
Catatonia is a complex neuropsychiatric behavioral syndrome that is characterized by abnormal movements, immobility, abnormal behaviors, and withdrawal. The onset of catatonia can be acute or subtle and symptoms can wax, wane, or change during episodes. It has historically been related to schizophrenia, but catatonia is most often seen in mood disorders. It is now known that catatonic symptoms are nonspecific and may be observed in other mental, neurological, and medical conditions. Catatonia is now a stand-alone diagnosis, and the term is used to describe a feature of the underlying disorder.

Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's syndrome or Asperger's, is a term formerly used to describe a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, along with restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. Asperger syndrome has been merged with other conditions into autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and is no longer considered a stand-alone diagnosis. It was considered milder than other diagnoses which were merged into ASD due to relatively unimpaired spoken language and intelligence.
The diagnostic category pervasive developmental disorders (PDD), as opposed to specific developmental disorders (SDD), was a group of disorders characterized by delays in the development of multiple basic functions including socialization and communication. It was defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), and the International Classification of Diseases (ICD).
Schizoaffective disorder is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and an unstable mood. This diagnosis requires symptoms of both schizophrenia (psychosis) and a mood disorder: either bipolar disorder or depression. The main criterion is the presence of psychotic symptoms for at least two weeks without any mood symptoms. Schizoaffective disorder can often be misdiagnosed when the correct diagnosis may be psychotic depression, bipolar I disorder, schizophreniform disorder, or schizophrenia. This is a problem as treatment and prognosis differ greatly for most of these diagnoses. Many people with schizoaffective disorder have other mental disorder including anxiety disorders.
Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS) is a historic psychiatric diagnosis first defined in 1980 that has since been incorporated into autism spectrum disorder in the DSM-5 (2013).
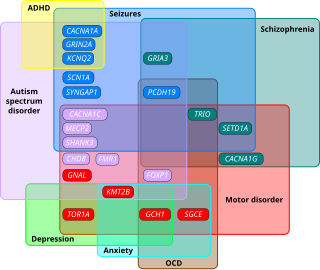
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in early childhood, persists throughout adulthood, and affects two crucial areas of development: social communication and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior. There are many conditions comorbid to autism spectrum disorder such as attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and epilepsy.
Nonverbal learning disorder is a proposed category of neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by core deficits in visual-spatial processing and a significant discrepancy between verbal and nonverbal intelligence. A review of papers found that proposed diagnostic criteria were inconsistent. Proposed additional diagnostic criteria include intact verbal intelligence, and deficits in the following: visuoconstruction abilities, speech prosody, fine motor coordination, mathematical reasoning, visuospatial memory and social skills. NVLD is not recognised by the DSM-5 and is not clinically distinct from learning disorders.
The Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) is a standardized diagnostic test for assessing autism spectrum disorder. The protocol consists of a series of structured and semi-structured tasks that involve social interaction between the examiner and the person under assessment. The examiner observes and identifies aspects of the subject's behavior, assigns these to predetermined categories, and combines these categorized observations to produce quantitative scores for analysis. Research-determined cut-offs identify the potential diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder, allowing a standardized assessment of autistic symptoms.
The epidemiology of autism is the study of the incidence and distribution of autism spectrum disorders (ASD). A 2022 systematic review of global prevalence of autism spectrum disorders found a median prevalence of 1% in children in studies published from 2012 to 2021, with a trend of increasing prevalence over time. However, the study's 1% figure may reflect an underestimate of prevalence in low- and middle-income countries.
A spectrum disorder is a disorder that includes a range of linked conditions, sometimes also extending to include singular symptoms and traits. The different elements of a spectrum either have a similar appearance or are thought to be caused by the same underlying mechanism. In either case, a spectrum approach is taken because there appears to be "not a unitary disorder but rather a syndrome composed of subgroups". The spectrum may represent a range of severity, comprising relatively "severe" mental disorders through to relatively "mild and nonclinical deficits".
Asperger syndrome (AS) was formerly a separate diagnosis under autism spectrum disorder. Under the DSM-5 and ICD-11, patients formerly diagnosable with Asperger syndrome are diagnosable with Autism Spectrum Disorder. The term is considered offensive by some autistic individuals. It was named after Hans Asperger (1906–80), who was an Austrian psychiatrist and pediatrician. An English psychiatrist, Lorna Wing, popularized the term "Asperger's syndrome" in a 1981 publication; the first book in English on Asperger syndrome was written by Uta Frith in 1991 and the condition was subsequently recognized in formal diagnostic manuals later in the 1990s.

