
Youngstown is a village in Niagara County, New York, United States. The population was 1,935 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Buffalo–Niagara Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area.

The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest, along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, Rochester and Syracuse. New York Central was headquartered in New York City's New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.

Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves "Western New Yorkers". Almost all sources agree WNY includes the cities of Buffalo, Niagara Falls, Jamestown, and the surrounding suburbs, as well as the outlying rural areas of Niagara Frontier, and Chautauqua-Alleghany. Many would also place Rochester and the Genesee Valley in the region, although those legally belong in the Finger Lakes Region and are separate from Western New York Region.

The Niagara Frontier Transportation Authority (NFTA) is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in the Buffalo–Niagara Falls metropolitan area. The NFTA, as an authority, oversees a number of subsidiaries, including the NFTA Metro bus and rail system, the Buffalo-Niagara International Airport, the Niagara Falls International Airport and NFTA Small Boat Harbor. The NFTA Metro bus and rail system is a multi-modal agency, utilizing various vehicle modes, using the brand names: NFTA Metro Bus, NFTA Metro Rail, NFTA Metrolink and NFTA PAL. In 2023, the system had a ridership of 15,429,900, or about 54,600 per weekday as of the second quarter of 2024.
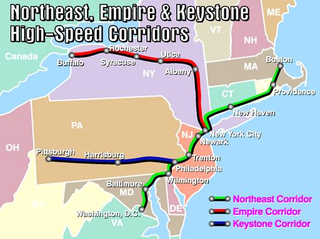
The Empire Corridor is a 461-mile (742 km) passenger rail corridor in New York State running between Penn Station in New York City and Niagara Falls, New York. Major cities on the route include Poughkeepsie, Albany, Schenectady, Amsterdam, Utica, Syracuse, Rochester, and Buffalo. Much of the corridor was once part of the New York Central Railroad's main line.

The Falls Road Railroad is a Class III short line railroad owned by Genesee Valley Transportation (GVT). The railroad operates in Niagara, Orleans, and Monroe counties in New York.

The Michigan Central Railroad was originally chartered in 1832 to establish rail service between Detroit, Michigan, and St. Joseph, Michigan. The railroad later operated in the states of Michigan, Indiana, and Illinois in the United States and the province of Ontario in Canada. After about 1867 the railroad was controlled by the New York Central Railroad, which later became part of Penn Central and then Conrail. After the 1998 Conrail breakup, Norfolk Southern Railway now owns much of the former Michigan Central trackage.

Buffalo Central Terminal is a historic former railroad station in Buffalo, New York. An active station from 1929 to 1979, the 17-story Art Deco style station was designed by architects Fellheimer & Wagner for the New York Central Railroad. The Central Terminal is located in the city of Buffalo's Broadway/Fillmore district. Closed since 1979, several attempts to redevelop the site were unsuccessful. In February 2024 a new development team was formed to plan a reuse for the terminal.
The Buffalo and Niagara Falls Railroad was a part of the New York Central Railroad system, connecting Buffalo, New York to Niagara Falls. It is still used by CSX for freight and Amtrak for passenger service.

New York State Route 31 (NY 31) is a state highway that extends for 208.74 miles (335.93 km) across western and central New York in the United States. The western terminus of the route is at an intersection with NY 104 in the city of Niagara Falls. Its eastern terminus is at a traffic circle with NY 26 in Vernon Center, a hamlet within the town of Vernon. Over its routing, NY 31 spans 10 counties and indirectly connects three major urban areas in Upstate New York: Buffalo–Niagara Falls, Rochester, and Syracuse. The route is one of the longest routes in New York State, paralleling two similarly lengthy routes, NY 104 to the north and NY 5 to the south, as well as the Erie Canal, as it proceeds east.

The Boehlert Transportation Center at Union Station is a train station served by Amtrak and the Adirondack Railroad in Utica, New York. It is owned by Oneida County, and named for retired U.S. Rep. Sherwood Boehlert.

The International Railway Company (IRC) was a transportation company formed in a 1902 merger between several Buffalo-area interurban and street railways. The city railways that merged were the West Side Street Railway, the Crosstown Street Railway and the Buffalo Traction Company. The suburban railroads that merged included the Buffalo & Niagara Electric Street Railway, and its subsidiary the Buffalo, Lockport & Olcott Beach Railway; the Buffalo, Depew & Lancaster Railway; and the Niagara Falls Park & River Railway. Later the IRC acquired the Niagara Gorge Railroad (NGRR) as a subsidiary, which was sold in 1924 to the Niagara Falls Power Company. The NGRR also leased the Lewiston & Youngstown Frontier Railroad.

The Medina Railroad Museum is a railroad museum located at 530 West Avenue in Medina, New York, which is northeast of Buffalo and northwest of Rochester.

The Niagara Falls Station and Customhouse Interpretive Center is an intermodal transit complex in Niagara Falls, New York. It serves Amtrak trains and Niagara Frontier Transportation Authority buses, houses U.S. Customs and Border Protection offices servicing the Canada–United States border, and houses the Niagara Falls Underground Railroad Heritage Center.

The Main Street Historic District in Medina, New York, United States, is the downtown commercial core of the village. It is a 12-acre (4.9 ha) area stretching south along Main Street from the Erie Canal to the railroad tracks.

Lehigh Valley Railroad Station is a historic railway station located at Rochester in Monroe County, New York. The Lehigh Valley Railroad built the station in 1905 but stopped using the station for passenger service in the 1950s. Later the station was used as a bus terminal and then as a night club. In the 1980s the building was added to the National Register of Historic Places and today it houses the Dinosaur Bar-B-Que restaurant.
The Rochester, Lockport and Buffalo Railroad was an electric interurban railway that was constructed between Rochester, New York, and Lockport, New York, connecting to the International Railway Co. at Lockport for service into Buffalo. Opened in 1909 as the Buffalo, Lockport and Rochester Railway, the route followed the Erie Canal and the New York Central Railroad's Falls Road branch for most of its length. The direct route took a little over two hours to travel from Lockport from Rochester. Most trains were local routes and took 2 hours 35 minutes. There were trains between the main stations every hour, however there were trains between Rochester and Brockport every 30 minutes and sometimes every 15 minutes. For a brief period of time, the railway was part of the Beebe Syndicate of affiliated interurban railways stretching from Syracuse to Buffalo. Entering receivership in 1917, it was reorganized as the Rochester, Lockport and Buffalo Railroad in 1919. After years of struggling with declining revenue during the Depression years, the railway's last day of service was April 30, 1931.
The Lewiston Railroad Company was an early railroad in Lewiston, NY, running to Niagara Falls, NY. The railroad eventually became a part of the New York Central Railroad system.
Medina sandstone is a geographic subset of the Medina Group stratigraphic formation in New York State and beyond. The name refers specifically to sandstone first quarried in Medina, New York, and later quarried in other locations in Orleans County and adjacent quarries in Monroe County to the east and Niagara County to the west. Medina sandstone was widely used to pave the streets of early U.S. cities because it was sufficiently hard to stand long and severe service, and in wearing, it maintained a flat, even surface where granite would wear round and acquire a smooth slippery polish. The Medina stone was also a highly desirable building stone that could be obtained in colors from light gray to pink, red and brown. It was used in the construction of hundreds of homes, churches, public buildings, monuments and other structures from the 1830s to the mid-1900s.























