
The Chicxulub crater is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore, but the crater is named after the onshore community of Chicxulub Pueblo. It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when an asteroid, about ten kilometers in diameter, struck Earth. The crater is estimated to be 200 kilometers in diameter and 1 kilometer in depth. It is believed to be the second largest impact structure on Earth, and the only one whose peak ring is intact and directly accessible for scientific research.

Meridiani Planum (alternatively Terra Meridiani) is a large plain straddling the equator of Mars. The plain sits on top of an enormous body of sediments that contains bound water. The iron oxide in the spherules is crystalline (grey) hematite (Fe2O3).
The Boltysh crater or Bovtyshka crater is a buried impact crater in the Kirovohrad Oblast of Ukraine, near the village of Bovtyshka. The crater is 24 kilometres (15 mi) in diameter and its age of 65.39 ± 0.14/0.16 million years, based on argon-argon dating techniques, less than 1 million years younger than Chicxulub crater in Mexico and the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. The Chicxulub impact is believed to have caused the mass extinction at the end of the Cretaceous period, which included the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs. The Boltysh crater is currently thought to be unrelated to the Chicxulub impact, and to have not generated major global environmental effects.
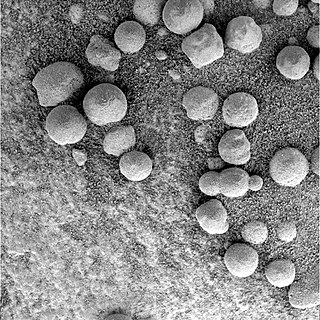
Martian spherules (also known as hematite spherules, blueberries, & Martian blueberries) are small spherules (roughly spherical pebbles) that are rich in an iron oxide (grey hematite, α-Fe2O3) and are found at Meridiani Planum (a large plain on Mars) in exceedingly large numbers.

Erebus is a crater lying situated within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars, this extraterrestrial geological feature was visited by the Opportunity rover on the way to the much larger crater Victoria. It is named after the polar exploration vessel HMS Erebus which was used by James Clark Ross in 1841 to discover the Great Ice Barrier, now known as the Ross Ice Shelf. The rover was in the immediate vicinity of the crater from approximately sol 550 to 750.

Holden is a 140 km wide crater situated within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars, located with the southern highlands. It is named after American astronomer Edward Singleton Holden. It is part of the Uzboi-Landon-Morava (ULM) system.
The Dampier Archipelago is a group of 42 islands near the town of Dampier in Pilbara, Western Australia.

Tooting is an impact crater with volcanic features at 23.1°N, 207.1°E, in Amazonis Planitia, due west of the volcano Olympus Mons, on Mars. It was identified by planetary geologist Peter Mouginis-Mark in September 2004. Scientists estimate that its age is on the order of hundreds of thousands of years, which is relatively young for a Martian crater. A later study confirms this order of magnitude estimate. A preliminary paper describing the geology and geometry of Tooting was published in 2007 by the journal Meteoritics and Planetary Science, vol. 42, pages 1615–1625. Further papers have been published, including a 2010 analysis of flows on the walls of Tooting crater by A. R. Morris et al., and a 2012 review paper by P.J. Mouginis-Mark and J.M. Boyce in Chemie der Erde Geochemistry, vol. 72, p. 1–23. A geologic map has also been submitted in 2012 to the U.S. Geological Survey for consideration and future publication.
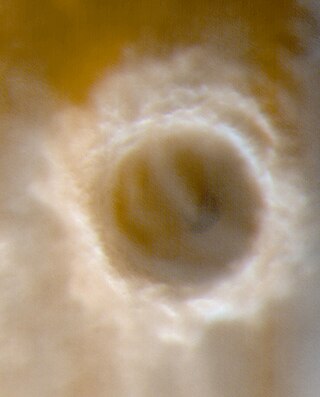
Lomonosov is a crater on Mars, with a diameter close to 150 km. It is located in the Martian northern plains. Since it is large and found close to the boundary between the Mare Acidalium quadrangle and the Mare Boreum quadrangle, it is found on both maps. The topography is smooth and young in this area, hence Lomonosov is easy to spot on large maps of Mars.

Mozart is a crater on Mercury, named by the IAU in 1976 after Austrian composer Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart.

Heimdal is a relatively recent impact crater on the planet Mars. It is a simple crater which lies in Vastitas Borealis, the northern plain. It is named after the Norwegian town of Heimdal.
The Carnarvon Basin is a geological basin located in the north west of Western Australia which extends from the Dampier Archipelago to the Murchison bioregion, and is the main geological feature that makes up the North West Shelf. The onshore part of the Carnarvon Basin covers about 115,000 km2 and the offshore part covers approximately 535,000 km2 with water depths up to 3,500 metres. It is separated into two major areas - the Northern Carnarvon Basin, and the Southern Carnarvon Basin.
Penticton is an impact crater in the Hellas quadrangle of Mars, located at 38.35° south latitude and 263.35° west longitude. Penticton is on the eastern rim of the Hellas impact crater. It is 8 kilometers in diameter and was named after Penticton, a city in British Columbia, Canada, nearby the little town of Okanagan Falls where is located the Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory. Images with HiRISE show gullies which were once thought to be caused by flowing water.
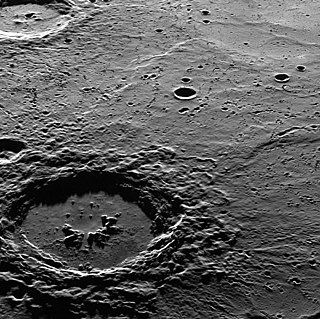
Hokusai is a rayed impact crater on Mercury, which was discovered in 1991 by ground-based radar observations conducted at Goldstone Observatory. The crater was initially known as feature B. Its appearance was so dissimilar to other impact craters that it was once thought to be a shield volcano. However, improved radar images by the Arecibo Observatory obtained later in 2000–2005 clearly showed that feature B is an impact crater with an extensive ray system. The bright appearance of rays in the radio images indicates that the crater is geologically young; fresh impact ejecta has a rough surface, which leads to strong scattering of radio waves.

Burton is an impact crater in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars. It is 123.0 km in diameter and was named after British astronomer Charles E. Burton; the name was approved in 1973.

Karratha is an impact crater in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars. It was named after the town of Karratha, Western Australia, in 2021.














