
In biochemistry, phosphorylases are enzymes that catalyze the addition of a phosphate group from an inorganic phosphate (phosphate+hydrogen) to an acceptor.
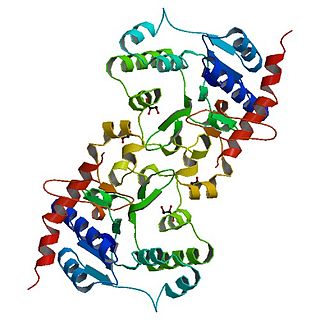
Glycogenin is an enzyme involved in converting glucose to glycogen. It acts as a primer, by polymerizing the first few glucose molecules, after which other enzymes take over. It is a homodimer of 37-kDa subunits and is classified as a glycosyltransferase.
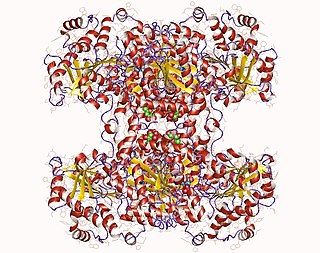
Glycogen synthase is a key enzyme in glycogenesis, the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase that catalyses the reaction of UDP-glucose and n to yield UDP and n+1.

1,4-alpha-glucan-branching enzyme, also known as brancher enzyme or glycogen-branching enzyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GBE1 gene.

β-Amylase is an enzyme with the systematic name 4-α-D-glucan maltohydrolase. It catalyses the following reaction:
Starch phosphorylase is a form of phosphorylase similar to glycogen phosphorylase, except that it acts upon starch instead of glycogen.
1,3-Beta-glucan synthase is a glucosyltransferase enzyme involved in the generation of beta-glucan in fungi. It serves as a pharmacological target for antifungal drugs such as caspofungin, anidulafungin, and micafungin, deemed 1,3-Beta-glucan synthase inhibitors. Under the CAZy classification system, fungi and plant members fall in the glycosyltransferase 48 family (GT48). Some members of the glycosyltransferase 2 family, such as the curdlan synthase CrdS, also has a similar activity.
In enzymology, a 1,3-beta-D-glucan phosphorylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alpha-1,3-glucan synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alpha-1,4-glucan-protein synthase (ADP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an amylosucrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cellulose synthase (GDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NDP-glucose—starch glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a starch synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sucrose-1,6-alpha-glucan 3(6)-alpha-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Sucrose-phosphate synthase (SPS) is a plant enzyme involved in sucrose biosynthesis. Specifically, this enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a hexosyl group from uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose) to D-fructose 6-phosphate to form UDP and D-sucrose-6-phosphate. This reversible step acts as the key regulatory control point in sucrose biosynthesis, and is an excellent example of various key enzyme regulation strategies such as allosteric control and reversible phosphorylation.
In enzymology, an alpha-glucan, water dikinase (EC 2.7.9.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phosphoglucan, water dikinase (EC 2.7.9.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

α-Glucans (alpha-glucans) are polysaccharides of D-glucose monomers linked with glycosidic bonds of the alpha form. α-Glucans use cofactors in a cofactor site in order to activate a glucan phosphorylase enzyme. This enzyme causes a reaction that transfers a glucosyl portion between orthophosphate and α-I,4-glucan. The position of the cofactors to the active sites on the enzyme are critical to the overall reaction rate thus, any alteration to the cofactor site leads to the disruption of the glucan binding site.
(1→4)-α-D-Glucan 1-α-D-glucosylmutase is an enzyme with systematic name (1->4)-alpha-D-glucan 1-alpha-D-glucosylmutase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction








