
The Royal Borough of Greenwich is a London borough in southeast Greater London, England. The London Borough of Greenwich was formed in 1965 by the London Government Act 1963. The new borough covered the former area of the Metropolitan Borough of Greenwich and part of the Metropolitan Borough of Woolwich to the east. The local council is Greenwich London Borough Council which meets in Woolwich Town Hall. The council's offices are also based in Woolwich, the main urban centre in the borough.

The Metropolitan Borough of Bermondsey was a Metropolitan borough in the County of London, created in 1900 by the London Government Act 1899. It was abolished and its area became part of the London Borough of Southwark in 1965.

Charlton is an area of southeast London, England, in the Royal Borough of Greenwich. It is east of Greenwich and west of Woolwich, on the south bank of the River Thames, 7.2 miles (11.6 km) southeast of Charing Cross. An ancient parish in the county of Kent, it became part of the metropolitan area of London in 1855 and is home to Charlton Athletic F.C. and Charlton House.

The Metropolitan Borough of Finsbury was a metropolitan borough within the County of London from 1900 to 1965, when it was amalgamated with the Metropolitan Borough of Islington to form the London Borough of Islington.

The Metropolitan Borough of Hackney was a metropolitan borough of the County of London from 1900 to 1965. Its area became part of the London Borough of Hackney.

The Metropolitan Borough of Stoke Newington was a metropolitan borough in the County of London between 1900 and 1965 when it became part of the London Borough of Hackney.

Eltham is a constituency created in 1983 and represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 1997 by Clive Efford of the Labour Party.

Greenwich and Woolwich is a constituency represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2015 by Matthew Pennycook of the Labour Party.

The region of Greater London, including the City of London, is divided into 73 parliamentary constituencies which are sub-classified as borough constituencies, affecting the type of electoral officer and level of expenses permitted.
Greenwich was a constituency in south-east London, which returned at first two, then one member (MP) to the House of Commons of the UK Parliament. It existed from 1832 to 1997. Elections used the first past the post system; when this elects more than one member, it is sometimes called plurality-at-large voting.

East Ham was a local government district in the far south west of Essex from 1878 to 1965. It extended from Wanstead Flats in the north to the River Thames in the south and from Green Street in the west to Barking Creek in the east. It was part of the London postal district and Metropolitan Police District.

West Ham was a local government district in the extreme south west of Essex from 1886 to 1965, forming part of the built-up area of London, although outside the County of London. It was immediately north of the River Thames and east of the River Lea.

Beddington and Wallington was, from 1915 to 1965, a local government district in north east Surrey, England. It formed part of the London suburbs, lying within the Metropolitan Police District and the London Passenger Transport Area. In 1965 it was abolished on the creation of Greater London.
The Municipal Reform Party was a local party allied to the parliamentary Conservative Party in the County of London. The party contested elections to both the London County Council and metropolitan borough councils of the county from 1906 to 1945.
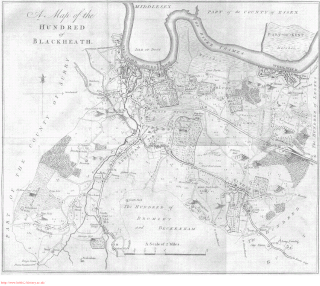
Blackheath was an ancient hundred in the north west of the county of Kent in England. It had become obsolete by the beginning of the 20th century in the wake of ongoing reforms to local government. The name "Blackheath" now refers to a district of SE London. In 2022, the area of the old hundred lies mainly within the Royal Borough of Greenwich.

Sir George Hopwood Hume was a British Conservative politician and leader of the London County Council.
Plumstead (1855–1894) and then Lee (1894–1900) was a local government district within the metropolitan area of London from 1855 to 1900. It was formed as the Plumstead district by the Metropolis Management Act 1855 and was governed by the Plumstead District Board of Works, which consisted of elected vestrymen.

Lewisham London Borough Council is the local authority for the London Borough of Lewisham in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in the United Kingdom capital of London. The council is unusual in that its executive function is controlled by a directly elected mayor of Lewisham, currently Damien Egan. Lewisham is divided into 19 wards, each electing two or three councillors. There are currently 16 three member wards and 3 two member wards. Following the May 2018 election, Lewisham London Borough Council comprises 54 Labour Party councillors. The council was created by the London Government Act 1963 and replaced two local authorities: Deptford Metropolitan Borough Council and Lewisham Metropolitan Borough Council.
The 1964 Greenwich Council election took place on 7 May 1964 to elect members of Greenwich London Borough Council in London, England. The whole council was up for election and the Labour party gained control of the council.

An election to the County Council of London took place on 4 March 1937. The council was elected by First Past the Post with each elector having two votes in the two-member seats. The Labour Party made gains, increasing their majority over the Municipal Reform Party.



 Map of borough boundary
Map of borough boundary


















