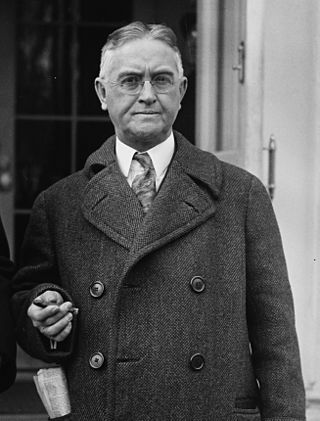The 1998 Nebraska gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1998. Term limits prevented incumbent Governor Ben Nelson, a Democrat, from seeking a third term in office. Republican nominee Mike Johanns, Mayor of Lincoln, defeated Democratic nominee, attorney Bill Hoppner. As of 2024, this was the last gubernatorial election in Nebraska in which the margin of victory was within single digits. Johanns later served Nebraska in the United States Senate with Nelson from 2009 to 2013.

From March 7 to June 6, through a series of primaries and caucuses, voters of the Republican Party elected delegates to the 1916 Republican National Convention, held June 7 to June 10, 1916, in Chicago, Illinois to choose the party's nominee for President of the United States. The delegate election process was inconclusive, with a majority of delegates not pledged to any candidate and a small plurality supporting Associate Justice of the Supreme Court Charles Evans Hughes. Hughes eventually secured the nomination at the convention on the third ballot.

United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 8, 2022, in 36 states and three territories. As most governors serve four-year terms, the last regular gubernatorial elections for all but two of the seats took place in the 2018 U.S. gubernatorial elections. The gubernatorial elections took place concurrently with several other federal, state, and local elections, as part of the 2022 midterm elections.

The 1974 Nebraska gubernatorial election was held on November 5, 1974, and featured incumbent Governor James Exon, a Democrat, defeating Republican nominee, state Senator Richard D. Marvel. Independent state Senator Ernie Chambers also captured 5% of the vote as a write-in candidate. This was the first gubernatorial election in Nebraska in which the nominees for Governor and Lieutenant Governor ran as a single ticket in the general election, though they were chosen in separate primary elections.
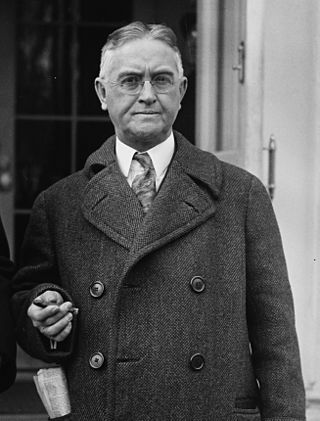
The 1924 Nebraska gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 1924, and featured former state Senator Adam McMullen, a Republican, defeating Democratic nominee, former state Representative John N. Norton, and Progressive nominee, Omaha City Commissioner Dan B. Butler.

The 1920 Nebraska gubernatorial election was held on November 2, 1920, and featured incumbent Governor Samuel R. McKelvie, a Republican, defeating Democratic nominee, former Governor John H. Morehead, and progressive-backed independent candidate, York Mayor Arthur G. Wray, to win a second and final two-year term in office.

The 1916 Nebraska gubernatorial election was held on November 7, 1916, and featured bank director and rancher Keith Neville, a Democrat, narrowly defeating Republican nominee, Douglas County District Judge Abraham L. Sutton.

The 2020 Vermont gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 2020, to elect the governor of Vermont. As Vermont does not impose term limits upon its governors, incumbent Republican governor Phil Scott was eligible to run for re-election to a third two-year term in office. On November 18, 2019, he confirmed that he was running for reelection, but did not yet publicly announce his campaign. On May 28, 2020, he officially announced his candidacy but stated that he would not campaign, maintain a campaign staff, or fundraise because of the state of emergency due to the COVID-19 pandemic in Vermont. The primary was held on August 11. Scott won re-election to a third term in a landslide, defeating Progressive and Democratic nominee, Lieutenant Governor David Zuckerman.

The 2022 Vermont gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 2022, to elect the governor of Vermont. Incumbent Republican governor Phil Scott won re-election to a fourth term in a landslide, defeating Democratic nominee Brenda Siegel.

James Douglas Pillen is an American politician, veterinarian and livestock producer serving as the 41st and current governor of Nebraska since 2023. A member of the Republican Party, Pillen served on the University of Nebraska Board of Regents from 2013 to 2023.

The 1898 Nebraska gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1898. Incumbent Populist Governor Silas A. Holcomb did not stand for re-election. Populist and Democratic fusion nominee William A. Poynter defeated Republican nominee Monroe Hayward with 50.19% of the vote.

The 1936 Nebraska lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1936, and featured incumbent Nebraska Lieutenant Governor Walter H. Jurgensen, a Democrat, defeating Republican nominee George A. Williams, who was a former Nebraska Lieutenant Governor.

The 1926 Nebraska lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 2, 1926, and featured incumbent Nebraska Lieutenant Governor George A. Williams, a Republican, defeating Democratic nominee Frank A. Dutton as well as Progressive nominee Lloyd H. Huffman.

The 1922 Nebraska lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 7, 1922, and featured Republican nominee Fred G. Johnson defeating Democratic nominee P. J. Mullin as well as Progressive nominee T. J. Ellsberry. Incumbent Nebraska Lieutenant Governor Pelham A. Barrows, a Republican, chose not to seek reelection to the office of lieutenant governor in order to run for the vacant seat of C. Frank Reavis, former US Representative from Nebraska's 1st congressional district. Barrows was unsuccessful at obtaining the Republican nomination.

The 1918 Nebraska lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 5, 1918, and featured Republican nominee Pelham A. Barrows defeating Democratic nominee William B. Banning as well as Prohibition Party nominee David B. Gilbert. Incumbent Nebraska Lieutenant Governor Edgar Howard decided not to seek reelection to the office of lieutenant governor in order to run for US Senate, but he was defeated in the Democratic primaries by John H. Morehead.

The 1914 Nebraska lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1914, and featured Democratic nominee James Pearson defeating Republican nominee Walter V. Hoagland as well as Progressive Party nominee G. L. E. Klingbiel, Socialist Party nominee Glen H. Abel, and Prohibition Party nominee Henry F. J. Hockenberger. Incumbent Nebraska Lieutenant Governor Samuel R. McKelvie did not seek reelection.

The 1910 Nebraska lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1910, and featured incumbent Nebraska Lieutenant Governor Melville R. Hopewell, a Republican, defeating Democratic nominee Ralph A. Clark as well as Socialist Party nominee George L. Slutter and Prohibition Party nominee Samuel Lichty.

The 1890 Nebraska lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 1890, and featured Republican nominee Thomas Jefferson Majors defeating Populist nominee William H. Dech and Democratic nominee Alex Bear as well as Prohibition Party nominee George W. Woodbey. Incumbent Nebraska Lieutenant Governor George D. Meiklejohn did not seek reelection as lieutenant governor in order to seek the Republican nomination for the US House of Representatives in Nebraska's 3rd congressional district, but he was unsuccessful.

The 1898 Nebraska lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1898, and featured Populist and Democratic fusion nominee Edward A. Gilbert defeating Republican nominee George A. Murphy as well as Prohibition nominee Newell S. Lowrie and Socialist Labor nominee J. J. Kerrigan.

The 1902 Nebraska lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 1902, and featured Republican nominee Edmund G. McGilton defeating Edward A. Gilbert, the Populist and Democratic fusion nominee, as well as Prohibition nominee Isaiah Lightner and Socialist nominee Andrew D. Peugh.