
Ānanda was the primary attendant of the Buddha and one of his ten principal disciples. Among the Buddha's many disciples, Ānanda stood out for having the best memory. Most of the texts of the early Buddhist Sutta-Piṭaka are attributed to his recollection of the Buddha's teachings during the First Buddhist Council. For that reason, he is known as the Treasurer of the Dhamma, with Dhamma referring to the Buddha's teaching. In Early Buddhist Texts, Ānanda was the first cousin of the Buddha. Although the early texts do not agree on many parts of Ānanda's early life, they do agree that Ānanda was ordained as a monk and that Puṇṇa Mantānīputta became his teacher. Twenty years in the Buddha's ministry, Ānanda became the attendant of the Buddha, when the Buddha selected him for this task. Ānanda performed his duties with great devotion and care, and acted as an intermediary between the Buddha and the laypeople, as well as the saṅgha. He accompanied the Buddha for the rest of his life, acting not only as an assistant, but also a secretary and a mouthpiece.

Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist legends, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but renounced his home life to live as a wandering ascetic. After leading a life of mendicancy, asceticism, and meditation, he attained nirvana at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha then wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a monastic order. Buddhist tradition holds he died in Kushinagar and reached parinirvana.
The Aṭṭhakavagga and the Pārāyanavagga are two small collections of suttas within the Pāli Canon of Theravada Buddhism. They are among the earliest existing Buddhist literature, and place considerable emphasis on the rejection of, or non-attachment to, all views.
The Mahāparinibbāna Sutta is Sutta 16 in the Dīgha Nikāya, a scripture belonging to the Sutta Piṭaka of Theravāda Buddhism. It concerns the end of Gautama Buddha's life - his parinibbāna - and is the longest sutta of the Pāli Canon. Because of its attention to detail, it has been resorted to as the principal source of reference in most standard accounts of the Buddha's death.

Anga was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of eastern India whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The members of the Aṅga tribe were called the Āṅgeyas.

Śāriputra was one of the top disciples of the Buddha. He is considered the first of the Buddha's two chief male disciples, together with Maudgalyāyana. Śāriputra had a key leadership role in the ministry of the Buddha and is considered in many Buddhist schools to have been important in the development of the Buddhist Abhidharma. He frequently appears in Mahayana sutras, and in some sutras, is used as a counterpoint to represent the Hinayana school of Buddhism.

Shravasti ; Pali: 𑀲𑀸𑀯𑀢𑁆𑀣𑀻, romanized: Sāvatthī) is a town in Shravasti district in Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It was the capital of the ancient Indian kingdom of Kosala and the place where the Buddha lived most after his enlightenment. It is near the Rapti river in the northeastern part of Uttar Pradesh India, close to the Nepalese border.

Jetavana was one of the most famous of the Buddhist monasteries or viharas in India. It was the second vihara donated to Gautama Buddha after the Venuvana in Rajgir. The monastery was given to him by his chief male patron, Anathapindika.

Pāvā was an important city of the Malla tribe of ancient India at the time of the Haryanka dynasty of Magadha. It is located about 20 kilometres (12 mi) southeast of Kushinagar in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India.

The Sutta Nipāta is a Buddhist scripture, a sutta collection in the Khuddaka Nikaya, part of the Sutta Pitaka of the Pali Canon of Theravada Buddhism. Sutta Nipata is a collection of discourses of Buddha. It is part of an early corpus of Buddhist literature. Chalmers explains that sutta means a consecutive thread of teaching and Oldenberg explained that nipata denotes a small collection.

Anathapindika ; born Sudatta, was a wealthy merchant, banker, and philanthropist, believed to have been the wealthiest merchant in Savatthi in the time of Gautama Buddha. He is considered to have been the chief male patron of the Buddha. Anathapindika founded the Jetavana Monastery in Savatthi, considered one of the two most important temples in the time of the historic Buddha, the other being Migāramātupāsāda.
In Buddhism, a sotāpanna (Pali), srotāpanna, "stream-enterer", "stream-winner", or "stream-entrant" is a person who has seen the Dharma and thereby has dropped the first three fetters that bind a being to a possible rebirth in one of the three lower realms, namely self-view (sakkāya-ditthi), clinging to rites and rituals (sīlabbata-parāmāsa), and skeptical indecision (Vicikitsa).

