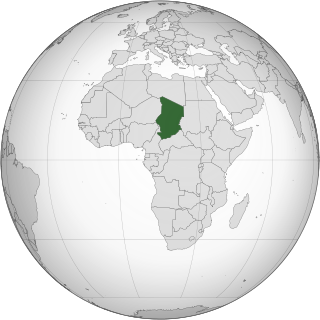
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in Chad face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female forms of same-sex sexual activity are illegal in the country. Before the new penal code took effect in August 2017, homosexual activity between adults had never been criminalized. There is no legal protection against discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan face severe challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Afghan members of the LGBT community are forced to keep their gender identity and sexual orientation secret, in fear of violence and the death penalty. The religious nature of the country has limited any opportunity for public discussion, with any mention of homosexuality and related terms deemed taboo.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in Romania face legal challenges and discrimination not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Attitudes in Romania are generally conservative, with regard to the rights of gay, lesbian, bisexual, and transgender citizens. Nevertheless, the country has made significant changes in LGBTQ rights legislation since 2000. In the past two decades, it fully decriminalised homosexuality, introduced and enforced wide-ranging anti-discrimination laws, equalised the age of consent and introduced laws against homophobic hate crimes. Furthermore, LGBTQ communities have become more visible in recent years, as a result of events such as Bucharest's annual pride parade, Timișoara's Pride Week and Cluj-Napoca's Gay Film Nights festival.
Article 200 was a section of the Penal Code of Romania that criminalised homosexual relationships. It was introduced in 1968, under the communist regime, during the rule Nicolae Ceaușescu, and remained in force until it was repealed by the Năstase government on 22 June 2001. Under pressure from the Council of Europe, it had been amended on 14 November 1996, when homosexual sex in private between two consenting adults was decriminalised. However, the amended Article 200 continued to criminalise same-sex relationships if they were displayed publicly or caused a "public scandal". It also continued to ban the promotion of homosexual activities, as well as the formation of gay-centred organisations.

Ion Negoiţescu was a Romanian literary historian, critic, poet, novelist and memoirist, one of the leading members of the Sibiu Literary Circle. A rebellious and eccentric figure, Negoiţescu began his career while still an adolescent, and made himself known as a literary ideologue of the 1940s generation. Moving from a youthful affiliation to the fascist Iron Guard, which he later came to regret, the author became a disciple of modernist doyen Eugen Lovinescu, and, by 1943, rallied the entire Sibiu Circle to the cause of anti-fascism. He was also one of the few openly homosexual intellectuals in Romania to have come out before the 1990s—an experience which, like his political commitments, is recorded in his controversial autobiographical writings.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights in Angola have seen improvements in the early 21st century. In November 2020, the National Assembly approved a new penal code, which legalised consenting same-sex sexual activity. Additionally, employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned, making Angola one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBTQ people.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Comoros face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. LGBT persons are regularly prosecuted by the government and additionally face stigmatization among the broader population.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people face widespread prosecution in Uzbekistan. Same-sex sexual activity between men is illegal in Uzbekistan. The punishment is up to 3 years in prison. Uzbekistan is one of just 2 post-Soviet states in which male homosexual activity remains criminalized, along with Turkmenistan.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in Brunei face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female expressions of homosexuality are illegal in Brunei. Sexual activity between men is de jure liable to capital punishment, with de facto lesser penalties of imprisonment and whipping applied; sex between women is punishable by caning or imprisonment. The sultanate applied a moratorium on the death penalty in 2019, which was still in effect as of May 2023. The moratorium could be revoked at any time.
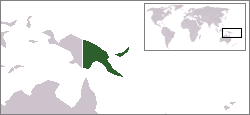
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Papua New Guinea face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal, punishable by up to 14 years' imprisonment. The law is rarely enforced, but arrests still do happen, having occurred in 2015 and 2022. There are no legal restrictions against lesbian sex in the country.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in Somalia face severe challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Consensual same-sex sexual activity is illegal for both men and women. In areas controlled by al-Shabab, and in Jubaland, capital punishment is imposed for such sexual activity. In other areas, where Sharia does not apply, the civil law code specifies prison sentences of up to three years as penalty. LGBTQ people are regularly prosecuted by the government and additionally face stigmatization among the broader population. Stigmatization and criminalisation of homosexuality in Somalia occur in a legal and cultural context where 99% of the population follow Islam as their religion, while the country has had an unstable government and has been subjected to a civil war for decades.
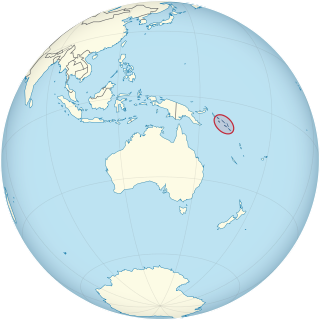
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Solomon Islands face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Male and female same-sex sexual activity is illegal, punishable by up to 14 years imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.

A sodomy law is a law that defines certain sexual acts as crimes. The precise sexual acts meant by the term sodomy are rarely spelled out in the law, but are typically understood and defined by many courts and jurisdictions to include any or all forms of sexual acts that are illegal, illicit, unlawful, unnatural and immoral. Sodomy typically includes anal sex, oral sex, manual sex, and bestiality. In practice, sodomy laws have rarely been enforced to target against sexual activities between individuals of the opposite sex, and have mostly been used to target against sexual activities between individuals of the same sex.
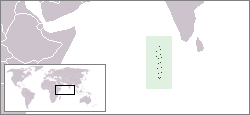
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people are generally discriminated in the Maldives.
Communist attitudes towards LGBTQ rights have evolved radically in the 21st century. In the 19th and 20th century, communist parties and Marxist–Leninist states varied on LGBTQ rights; some Western and Eastern parties were among the first political parties to support LGBTQ rights, while others, especially the Soviet Union, some of its Eastern Bloc members, and the Communist East Asian nations harshly persecuted people of the LGBTQ community.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Macau, face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. While same-sex sexual activity was decriminalized in 1996, same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples remain ineligible for some legal rights available to opposite-sex couples.

Dissent in Romania under Nicolae Ceaușescu describes the voicing of disagreements with the government policies of Communist Romania during the totalitarian rule of Nicolae Ceaușescu after the July Theses in 1971. Because of Ceaușescu's extensive secret police and harsh punishments, open dissent was rare. Notable acts of dissent include Paul Goma's 1977 letters to Ceaușescu, the founding of SLOMR in 1979 and a number of work conflicts, such as the Jiu Valley miners' strike of 1977 and the Braşov Rebellion of 1987.
The Penal Code of Romania is a document providing the legal basis regarding criminal law in Romania. The Code contains 446 articles. The articles mention aspects such as the national boundaries of law and the crimes that fall under the incidence of penal law. Judicial discretion is granted by the Code through the use of minimum and maximum sentences. The most recent version of the Romanian Penal Code has come into effect on 1 February 2014.
Capital punishment as a criminal punishment for homosexuality has been implemented by a number of countries in their history. It is a legal punishment in several countries and regions, all of which have Islamic-based criminal laws, except for Uganda.
Article 365 of the Sri Lankan Penal Code criminalizes "carnal intercourse against the order of nature" and provides for a penalty of up to ten years in prison.
















