Related Research Articles

An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment, interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.

In earth science, erosion is the action of surface processes that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as physical or mechanical erosion; this contrasts with chemical erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres.
Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a stable soil. Retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession reverts the land to its natural physical state. Degradation is an evolution, different from natural evolution, related to the local climate and vegetation. It is due to the replacement of primary plant communities by the secondary communities. This replacement modifies the humus composition and amount, and affects the formation of the soil. It is directly related to human activity. Soil degradation may also be viewed as any change or ecological disturbance to the soil perceived to be deleterious or undesirable.

The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmosphere, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is atmospheric nitrogen, making it the largest source of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems.

Environmental science is an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates physical, biological and information sciences to the study of the environment, and the solution of environmental problems. Environmental science emerged from the fields of natural history and medicine during the Enlightenment. Today it provides an integrated, quantitative, and interdisciplinary approach to the study of environmental systems.

Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soils, and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs in situ, and should not be confused with erosion, which involves the transport of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity.
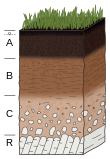
Pedogenesis is the process of soil formation as regulated by the effects of place, environment, and history. Biogeochemical processes act to both create and destroy order (anisotropy) within soils. These alterations lead to the development of layers, termed soil horizons, distinguished by differences in color, structure, texture, and chemistry. These features occur in patterns of soil type distribution, forming in response to differences in soil forming factors.

Grasslands are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica and are found in most ecoregions of the Earth. Furthermore, grasslands are one of the largest biomes on earth and dominate the landscape worldwide. They cover 31-43% of the Earth's land area. There are different types of grasslands: natural grasslands, semi-natural grasslands, and agricultural grasslands.
Soil structure describes the arrangement or the way of soil in of the solid parts of the soil and of the pore space located between them. It is determined by how individual soil granules clump, bind together, and aggregate, resulting in the arrangement of soil pores between them. Soil has a major influence on water and air movement, biological activity, root growth and seedling emergence. There are several different types of soil structure. It is inherently a dynamic and complex system that is affected by different factors

Ecological succession is the process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time. The time scale can be decades, or even millions of years after a mass extinction.

In agriculture, cover crops are plants that are planted to cover the soil rather than for the purpose of being harvested. Cover crops manage soil erosion, soil fertility, soil quality, water, weeds, pests, diseases, biodiversity and wildlife in an agroecosystem—an ecological system managed and shaped by humans. Cover crops may be an off-season crop planted after harvesting the cash crop. They may grow over winter.

In the geosciences, paleosol can have two meanings. The first meaning, common in geology and paleontology, refers to a former soil preserved by burial underneath either sediments or volcanic deposits, which in the case of older deposits have lithified into rock. In Quaternary geology, sedimentology, paleoclimatology, and geology in general, it is the typical and accepted practice to use the term "paleosol" to designate such "fossil soils" found buried within sedimentary and volcanic deposits exposed in all continents as illustrated by Retallack (2001), Kraus (1999), and other published papers and books.

Biological soil crusts are communities of living organisms on the soil surface in arid and semi-arid ecosystems. They are found throughout the world with varying species composition and cover depending on topography, soil characteristics, climate, plant community, microhabitats, and disturbance regimes. Biological soil crusts perform important ecological roles including carbon fixation, nitrogen fixation and soil stabilization; they alter soil albedo and water relations and affect germination and nutrient levels in vascular plants. They can be damaged by fire, recreational activity, grazing and other disturbances and can require long time periods to recover composition and function. Biological soil crusts are also known as biocrusts or as cryptogamic, microbiotic, microphytic, or cryptobiotic soils.

Forest ecology is the scientific study of the interrelated patterns, processes, flora, fauna and ecosystems in forests. The management of forests is known as forestry, silviculture, and forest management. A forest ecosystem is a natural woodland unit consisting of all plants, animals and micro-organisms in that area functioning together with all of the non-living physical (abiotic) factors of the environment. The forest ecosystem is very important.

In ecology, a disturbance is a temporary change in environmental conditions that causes a pronounced change in an ecosystem. Disturbances often act quickly and with great effect, to alter the physical structure or arrangement of biotic and abiotic elements. A disturbance can also occur over a long period of time and can impact the biodiversity within an ecosystem.

Tiger bush, or brousse tigrée in the French language, is a patterned vegetation community and ground consisting of alternating bands of trees, shrubs, or grass separated by bare ground or low herb cover, that run roughly parallel to contour lines of equal elevation. The patterns occur on low slopes in arid and semi-arid regions, such as in Australia, Sahelian West Africa, and North America.
Soil biodiversity refers to the relationship of soil to biodiversity and to aspects of the soil that can be managed in relation to biodiversity. Soil biodiversity relates to some catchment management considerations.
This is a glossary of environmental science.

Riparian-zone restoration is the ecological restoration of riparian-zonehabitats of streams, rivers, springs, lakes, floodplains, and other hydrologic ecologies. A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the fifteen terrestrial biomes of the earth; the habitats of plant and animal communities along the margins and river banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by Aquatic plants and animals that favor them. Riparian zones are significant in ecology, environmental management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on fauna and aquatic ecosystems, including grassland, woodland, wetland or sub-surface features such as water tables. In some regions the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, or riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone.
The fungal loop hypothesis suggests that soil fungi in arid ecosystems connect the metabolic activity of plants and biological soil crusts which respond to different soil moisture levels. Compiling diverse evidence such as limited accumulation of soil organic matter, high phenol oxidative and proteolytic enzyme potentials due to microbial activity, and symbioses between plants and fungi, the fungal loop hypothesis suggests that carbon and nutrients are cycled in biotic pools rather than leached or effluxed to the atmosphere during and between pulses of precipitation.
References
- ↑ Belnap, Jayne, et al. 2001. Biological Soil Crusts: Ecology and Management. U. S. Department of Interior, Bureau of Land Management and U. S. Geological Survey. Technical Reference 1730-2. 118p.