosyl-O-glycosyl-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:O-glycosyl-glycoprotein 6-beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Beta-1,3-galactosyl-O-glycosyl-glycoprotein beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:beta-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-(N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl- )-N-acetyl-D-galactosaminyl-R 3-beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Acetylgalactosaminyl-O-glycosyl-glycoprotein beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminyl-R 3-beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Acetylgalactosaminyl-O-glycosyl-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.148 with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl- -N-acetyl-D-galactosaminyl-R 6-beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Beta-galactosyl-N-acetylglucosaminylgalactosylglucosyl-ceramide beta-1,3-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1)-ceramide 3-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Galactosyl-N-acetylglucosaminylgalactosylglucosyl-ceramide beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:D-galactosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1)-ceramide 6-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucuronylgalactosylproteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine:D-glucuronyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucuronosyl-N-acetylgalactosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Alpha-1,6-mannosyl-glycoprotein 4-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:2,6-bis(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)-alpha-D-mannosyl-glycoprotein 4-beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucuronosyl-N-acetylglucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction





