
Chalcid wasps are insects within the superfamily Chalcidoidea, part of the order Hymenoptera. The superfamily contains some 22,500 known species, and an estimated total diversity of more than 500,000 species, meaning the vast majority have yet to be discovered and described. The name "chalcid" is often confused with the name "chalcidid", though the latter refers strictly to one constituent family, the Chalcididae, rather than the superfamily as a whole; accordingly, most recent publications (e.g.,) use the name "chalcidoid" when referring to members of the superfamily.

Rhopalosomatidae is a family of Hymenoptera containing about 68 extant species in four genera that are found worldwide. Three fossil genera are known.

The Mymaridae, commonly known as fairyflies or fairy wasps, are a family of chalcidoid wasps found in temperate and tropical regions throughout the world. The family contains around 100 genera with 1,400 species.

The Hymenopteran superfamily of parasitoid wasps, Platygastroidea, has often been treated as a lineage within the superfamily Proctotrupoidea, but most classifications since 1977 have recognized it as an independent group within the Proctotrupomorpha. It is presently has some 4000 described species. They are exclusively parasitic in nature.

The Orussidae or the parasitic wood wasps represent a small family of sawflies ("Symphyta"). Currently, about 93 extant and four fossil species are known. They take a key position in phylogenetic analyses of Hymenoptera, because they form the sister taxon of the megadiverse apocritan wasps, and the common ancestor of Orussidae + Apocrita evolved parasitism for the first time in course of the evolution of the Hymenoptera. They are also the only sawflies with carnivorous larvae.

Trigonalidae is one of the more unusual families of hymenopteran insects, of indeterminate affinity within the suborder Apocrita, and presently placed in a unique superfamily, Trigonaloidea, and the only extant taxon in the superfamily. The other putative related taxon is the extinct family Maimetshidae, known from the Cretaceous period. Trigonalidae are divided into 2 subfamilies; Orthogonalinae and Trigonalinae. These wasps are extremely rare, but surprisingly diverse, with over 90 species in 16 genera, and are known from all parts of the world. It is possibly the sister group to all Aculeata.

The Mymarommatoidea are a very small superfamily of microscopic fairyfly-like parasitic wasps. It contains only a single living family, Mymarommatidae, and three other extinct families known from Cretaceous aged amber. Less than half of all described species are living taxa, but they are known from all parts of the world. Undoubtedly, many more await discovery, as they are easily overlooked and difficult to study due to their extremely small size.

The Eucharitidae are a family of parasitic wasps. Eucharitid wasps are members of the superfamily Chalcidoidea and consist of three subfamilies: Oraseminae, Eucharitinae, and Gollumiellinae. Most of the 55 genera and 417 species of Eucharitidae are members of the subfamilies Oraseminae and Eucharitinae, and are found in tropical regions of the world.
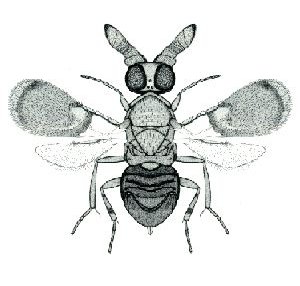
Encyrtidae is a large family of parasitic wasps, with some 3710 described species in about 455 genera. The larvae of the majority are primary parasitoids on Hemiptera, though other hosts are attacked, and details of the life history can be variable. They are found throughout the world in virtually all habitats, and are extremely important as biological control agents. They may also present as an ecological threat to the population of some species. For example, the endangered Papilio homerus butterfly is parasitized at a rate of 77%, making them the main contributor to egg mortality in this butterfly species.

The Chalcididae are a moderate-sized family within the Chalcidoidea, composed mostly of parasitoids and a few hyperparasitoids. The family is apparently polyphyletic, though the different subfamilies may each be monophyletic, and some may be elevated to family status in the near future. As presently defined, there are over 85 genera and over 1460 species worldwide. They are often black with yellow, red, or white markings, rarely brilliantly metallic, with a robust mesosoma and very strong sculpturing. The hind femora are often greatly enlarged, with a row of teeth or serrations along the lower margin.

The Ormyridae are a small family of parasitic wasps in the superfamily Chalcidoidea. They are either parasitoids or hyperparasitoids on gall-forming insects, primarily cynipid wasps and tephritid flies. The 120 or so species are cosmopolitan, except almost entirely absent from South America.

The Tetracampidae are a small family of parasitic wasps in the superfamily Chalcidoidea. They are parasitoids of phytophagous insects, primarily flies. The 44 species in 15 genera are almost entirely absent from the New World.

The Rotoitidae are a very small family of rare, relictual parasitic wasps in the superfamily Chalcidoidea, known primarily from fossils. Only two extant species are known, each in its own genus, one from New Zealand and one from Chile, and little is known about their biology. Females of the Chilean species, Chiloe micropteron, have their wings reduced to tiny bristles. Most fossil species are known from the Late Cretaceous (Santonian) Taimyr amber of Russia and Late Cretaceous (Campanian) Canadian amber, but one species, Baeomorpha liorum is known from the mid Creaceous Burmese amber.

The Stephanidae, sometimes called crown wasps, are a family of parasitoid wasps. They are the only living members of the superfamily Stephanoidea. Stephanidae has at least 345 living species in 11 genera. The family is considered cosmopolitan in distribution, with the highest species concentrations in subtropical and moderate climate zones. Stephanidae also contain four extinct genera described from both compression fossils and inclusions in amber.

Megalyroidea is a small hymenopteran superfamily of wasps that includes a single family, Megalyridae, with eight extant genera and 49 described species. Modern megalyrids are found primarily in the southern hemisphere, though fossils have only been found in the northern hemisphere. The most abundant and species-rich megalyrid fauna is in Australia. Another peak of diversity appears to be in the relict forests of Madagascar, but most of these species are still undescribed.

Myanmymar is an extinct genus of fairyfly preserved in Burmese amber from Myanmar. It has only one species, Myanmymar aresconoides. It is dated to the earliest part of the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, around 99 million years old. As of 2011, it is the oldest known fossil mymarid.
Rotoita basalis is a small parasitic wasp in the relictual family Rotoitidae. It is known only from New Zealand, and its closest known living relative is endemic to Chile.
Serphitidae is a family of microscopic parasitic wasps known from the Cretaceous period.
The Gallorommatidae is an extinct family of microscopic parasitoid wasps, belonging to the Mymarommatoidea. It is known from several species found in Cretaceous aged amber.

Baeomorpha is an extinct genus of rotoitid parasitic wasp, known from the Late Cretaceous of Laurasia. The type species, B. dubitata was named by Charles Thomas Brues for a specimen found in 72 million year old Canadian Amber. The vast majority of species are known from the Russian Taimyr amber, of upper Santonian age but two species are known from the upper Campanian Canadian amber, while one species is known from the lower Cenomanian Burmese amber.

















