Neognathae is an infraclass of birds, called neognaths, within the class Aves of the clade Archosauria. Neognathae includes the majority of living birds; the exceptions being the tinamous and the flightless ratites, which belong instead to the sister taxon Palaeognathae. There are nearly 10,000 living species of neognaths.

The evolution of birds began in the Jurassic Period, with the earliest birds derived from a clade of theropod dinosaurs named Paraves. Birds are categorized as a biological class, Aves. For more than a century, the small theropod dinosaur Archaeopteryx lithographica from the Late Jurassic period was considered to have been the earliest bird. Modern phylogenies place birds in the dinosaur clade Theropoda. According to the current consensus, Aves and a sister group, the order Crocodilia, together are the sole living members of an unranked reptile clade, the Archosauria. Four distinct lineages of bird survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago, giving rise to ostriches and relatives (Palaeognathae), waterfowl (Anseriformes), ground-living fowl (Galliformes), and "modern birds" (Neoaves).

Avemetatarsalia is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all archosaurs more closely related to birds than to crocodilians. The two most successful groups of avemetatarsalians were the dinosaurs and pterosaurs. Dinosaurs were the largest terrestrial animals for much of the Mesozoic Era, and one group of small feathered dinosaurs has survived up to the present day. Pterosaurs were the first flying vertebrates and persisted through the Mesozoic before dying out at the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event. Both dinosaurs and pterosaurs appeared in the Triassic Period, shortly after avemetatarsalians as a whole. The name Avemetatarsalia was first established by British palaeontologist Michael Benton in 1999. An alternate name is Pan-Aves, or "all birds", in reference to its definition containing all animals, living or extinct, which are more closely related to birds than to crocodilians.

Ichthyornithes is an extinct group of toothed avialan dinosaurs very closely related to the common ancestor of all modern birds. They are known from fossil remains found throughout the late Cretaceous period of North America, though only two genera, Ichthyornis and Janavis, are represented by complete enough fossils to have been named. Ichthyornitheans became extinct at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, along with enantiornitheans, all other non-avian dinosaurs, and many other animal and plant groups.

Pterosauromorpha is one of the two basic divisions of Ornithodira that includes pterosaurs and all taxa that are closer to them than to dinosaurs and their close relatives. In addition to pterosaurs, Pterosauromorpha also includes the basal clade Lagerpetidae and some other Late Triassic ornithodirans.

Avialae is a clade containing the only living dinosaurs, the birds, and their closest relatives. It is usually defined as all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds (Aves) than to deinonychosaurs, though alternative definitions are occasionally used.

John Alan Feduccia is a paleornithologist specializing in the origins and phylogeny of birds. He is S. K. Heninger Distinguished Professor Emeritus at the University of North Carolina. Feduccia's authored works include three major books, The Age of Birds, The Origin and Evolution of Birds, and Riddle of the Feathered Dragons.

Ornithurae is a natural group which includes the common ancestor of Ichthyornis, Hesperornis, and all modern birds as well as all other descendants of that common ancestor.

Pygostylia is a group of avialans which includes the Confuciusornithidae and all of the more advanced species, the Ornithothoraces.

Avifilopluma is a clade containing all animals with feathers. Unlike most clades, which are defined based on relative relationships, Avifilopluma is defined based on an apomorphy, that is, a unique physical characteristic shared by one group and not found outside that group. Its content is unclear, and has been speculated to range from Coelurosauria to all of Ornithodira.

Neoaves is a clade that consists of all modern birds with the exception of Palaeognathae and Galloanserae. Almost 95% of the roughly 10,000 known species of extant birds belong to the Neoaves.

The Maastricht Formation, named after the city of Maastricht in the Netherlands, is a geological formation in the Netherlands and Belgium whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous, within 500,000 years of the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, now dated at 66 million years ago. The formation is part of the Chalk Group and is between 30 and 90 metres thick. It crops out in southern parts of Dutch and Belgian Limburg and adjacent areas in Germany. It can be found in the subsurface of northern Belgium and southeastern Netherlands, especially in the Campine Basin and Roer Valley Graben. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.

Pangalliformes is the scientific name of a provisional clade of birds within the group Galloanserae. It is defined as all birds more closely related to chickens than to ducks, and includes all modern chickens, turkeys, pheasants, and megapodes, as well as extinct species that do not fall within the crown group Galliformes.

Vegaviidae is an extinct family of ornithurine dinosaurs, often regarded as primitive anseriforms, which existed during the Late Cretaceous and possibly the Paleocene. Fossils attributed to the family have been found in Canada, Chile, New Zealand, and Antarctica.

The biogeography of Paravian dinosaurs is the study of the global distribution of Paraves through geological history. Paraves is a clade that includes all of the Theropoda that are more closely related to birds than to oviraptorosaurs. These include Dromaeosauridae and Troodontidae and Avialae. The distribution of paraves is closely related to the evolution of the clade. Understanding the changes in their distributions may shed light on problems like how and why paraves evolve, eventually gaining the ability to fly.
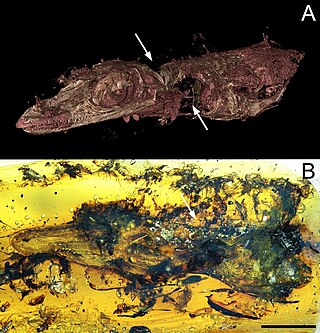
Oculudentavis is an extinct genus of lizard of uncertain taxonomic placement, originally identified as an avialan dinosaur. It contains two known species, O. khaungraae and O. naga. Each species is known from one partial fossil specimen in Burmese amber, which differ in several proportions. Their skulls measure 1.4–1.7 centimetres (0.55–0.67 in) in length, indicating that Oculudentavis would have been comparable in size with the modern bee hummingbird if it were an avialan. Both specimens were retrieved from 99-million-year-old deposits of the Hukawng Basin in Kachin State, northern Myanmar. The type specimen of O. khaungraae is embroiled in controversy regarding its identity and the ethical issues surrounding the acquisition and study of Burmese amber. The original description advocating for an avialan identity was published in Nature, but has since then been retracted from the journal.

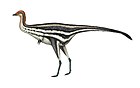
Asteriornis is an extinct genus of bird from the Late Cretaceous of Belgium which is known from a single species, Asteriornis maastrichtensis. It was closely related to birds of the extant superorder Galloanserae such as chickens and ducks. Members of the genus were small, long-legged birds that lived near the coastline and co-existed with more "primitive" types of birds such as Ichthyornis. Asteriornis is one of the oldest-known birds irrefutably belonging to the group Neornithes, which encompasses all modern birds. It possesses characteristics of both galliformes and anseriformes, indicating its position as a close relative of the last common ancestor for both groups.
Rc-o319 is a bat-derived strain of severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus collected in little Japanese horseshoe bats from sites in Iwate, Japan. Its has 81% similarity to SARS-CoV-2 and is the earliest strain branch of the SARS-CoV-2 related coronavirus.

Janavis is an extinct toothed bird, belonging to the Ichthyornithes, from the Late Cretaceous of Belgium. The genus has one named species, Janavis finalidens that was discovered in the 1990s, reported in 2002, and described in 2022. Recovered almost simultaneously from the same area and age as Asteriornis maastrichtensis, then the oldest known modern bird, it provides information on the evolution and divergence of basal and modern birds, especially on the evolutionary modifications of bird skulls.