
The Cedar Fire was a massive, highly-destructive wildfire, which burned 273,246 acres (1,106 km2) of land in San Diego County, California, during October and November 2003. The fire's rapid growth was driven by the Santa Ana winds, causing the fire to spread at a rate of 3,600 acres (15 km2) per hour. By the time the fire was fully contained on November 4, it had destroyed 2,820 buildings and killed 15 people, including one firefighter. Hotspots continued to burn within the Cedar Fire's perimeter until December 5, 2003, when the fire was fully brought under control.

The California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection is the fire department of the California Natural Resources Agency in the U.S. state of California. It is responsible for fire protection in various areas under state responsibility totaling 31 million acres, as well as the administration of the state's private and public forests. In addition, the department provides varied emergency services in 36 of the state's 58 counties via contracts with local governments. The department's current director is Joe Tyler, who was appointed March 4, 2022, by Governor of California Gavin Newsom.

The 2009 California wildfires were a series of 9,159 wildfires that were active in the US state of California, during the year 2009. The fires burned more than 422,147 acres of land from early February through late November, due to Red Flag conditions, destroying hundreds of structures, injuring 134 people, and killing four. The wildfires also caused at least US$134.48 million in damage. Although the fires burned many different regions of California in August, the month was especially notable for several very large fires which burned in Southern California, despite being outside of the normal fire season for that region.
The Lake Fire was a wildfire that burned in the San Bernardino National Forest. The fire started on June 17, 2015, and burned over 31,359 acres before it was fully contained on July 21, 2015.

The Barry Point Fire was a wildfire that burned over 92,977 acres (376.26 km2) of Oregon and California forest land during the summer of 2012. The fire began on 5 August 2012, the result of a lightning strike. The fire consumed public forest and rangeland as well as private forest and grazing land located in Lake County, Oregon and Modoc County, California. The public lands affected by the fire are administered by the United States Forest Service and the Oregon Department of Forestry. The largest part of the private land was owned by the Collins Timber Company. At the peak of the firefighting effort, there were 1,423 personnel working on the fire. It took 22 days to fully contain the fire and then an additional three weeks to mop it up.

The Blue Cut Fire was a wildfire in the Cajon Pass, northeastern San Gabriel Mountains, and Mojave Desert in San Bernardino County, California. The fire, which began on the Blue Cut hiking trail in the San Bernardino National Forest, was first reported on August 16, 2016 at 10:36 a.m., just west of Interstate 15. A red flag warning was in effect in the area of the fire, with temperatures near 100 °F (38 °C) and winds gusting up to 30 miles per hour (48 km/h).

In terms of property damage, 2017 was the most destructive wildfire season on record in California at the time, surpassed by only the 2018 season and the 2020 season, with a total of 9,560 fires burning 1,548,429 acres (6,266.27 km2) of land, according to the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection, including five of the 20 most destructive wildland-urban interface fires in the state's history. Throughout 2017, the fires destroyed or damaged more than 10,000 structures in the state, a higher tally than the previous nine years combined. State data showed that the large wildfires killed 47 people – 45 civilians and 2 firefighters – almost higher than the previous 10 years combined. The total property damage and total amount of burned land were both surpassed by the 2018 California wildfires.
The Holcomb Fire was a wildfire that burned due north of Big Bear Lake near Highway 18 in the San Bernardino National Forest in San Bernardino County, California. Within several days, the fire would consume some 1,500 plus acres as it threatened the areas of Baldwin Lake and Highway 18. However, while the fire rapidly grew in size, the head of the fire was seen to be moving away from structures, thus leaving evacuated areas under voluntary evacuation.

A series of 29 wildfires ignited across Southern California in December 2017. Six of the fires became significant wildfires, and led to widespread evacuations and property losses. The wildfires burned over 307,900 acres (1,246 km2), and caused traffic disruptions, school closures, hazardous air conditions, and power outages; over 230,000 people were forced to evacuate. The largest of the wildfires was the Thomas Fire, which grew to 281,893 acres (1,140.78 km2), and became the largest wildfire in modern California history, until it was surpassed by the Ranch Fire in the Mendocino Complex, in the following year.

The 2019 California wildfire season was a series of wildfires that burned across the U.S. state of California as part of the 2019 wildfire season. By the end of the year, according to Cal Fire and the US Forest Service, 7,860 fires were recorded, totaling an estimated of 259,823 acres of burned land. These fires caused 22 injuries, 3 fatalities, and damaged or destroyed 732 structures. The 2019 California fire season was less active than that of the two previous years, which set records for acreage, destructiveness, and deaths.

The CZU Lightning Complex fires were wildfires that burned in Northern California starting in August 2020. The fire complex consisted of fires in San Mateo and Santa Cruz counties, including fires that had previously been separately tracked as the Warnella and Waddell fires. The firefighting effort was primarily administered by the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection.

