
The geography of Canada describes the geographic features of Canada, the world's second largest country in total area.

The provinces and territories of Canada are the sub-national governments within the geographical areas of Canada under the authority of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —were united to form a federated colony, becoming a sovereign nation in the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times, and the country has grown from the original four provinces to the current ten provinces and three territories. Together, the provinces and territories make up the world's second-largest country by area.
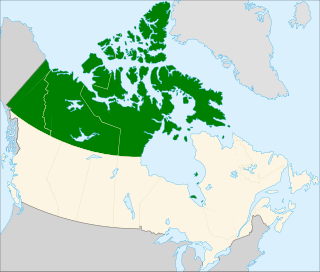
Northern Canada, colloquially the North, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. Similarly, the Far North may refer to the Canadian Arctic: the portion of Canada north of the Arctic Circle and lies east of Alaska and west of Greenland. This area covers about 39 percent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 1 percent of Canada's population.

The Magdalen Islands is a small archipelago in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence with a land area of 205.53 square kilometres (79.36 sq mi). Though closer to Prince Edward Island and Nova Scotia, the islands are part of the Canadian province of Quebec.

James Wolfe was a British Army officer, known for his training reforms and remembered chiefly for his victory in 1759 over the French at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham in Quebec as a major general. The son of a distinguished general, Edward Wolfe, he received his first commission at a young age and saw extensive service in Europe where he fought during the War of the Austrian Succession. His service in Flanders and in Scotland, where he took part in the suppression of the Jacobite Rebellion, brought him to the attention of his superiors. The advancement of his career was halted by the Peace Treaty of 1748 and he spent much of the next eight years on garrison duty in the Scottish Highlands. Already a brigade major at the age of 18, he was a lieutenant-colonel by 23.

Nunavik comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, Canada in Kativik, part of the Nord-du-Québec region. Covering a land area of 443,684.71 km2 (171,307.62 sq mi) north of the 55th parallel, it is the homeland of the Inuit of Quebec. Almost all of the 12,090 inhabitants of the region, of whom 90% are Inuit, live in fourteen northern villages on the coast of Nunavik and in the Cree reserved land (TC) of Whapmagoostui, near the northern village of Kuujjuarapik.

The term "British North America" refers to the former territories of the British Empire in North America, not including the Caribbean. The term was first used informally in 1783, but it was uncommon before the Report on the Affairs of British North America (1839), called the Durham Report. These territories today form modern-day Canada and the Pacific Northwest of the United States.

Guy Carleton, 1st Baron Dorchester, KB, known between 1776 and 1786 as Sir Guy Carleton, was an Anglo-Irish soldier and administrator. He twice served as Governor of the Province of Quebec, from 1768 to 1778, concurrently serving as Governor General of British North America in that time, and again from 1785 to 1795. The title Baron Dorchester was created on 21 August 1786.

Quebec, Canada's largest province, occupies a vast territory, most of which is very sparsely populated. With an area of 1,542,056 square kilometres, it is the second largest of Canada's provinces and territories and the tenth largest country subdivision in the world. More than 90 percent of Quebec's area lies within the Canadian Shield, and includes the greater part of the Labrador Peninsula. Quebec's highest mountain is Mont D'Iberville, which is located on the border with Newfoundland and Labrador in the northeastern part of the province in the Torngat Mountains. The addition of parts of the vast and scarcely populated District of Ungava of the Northwest Territories between 1898 and 1912 gave the province its current form.

An inuksuk is a manmade stone landmark or cairn built for use by the Inuit, Iñupiat, Kalaallit, Yupik, and other peoples of the Arctic region of North America. These structures are found in northern Canada, Greenland, and Alaska. This combined region, above the Arctic Circle, is dominated by the tundra biome and has areas with few natural landmarks.

Events from the year 1760 in Canada.

Magdalen Islands is one of two municipalities forming the urban agglomeration of Magdalen Islands in Quebec, Canada. It is part of the Gaspésie–Îles-de-la-Madeleine region and the population is 12,291 as of the Canada 2011 Census.

The Queen Elizabeth Islands are the northernmost cluster of islands in Canada's Arctic Archipelago, split between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories in Northern Canada. The Queen Elizabeth Islands contain approximately 14% of the global glacier and ice cap area..

Resolute or Resolute Bay is an Inuit hamlet on Cornwallis Island in Nunavut, Canada. It is situated at the northern end of Resolute Bay and the Northwest Passage and is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region.

The Battle of the Thousand Islands was an engagement fought on 16–24 August 1760, in the upper St. Lawrence River, among the Thousand Islands, along the present day Canada–United States border, by British and French forces during the closing phases of the Seven Years' War, as it is called in Canada and Europe, or the French and Indian War as it is referred to in the United States.

Île aux Noix is an island on the Richelieu River in Quebec, close to Lake Champlain. The island is the site of Fort Lennox National Historic Site of Canada. Politically, it is part of Saint-Paul-de-l'Île-aux-Noix.

Quebec is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is bordered to the west by the province of Ontario and the bodies of water James Bay and Hudson Bay; to the north by Hudson Strait and Ungava Bay; to the east by the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the province of Newfoundland and Labrador; and to the south by the province of New Brunswick and the U.S. states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York. It also shares maritime borders with Nunavut, Prince Edward Island, and Nova Scotia. Quebec is Canada's largest province by area and its second-largest administrative division; only the territory of Nunavut is larger. It is historically and politically considered to be part of Central Canada.
The Twin Islands are similarly shaped Arctic islands in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. They are located in central James Bay, 56 km (35 mi) north east of Akimiski Island, and 58 km (36 mi) west of Quebec. The group includes North Twin and South Twin islands.
The Cape Hope Islands are an uninhabited Canadian arctic islands group located within the midsection of James Bay in Nunavut, Canada. They are situated south of Vieux-Comptoir.























