
Yoho National Park is a national park of Canada. It is located within the Rocky Mountains along the western slope of the Continental Divide of the Americas in southeastern British Columbia, bordered by Kootenay National Park to the south and Banff National Park to the east in Alberta. The word Yoho is a Cree expression of amazement or awe, and it is an apt description for the park's spectacular landscape of massive ice fields and mountain peaks, which rank among the highest in the Canadian Rockies.

Jasper National Park, in Alberta, Canada, is the largest national park within Alberta's Rocky Mountains, spanning 11,000 km2 (4,200 sq mi). It was established as Jasper Forest Park in 1907, renamed as a national park in 1930, and declared a UNESCO world heritage site in 1984. Its location is north of Banff National Park and west of Edmonton. The park contains the glaciers of the Columbia Icefield, springs, lakes, waterfalls and mountains.

Banff National Park is Canada's oldest national park, established in 1885 as Rocky Mountains Park. Located in Alberta's Rocky Mountains, 110–180 kilometres (68–112 mi) west of Calgary, Banff encompasses 6,641 square kilometres (2,564 sq mi) of mountainous terrain, with many glaciers and ice fields, dense coniferous forest, and alpine landscapes. Provincial forests and Yoho National Park are neighbours to the west, while Kootenay National Park is located to the south and Kananaskis Country to the southeast. The main commercial centre of the park is the town of Banff, in the Bow River valley.

Willmore Wilderness Park, in Alberta, Canada, is a 4,600-square-kilometre (1,800 sq mi) wilderness area adjacent to Jasper National Park. It is lesser known and less visited than Jasper National Park. There are no public roads, bridges or buildings. There are, however, several ranger cabins in the park that are available as a courtesy to visitors.

Waterton Lakes National Park is in the southwest corner of Alberta, Canada. The national park borders Glacier National Park in Montana, United States. Waterton was the fourth Canadian national park, formed in 1895 as Kootenay Lakes Forest Reserve. It is named after Waterton Lake, in turn after the Victorian naturalist and conservationist Charles Waterton. Its range is between the Rocky Mountains and the Prairies. This park contains 505 km2 (195 sq mi) of rugged mountains and wilderness. It has a diverse ecosystem.

Banff Sunshine Village is a ski resort in western Canada, located on the Continental Divide of the Canadian Rockies within Banff National Park in Alberta and Mount Assiniboine Provincial Park in British Columbia. It is one of three major ski resorts located in the Banff National Park. Because of its location straddling the Continental Divide, Sunshine receives more snow than the neighbouring ski resorts. The Sunshine base area is located 15 km (9 mi) southwest of the town of Banff. By car, it is about a ninety-minute drive from the city of Calgary; the Sunshine exit on the Trans Canada Highway is 8 km (5 mi) west of the town of Banff.
Height of the Rockies Provincial Park is a provincial park in the Canadian Rockies of south eastern British Columbia, Canada. It is located west of the Continental Divide, adjacent to Elk Lakes Provincial Park.

Mount Assiniboine Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located around Mount Assiniboine.

Alberta has been a tourist destination since the early days of the 20th Century, with attractions including national parks, National Historic Sites of Canada, urban arts and cultural facilities, outdoor locales for skiing, hiking and camping, shopping locales such as West Edmonton Mall, outdoor festivals, professional athletic events, international sporting competitions such as the Commonwealth Games and Olympic Winter Games, as well as more eclectic attractions.

The Ghost River Wilderness Area is a provincially designated wilderness area in the Canadian Rockies of Alberta protecting the headwaters of the Ghost River. It was established in 1967 and it, as one of the three wilderness areas of Alberta, has the strictest form of government protection available in Canada. All development is forbidden, and only travel by foot is permitted. Hunting and fishing are not allowed. The other two wilderness areas are White Goat Wilderness Area and Siffleur Wilderness Area and together the three areas total 1,009.8882 square kilometres.
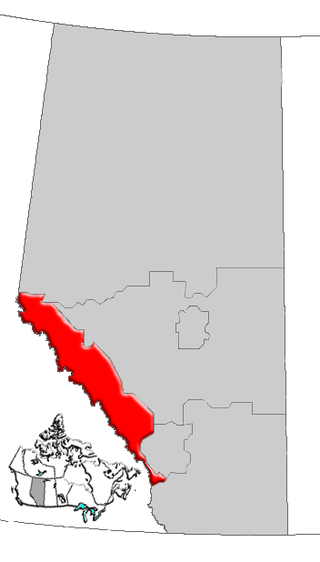
Alberta's Rockies comprise the Canadian Rocky Mountains in Alberta, Canada. On the southwestern part of the province along the British Columbia border, the region covers all but the south of Census Division 15.
The Skyline Trail is a hiking trail in Jasper National Park, Alberta, Canada. It is known for its views, with much of the hike being located above the tree line. It is also known for challenging weather conditions above the tree line, which can be a problem for hikers, who can lose sight of trails.

The Ecology of the North Cascades is heavily influenced by the high elevation and rain shadow effects of the mountain range. The North Cascades is a section of the Cascade Range from the South Fork of the Snoqualmie River in Washington, United States, to the confluence of the Thompson and Fraser Rivers in British Columbia, Canada, where the range is officially called the Cascade Mountains but is usually referred to as the Canadian Cascades. The North Cascades Ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion in the Commission for Environmental Cooperation's classification system.

The Alberta Mountain forests are a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion of Western Canada, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) categorization system.

The North Central Rockies forests is a temperate coniferous forest ecoregion of Canada and the United States. This region overlaps in large part with the North American inland temperate rainforest and gets more rain on average than the South Central Rockies forests and is notable for containing the only inland populations of many species from the Pacific coast.

The White Goat Wilderness Area is a provincially designated wilderness area in the Canadian Rockies of Alberta. It was established in 1961 and it, as one of the three wilderness areas of Alberta, has the strictest form of government protection available in Canada. All development is forbidden and only travel by foot is permitted. Hunting and fishing are not allowed. The other two wilderness areas are Ghost River Wilderness Area and Siffleur Wilderness Area and together the three areas total 249,548.80 acres (100,988.82 ha).
The Rocky Mountains Forest Reserve is a tract of land owned by the government of the Canadian province of Alberta along the eastern slopes and foothills of the Albertan section of the Canadian Rockies. It is a long strip of land just east of the more famous Canadian Rocky Mountain parks, which is managed for forest and water conservation, public recreation, and industrial goals, rather than aesthetic and preservation goals, as in the Rocky Mountain parks.

Siffleur Mountain is a 3,129-metre (10,266 ft) mountain summit located in the North Saskatchewan River valley of Alberta, Canada. Siffleur Mountain is situated in the Siffleur Wilderness Area of the Canadian Rockies. Its nearest higher peak is Mount Loudon, 3 km (1.9 mi) to the southwest. The mountain can be seen from Highway 11, the David Thompson Highway. Precipitation runoff from Siffleur Mountain flows north via Loudon Creek and Siffleur River.

Marmot Mountain is a 2,608-metre (8,556-foot) mountain summit located in Alberta, Canada.
Rock Lake–Solomon Creek Wildland Provincial Park is a wildland provincial park in west-central Alberta, Canada. The park was established on 20 December 2000 and has an area of 34,682.9 hectares. The park is included in the Upper Athabasca Region Land Use Framework. The park is named for the local lake and creek within the boundaries of the park.

