The El Dorado Fire was a wildfire that burned 22,744 acres in San Bernardino and Riverside counties of California from September to November 2020. It was ignited on September 5 by a pyrotechnic device at a gender reveal party in El Dorado Ranch Park; it quickly spread to the San Gorgonio Wilderness Area of the San Bernardino National Forest. Burning over a 71-day period, the fire destroyed 20 structures and resulted in one firefighter fatality, for which the couple hosting the party were charged with involuntary manslaughter.

The River Fire was a destructive 2021 wildfire that burned 2,619 acres (1,060 ha) near Colfax in Nevada County and Placer County, California. The fire broke out on August 4, 2021, and burned 2,619 acres (1,060 ha) before it was fully contained on August 13, 2021. The River Fire destroyed 142 structures, damaged 21 more, and resulted in four injuries to firefighters and civilians. It was the fifth most destructive fire of California's 2021 wildfire season. The exact cause of the fire is unknown, but it was determined to have been of human origin by investigators who traced the ignition to a campground by the Bear River west of Colfax.

The Fawn Fire was a destructive wildfire in Northern California's Shasta County, near Redding, in late September and early October 2021. The fire, which was caused by an alleged act of arson, ignited on September 22 in mountains to the northeast of Redding. High winds the following day drove the fire south and west into neighborhoods in the wildland-urban interface, where it destroyed 185 buildings and damaged 26 more. At least three firefighters were injured. The Fawn Fire cost more than $25 million to suppress and burned 8,578 acres before being fully contained on October 2. A woman was arrested the day of the Fawn Fire's ignition and charged with starting the fire. As of 2024, legal proceedings remained ongoing.

The 1992 Fountain Fire was a large and destructive wildfire in Shasta County, California. The fire ignited on August 20 in an act of probable but unattributed arson, and was quickly driven northeast by strong winds. It outpaced firefighters for two days, exhibiting extreme behavior such as long-range spot fires, crown fire runs, and pyrocumulonimbus clouds with dry lightning. The fire was contained after burning for nine days, though work to strengthen and repair fire lines continued for more than two months.

The 49er Fire was a destructive wildfire in 1988 in Northern California's Nevada County and Yuba County. The fire ignited on September 11 when a man accidentally set brush on fire by burning toilet paper near Highway 49. Driven by severe drought conditions and strong, dry winds, firefighting crews were hard-pressed to stop the fire's advance until winds calmed and humidity levels recovered. The fire burned 33,700 acres throughout the foothills of the Sierra Nevada, impinging on the communities of Lake Wildwood, Rough and Ready, and Smartsville before officials declared it fully contained on September 16.

The Kinneloa Fire was a destructive wildfire in Los Angeles County, Southern California in October of 1993. The fire destroyed 196 buildings in the communities of Altadena, Kinneloa Mesa, and Sierra Madre in the foothills of the San Gabriel Mountains, becoming at the time the twelfth-most destructive wildfire in California's history and one of the most destructive wildfires ever in Los Angeles County. The fire caused a multitude of minor injuries and one fatality; an elderly man died of pneumonia complicated by smoke inhalation. A father and son were killed by a debris flow in the burn area more than four months later.
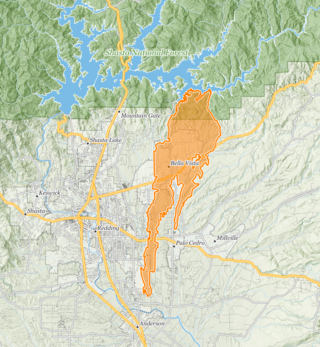
The 1999 Jones Fire was a destructive wildfire in the U.S. state of California's Shasta County. The fire ignited on October 16, and was contained on October 19, 1999. It burned 26,200 acres (10,600 ha), destroyed 954 structures, and resulted in one fatality, becoming the then-second most destructive wildfire ever recorded in California, behind only the Oakland firestorm of 1991. As of 2023 it remains one of the 20 most destructive wildfires in the history of the state. The cause of the fire was never determined.

The 2001 California wildfire season was a series of wildfires that burned throughout the U.S. state of California during 2001. According to California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection statistics, 9,317 fires burned a total of 377,340 acres.

The 1993 Laguna Fire or Laguna Canyon Fire was a destructive wildfire in Orange County, California. After igniting on October 27, the fire burned more than 16,000 acres and destroyed hundreds of homes in Laguna Beach and Emerald Bay before it was fully contained on October 31. The fire forced almost 25,000 people to evacuate and caused approximately $528 million in damage, becoming one of the most costly fires in United States history. It was part of a larger outbreak of wildfires that week in Southern California, largely driven by Santa Ana winds.





