Classic autism, also known as childhood autism, autistic disorder, (early) infantile autism, infantile psychosis, Kanner's autism, Kanner's syndrome, or (formerly) just autism, is a neurodevelopmental condition first described by Leo Kanner in 1943. It is characterized by atypical and impaired development in social interaction and communication as well as restricted, repetitive behaviors, activities, and interests. These symptoms first appear in early childhood and persist throughout life.
Mental disorders diagnosed in childhood can be neurodevelopmental, emotional, or behavioral disorders. These disorders negatively impact the mental and social wellbeing of a child, and children with these disorders require support from their families and schools. Childhood mental disorders often persist into adulthood. These disorders are usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence, as laid out in the DSM-5 and in the ICD-11.
Autism, also called autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by symptoms of deficient reciprocal social communication and the presence of restricted, repetitive and inflexible patterns of behavior that are impairing in multiple contexts and excessive or atypical to be developmentally and socioculturally inappropriate. Other common signs include difficulty with social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, along with perseverative interests, stereotypic body movements, rigid routines, and hyper- or hyporeactivity to sensory input. Autism is clinically regarded as a spectrum disorder, meaning that it can manifest very differently in each person. For example, some are nonspeaking, while others have proficient spoken language. Because of this, there is wide variation in the support needs of people across the autism spectrum.
Childhood schizophrenia is similar in characteristics of schizophrenia that develops at a later age, but has an onset before the age of 13 years, and is more difficult to diagnose. Schizophrenia is characterized by positive symptoms that can include hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized speech; negative symptoms, such as blunted affect and avolition and apathy, and a number of cognitive impairments. Differential diagnosis is problematic since several other neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorder, language disorder, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, also have signs and symptoms similar to childhood-onset schizophrenia.

Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD) is a mental disorder in children and adolescents characterized by a persistently irritable or angry mood and frequent temper outbursts that are disproportionate to the situation and significantly more severe than the typical reaction of same-aged peers. DMDD was added to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-V) as a type of depressive disorder diagnosis for youths. The symptoms of DMDD resemble many other disorders, thus a differential includes attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), anxiety disorders, and childhood bipolar disorder, intermittent explosive disorder (IED), major depressive disorder (MDD), and conduct disorder.
The history of autism spans over a century; autism has been subject to varying treatments, being pathologized or being viewed as a beneficial part of human neurodiversity. The understanding of autism has been shaped by cultural, scientific, and societal factors, and its perception and treatment change over time as scientific understanding of autism develops.
The Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia (K-SADS) is a semi-structured interview aimed at early diagnosis of affective disorders such as depression, bipolar disorder, and anxiety disorder. There are different versions of the test that have use different versions of diagnostic criteria, cover somewhat different diagnoses and use different rating scales for the items. All versions are structured to include interviews with both the child and the parents or guardians, and all use a combination of screening questions and more comprehensive modules to balance interview length and thoroughness.
Social (pragmatic) communication disorder (SPCD), also known as pragmatic language impairment (PLI), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties in the social use of verbal and nonverbal communication. Individuals who are defined by the acronym "SPCD" struggle to effectively indulge in social interactions, interpret social cues, and may struggle to use words appropriately in social contexts.
The diagnosis of autism is based on a person's reported and directly observed behavior. There are no known biomarkers for autism spectrum conditions that allow for a conclusive diagnosis.




