Chymotrypsin (EC 3.4.21.1, chymotrypsins A and B, alpha-chymar ophth, avazyme, chymar, chymotest, enzeon, quimar, quimotrase, alpha-chymar, alpha-chymotrypsin A, alpha-chymotrypsin) is a digestive enzyme component of pancreatic juice acting in the duodenum, where it performs proteolysis, the breakdown of proteins and polypeptides. Chymotrypsin preferentially cleaves peptide amide bonds where the side chain of the amino acid N-terminal to the scissile amide bond (the P1 position) is a large hydrophobic amino acid (tyrosine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine). These amino acids contain an aromatic ring in their side chain that fits into a hydrophobic pocket (the S1 position) of the enzyme. It is activated in the presence of trypsin. The hydrophobic and shape complementarity between the peptide substrate P1 side chain and the enzyme S1 binding cavity accounts for the substrate specificity of this enzyme. Chymotrypsin also hydrolyzes other amide bonds in peptides at slower rates, particularly those containing leucine at the P1 position.

Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the digestive system of many vertebrates, where it hydrolyzes proteins. Trypsin is formed in the small intestine when its proenzyme form, the trypsinogen produced by the pancreas, is activated. Trypsin cuts peptide chains mainly at the carboxyl side of the amino acids lysine or arginine. It is used for numerous biotechnological processes. The process is commonly referred to as trypsinogen proteolysis or trypsinization, and proteins that have been digested/treated with trypsin are said to have been trypsinized. Trypsin was discovered in 1876 by Wilhelm Kühne and was named from the Ancient Greek word for rubbing since it was first isolated by rubbing the pancreas with glycerin.

A protease is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in numerous biological pathways, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism, and cell signaling.
In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors, or antiproteases, are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases. Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins.
Serine proteases are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins. Serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the (enzyme's) active site. They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Serine proteases fall into two broad categories based on their structure: chymotrypsin-like (trypsin-like) or subtilisin-like.

A metalloproteinase, or metalloprotease, is any protease enzyme whose catalytic mechanism involves a metal. An example is ADAM12 which plays a significant role in the fusion of muscle cells during embryo development, in a process known as myogenesis.

Papain, also known as papaya proteinase I, is a cysteine protease enzyme present in papaya and mountain papaya. It is the namesake member of the papain-like protease family.
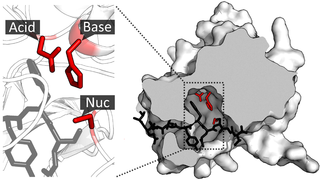
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes. An acid-base-nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to release the product and regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine or even selenocysteine. The 3D structure of the enzyme brings together the triad residues in a precise orientation, even though they may be far apart in the sequence.
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad.

Subtilisin is a protease initially obtained from Bacillus subtilis.
Protein metabolism denotes the various biochemical processes responsible for the synthesis of proteins and amino acids (anabolism), and the breakdown of proteins by catabolism.
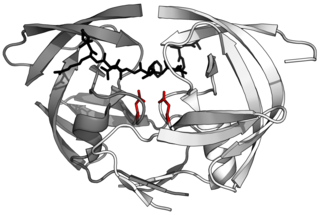
Aspartic proteases are a catalytic type of protease enzymes that use an activated water molecule bound to one or more aspartate residues for catalysis of their peptide substrates. In general, they have two highly conserved aspartates in the active site and are optimally active at acidic pH. Nearly all known aspartyl proteases are inhibited by pepstatin.
Serine hydrolases are one of the largest known enzyme classes comprising approximately ~200 enzymes or 1% of the genes in the human proteome. A defining characteristic of these enzymes is the presence of a particular serine at the active site, which is used for the hydrolysis of substrates. The hydrolysis of the ester or peptide bond proceeds in two steps. First, the acyl part of the substrate is transferred to the serine, making a new ester or amide bond and releasing the other part of the substrate is released. Later, in a slower step, the bond between the serine and the acyl group is hydrolyzed by water or hydroxide ion, regenerating free enzyme. Unlike other, non-catalytic, serines, the reactive serine of these hydrolases is typically activated by a proton relay involving a catalytic triad consisting of the serine, an acidic residue and a basic residue, although variations on this mechanism exist.
Kexin is a prohormone-processing protease, specifically a yeast serine peptidase, found in the budding yeast. It catalyzes the cleavage of -Lys-Arg- and -Arg-Arg- bonds to process yeast alpha-factor pheromone and killer toxin precursors. The human homolog is PCSK4. It is a family of subtilisin-like peptidases. Even though there are a few prokaryote kexin-like peptidases, all kexins are eukaryotes. The enzyme is encoded by the yeast gene KEX2, and usually referred to in the scientific community as Kex2p. It shares structural similarities with the bacterial protease subtilisin. The first mammalian homologue of this protein to be identified was furin. In the mammal, kexin-like peptidases function in creating and regulating many differing proproteins.

In molecular biology, Proteinase K is a broad-spectrum serine protease. The enzyme was discovered in 1974 in extracts of the fungus Parengyodontium album. Proteinase K is able to digest hair (keratin), hence, the name "Proteinase K". The predominant site of cleavage is the peptide bond adjacent to the carboxyl group of aliphatic and aromatic amino acids with blocked alpha amino groups. It is commonly used for its broad specificity. This enzyme belongs to Peptidase family S8 (subtilisin). The molecular weight of Proteinase K is 28,900 daltons.

Tripeptidyl-peptidase 1, also known as Lysosomal pepstatin-insensitive protease, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TPP1 gene. TPP1 should not be confused with the TPP1 shelterin protein which protects telomeres and is encoded by the ACD gene. Mutations in the TPP1 gene leads to late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis.
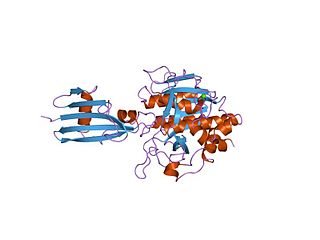
In molecular biology the protein SSI is a Subtilisin inhibitor-like which stands for Streptomyces subtilisin inhibitor. This is a protease inhibitor. These are often synthesised as part of a larger precursor protein, either as a prepropeptide. The function of this protein domain is to prevent access of the substrate to the active site. It is found only in bacteria.

The PA clan is the largest group of proteases with common ancestry as identified by structural homology. Members have a chymotrypsin-like fold and similar proteolysis mechanisms but can have identity of <10%. The clan contains both cysteine and serine proteases. PA clan proteases can be found in plants, animals, fungi, eubacteria, archaea and viruses.

Glutamic proteases are a group of proteolytic enzymes containing a glutamic acid residue within the active site. This type of protease was first described in 2004 and became the sixth catalytic type of protease. Members of this group of protease had been previously assumed to be an aspartate protease, but structural determination showed it to belong to a novel protease family. The first structure of this group of protease was scytalidoglutamic peptidase, the active site of which contains a catalytic dyad, glutamic acid (E) and glutamine (Q), which give rise to the name eqolisin. This group of proteases are found primarily in pathogenic fungi affecting plant and human.

The sedolisin family of peptidases are a family of serine proteases structurally related to the subtilisin (S8) family. Well-known members of this family include sedolisin ("pseudomonalisin") found in Pseudomonas bacteria, xanthomonalisin ("sedolisin-B"), physarolisin as well as animal tripeptidyl peptidase I. It is also known as sedolysin or serine-carboxyl peptidase. This group of enzymes contains a variation on the catalytic triad: unlike S8 which uses Ser-His-Asp, this group runs on Ser-Glu-Asp, with an additional acidic residue Asp in the oxyanion hole.
















