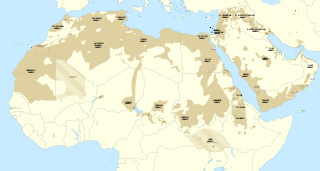
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew, Maltese and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large immigrant and expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis.
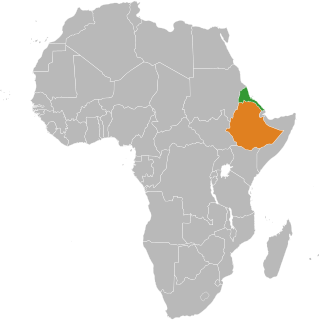
Tigrinya, sometimes spelled Tigrigna, is an Ethio-Semitic language commonly spoken in Eritrea and in northern Ethiopia's Tigray Region by the Tigrinya and Tigrayan peoples respectively. It is also spoken by the global diaspora of these regions.
Amharic is an Ethiopian Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It is spoken as a first language by the Amharas, and also serves as a lingua franca for all other populations residing in major cities and towns in Ethiopia.

Arabic grammar is the grammar of the Arabic language. Arabic is a Semitic language and its grammar has many similarities with the grammar of other Semitic languages. Classical Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic have largely the same grammar; colloquial spoken varieties of Arabic can vary in different ways.
Phoenician is an extinct Canaanite Semitic language originally spoken in the region surrounding the cities of Tyre and Sidon. Extensive Tyro-Sidonian trade and commercial dominance led to Phoenician becoming a lingua franca of the maritime Mediterranean during the Iron Age. The Phoenician alphabet spread to Greece during this period, where it became the source of all modern European scripts.

Catalan grammar, the morphology and syntax of the Catalan language, is similar to the grammar of most other Romance languages. Catalan is a relatively synthetic, fusional language.
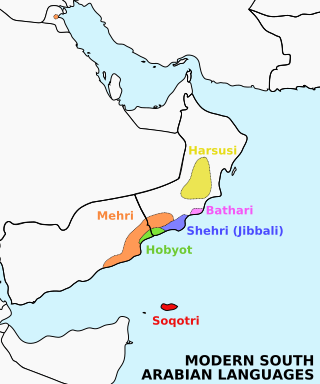
Soqotri is a South Semitic language spoken by the Soqotri people on the island of Socotra and the two nearby islands of Abd al Kuri and Samhah, in the Socotra archipelago, in the Guardafui Channel. Soqotri is one of six languages that form a group called Modern South Arabian languages (MSAL). These additional languages include Mehri, Shehri, Bathari, Harsusi and Hobyot. All are spoken in different regions of Southern Arabia.

Biblical Hebrew, also called Classical Hebrew, is an archaic form of the Hebrew language, a language in the Canaanitic branch of the Semitic languages spoken by the Israelites in the area known as the Land of Israel, roughly west of the Jordan River and east of the Mediterranean Sea. The term ʿiḇrîṯ "Hebrew" was not used for the language in the Hebrew Bible, which was referred to as שְֹפַת כְּנַעַןśəp̄aṯ kənaʿan "language of Canaan" or יְהוּדִיתYəhûḏîṯ, "Judean", but it was used in Koine Greek and Mishnaic Hebrew texts.

Neo-Mandaic, also known as Modern Mandaic, sometimes called the "ratna", is the modern reflex of the Mandaic language, the liturgical language of the Mandaean religious community of Iraq and Iran. Although severely endangered, it survives today as the first language of a small number of Mandaeans in Iran and in the Mandaean diaspora. All Neo-Mandaic speakers are multilingual in the languages of their neighbors, Arabic and Persian, and the influence of these languages upon the grammar of Neo-Mandaic is considerable, particularly in the lexicon and the morphology of the noun. Nevertheless, Neo-Mandaic is more conservative even in these regards than most other Neo-Aramaic languages.

The Ghomara language is a Northern Berber language spoken in Morocco. It is the mother tongue of the Ghomara Berbers, who total around 10,000 people. Ghomara Berber is spoken on the western edge of the Rif, among the Beni Bu Zra and Beni Mansur tribes of the Ghomara confederacy. Despite being listed as endangered, it is still being passed on to children in these areas.
Proto-Semitic is the reconstructed proto-language common ancestor to the Semitic language family. There is no consensus regarding the location of the Proto-Semitic Urheimat: scholars hypothesize that it may have originated in the Levant, the Sahara, the Horn of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, or northern Africa.

Algerian Arabic, natively known as Dziria, Darja or Derja, is a variety of Arabic spoken in Algeria. It belongs to the Maghrebi Arabic dialect continuum and is mostly intelligible with the Tunisian and Moroccan dialects. Darja (الدارجة) means "everyday/colloquial dialect".
This article describes the grammar of Tigrinya, a South Semitic language which is spoken primarily in Eritrea and Ethiopia, and is written in Ge'ez script.

Hejazi Arabic or Hijazi Arabic (HA), also known as West Arabian Arabic, is a variety of Arabic spoken in the Hejaz region in Saudi Arabia. Strictly speaking, there are two main groups of dialects spoken in the Hejaz region, one by the urban population, originally spoken mainly in the cities of Jeddah, Mecca, Medina and partially in Ta'if and another dialect by the urbanized rural and bedouin populations. However, the term most often applies to the urban variety which is discussed in this article.

The Tarahumara language is a Mexican Indigenous language of the Uto-Aztecan language family spoken by around 70,000 Tarahumara (Rarámuri/Ralámuli) people in the state of Chihuahua, according to a 2002 census conducted by the government of Mexico.

Nabataean Aramaic is the extinct Aramaic variety used in inscriptions by the Nabataeans of the East Bank of the Jordan River, the Negev, and the Sinai Peninsula. Compared with other varieties of Aramaic, it is notable for the occurrence of a number of loanwords and grammatical borrowings from Arabic or other North Arabian languages.
Ugaritic is an extinct Northwest Semitic language. This article describes the grammar of the Ugaritic language. For more information regarding the Ugaritic language in general, see Ugaritic language.

Varieties of Arabic are the linguistic systems that Arabic speakers speak natively. Arabic is a Semitic language within the Afroasiatic family that originated in the Arabian Peninsula. There are considerable variations from region to region, with degrees of mutual intelligibility that are often related to geographical distance and some that are mutually unintelligible. Many aspects of the variability attested to in these modern variants can be found in the ancient Arabic dialects in the peninsula. Likewise, many of the features that characterize the various modern variants can be attributed to the original settler dialects as well as local native languages and dialects. Some organizations, such as SIL International, consider these approximately 30 different varieties to be separate languages, while others, such as the Library of Congress, consider them all to be dialects of Arabic.
This page describes the grammar of Maithili language, which has a complex verbal system, nominal declension with a few inflections, and extensive use of honoroficity. It is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Maithili people and is spoken in the Indian state of Bihar with some speakers in Jharkhand and nearby states.The language has a large number of speakers in Nepal too, which is second in number of speakers after Bihar.

Rijāl Almaʿ is a speech variety of questionable genetic affiliation spoken in the area in and around the village after which it is named, Rijāl Almaʿ. Amongst the features that make this speech variety so distinctive in the area where it is spoken is the seemingly preserved demonstrative pronominal paradigm from the Sayhadic languages and the presence of the a nasal definite article similar to the proposed modern Sayhadic languages Faifi and Razihi. The speech variety is seemingly gradually being phased out due to increased language convergence with neighboring varieties of Arabic, further complicating the situation regarding where this speech variety belongs within Central Semitic.