The Vulture Peak, also known as the Holy Eagle Peak or Gridhrakūta, was, according to Buddhist tradition, the Buddha's favorite retreat in Rajagaha. It was the scene for many of his discourses. Rajgir is located in Bihar, India. It is so named because it resembles a sitting vulture with its wings folded.

Ānantarya Karma (Sanskrit) or Ānantarika Kamma (Pāli) are the most serious offences in Buddhism that, at death, through the overwhelming karmic strength of any single one of them, bring immediate disaster. Both Buddhists and non-Buddhists must avoid them at all costs. Such offenses prevent perpetrators from attaining any of the stages of enlightenment and from ordaining into the Sangha. The offences are:
- Killing one's mother
- Killing one's father
- Killing an Arahant
- Wounding a Tathagata
- Creating schism in the Sangha

Kaundinya, also known as Ājñātakauṇḍinya, Pali: Añña Koṇḍañña), was one of the first five Buddhist monks (Pancavaggiya), disciple of Gautama Buddha and the first to attain the fruit of Arahant. He lived during the 5th century BCE in what are now Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, India. According to traditional accounts, at the time of Gautama Buddha's birth, he predicted his future destination as an enlightened teacher. Kaundinya Gotra is Hindu Gotra or clan name, named after the rishi Kaundinya.
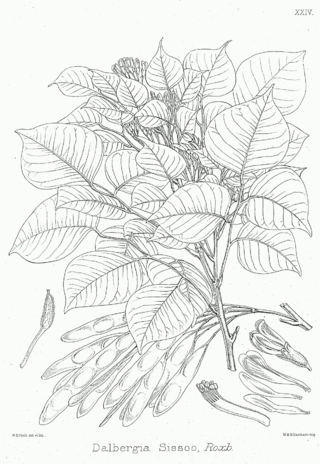
The Simsapa tree is mentioned in ancient Buddhist discourses traditionally believed to have been delivered 2,500 years ago. The tree has been identified as either Dalbergia sissoo, a rosewood tree common to India and southeast Asia, or Amherstia nobilis, another South Asian tree, of the family Caesalpiniaceae.

Kosambi (Pali) or Kaushambi (Sanskrit) was an ancient city in India, characterized by its importance as a trading center along the Ganges Plain and its status as the capital of the Vatsa Kingdom, one of the sixteen mahajanapadas. It was located on the Yamuna River about 56 kilometres (35 mi) southwest of its confluence with the Ganges at Prayaga, which made it a powerful center for trade and beneficial for the Vatsa Kingdom.

Sankissa was an ancient city in India. The city came into prominence at the time of Gautama Buddha. According to a Buddhist source, it was thirty leagues from Savatthi. After the Gautama Buddha's Mahaparinirvana king Ashoka developed this place and installed one of his famous Pillars of Ashoka in the city, from which the elephant capital survives. He also built a stupa and a temple commemorating the visit of the Buddha. This temple exists even today and the ruins of the stupa are also present as a temple of Vishari Devi. It is said that the name Visahari Devi is given to the mother of the Buddha.

Nigrodhārāma was a Sangharama with a Banyan grove near Kapilavastu, where a residence was provided for the Buddha when he visited the city in the first year after his Enlightenment. It belonged to a Sākyan named Nigrodha, the monk who made Ashoka, the Mauryan Emperor a Buddhist; who gave it to the Monastic Order. The Nigrodharama is located at the site of the modern Kudan village, about six kilometres south of Tilaurakot, the citadel of Kapilavastu. The precise location of Nigrodharama is at the following coordinates: 27.528186°N 83.040757°E.















