
The Kofun period is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD,following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is the earliest era of recorded history in Japan,but studies depend heavily on archaeology since the chronology of historical sources tends to be distorted. The word kofun is Japanese for the type of burial mound dating from this era.

The Complete Classics Collection of Ancient China is a vast encyclopedic work written in China during the reigns of the Qing dynasty emperors Kangxi and Yongzheng. It was begun in 1700 and completed in 1725. The work was headed and compiled mainly by scholar Chen Menglei (陳夢雷). Later on the Chinese painter Jiang Tingxi helped work on it as well.

Gimbap,also romanized as kimbap,is a Korean dish made from cooked rice,vegetables,fish,and meat rolled in gim—dried sheets of seaweed—and served in bite-sized slices. The origins of gimbap are debated. Some sources suggest it originates from Japanese norimaki,introduced during Japanese colonial rule,while others argue it is a modernized version of bossam from the Joseon era. The dish is often part of a packed meal,or dosirak,to be eaten at picnics and outdoor events,and can serve as a light lunch along with danmuji and kimchi. It is a popular takeaway food in South Korea and abroad and is known as a convenient food because of its portability.

Donggung Palace and Wolji Pond,formerly known as Anapji (Korean: 안압지),is an artificial pond in Gyeongju National Park,South Korea. It was part of the palace complex of ancient Silla. It was constructed by order of King Munmu in 674 CE. The pond is situated at the northeast edge of the Banwolseong palace site,in central Gyeongju. It is an oval shape;200m from east to west and 180m from north to south. It contains three small islands.

Shiga Shigetaka was the editor of the magazine Nihonjin during the Meiji period,in which he argued against extreme Westernization.

The Dongyi or Eastern Yi was a collective term for ancient peoples found in Chinese records. The definition of Dongyi varied across the ages,but in most cases referred to inhabitants of eastern China. Then later,the Korean peninsula and Japanese Archipelago. Dongyi refers to different group of people in different periods. As such,the name "Yí" 夷 was something of a catch-all and was applied to different groups over time. According to the earliest Chinese record,the Zuo Zhuan,the Shang dynasty was attacked by King Wu of Zhou while attacking the Dongyi and collapsed afterward.

Beomeosa is one of the head temples of the Jogye Order of Korean Buddhism in Cheongnyeongnopo-dong,Geumjeong District,Busan,South Korea. Built on the slopes of the mountain Geumjeongsan,it is one of the country's best known temples.

Gim (Korean: 김),also romanized as kim,is a generic term for a group of edible seaweeds dried to be used as an ingredient in Korean cuisine,consisting of various species in the genera Pyropia and Porphyra,including P. tenera,P. yezoensis,P. suborbiculata,P. pseudolinearis,P. dentata,and P. seriata.

The Shanhai Yudi Quantu is a Ming dynasty Chinese map published in 1609 in the leishu encyclopedia Sancai Tuhui.

Yu Hyeong-won,also spelled as Yoo Hyung-Won,was a Korean philosopher. His art name was Ban'gye (磻溪). He was a Neo-Confucianist and science scholar of the Korean Joseon Dynasty. He was a Korean pioneer of the early silhak school as well as a social critic and scholar of the late Joseon period. He was the disciple of Misu Heo Mok and second cousin of the silhak scholar Seongho Yi Ik.
Kunyu Wanguo Quantu,printed in Ming China at the request of the Wanli Emperor in 1602 by the Italian Catholic missionary Matteo Ricci and Chinese collaborators,the mandarin Zhong Wentao,and the technical translator Li Zhizao,is the earliest known Chinese world map with the style of European maps. It has been referred to as the Impossible Black Tulip of Cartography,"because of its rarity,importance and exoticism". The map was crucial in expanding Chinese knowledge of the world. It was eventually exported to Korea then Japan and was influential there as well,though less so than Giulio Aleni's Zhifang Waiji.

Xia Qifeng was a politician,diplomat and journalist in the Chinese Republic. He engaged in foreign affairs in the Beiyang Government and the Nationalist Government. In the end,he became an important politician during the Reformed Government of the Republic of China and the Reorganized National Government of China. His former name was Yun (雲). He was born in Taizhou,Jiangsu.

He Fenglin was a Chinese general and warlord. He belonged to the Anhui clique and the Fengtian clique,and later served as the Minister of War of the Republic of China.
The Cihai is a large-scale dictionary and encyclopedia of Standard Mandarin Chinese. The Zhonghua Book Company published the first Cihai edition in 1938,and the Shanghai Lexicographical Publishing House revised editions in 1979,1989,1999,and 2009. A standard bibliography of Chinese reference works calls the Cihai an "outstanding dictionary".

Daehanjiji is an elementary school geography text about the Korean Empire by Hyeon Chae. Hyeon Chae wrote the book in 1899,translating and compiling Japanese and Korean sources. It was published by Gwangmun-sa,Seoul.
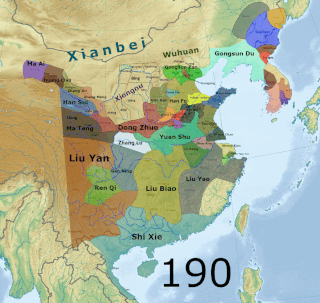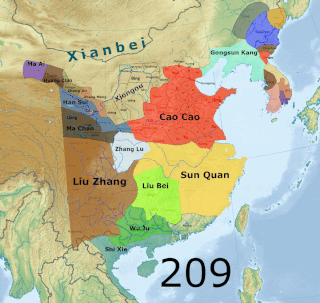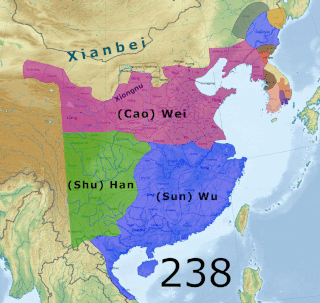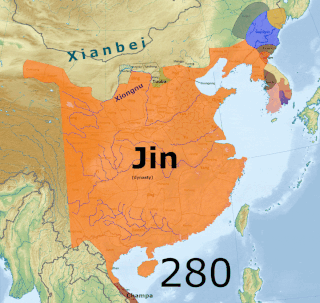
Yan was a Chinese kingdom that existed from July 237 to September 238 CE in the Liaodong Peninsula during the Three Kingdoms period. Its predecessor was an independent regime ruled by Gongsun Du and his son Gongsun Kang from 190 to 237. Though it only claimed independence in 237,historians such as Wang Zhongshu and Hou Tao consider it to be a de facto independent regime from when Gongsun Du established his rule in Liaodong in 190. Although it existed during the Three Kingdoms period,it is not counted as one of the eponymous three kingdoms:Cao Wei,Shu Han,and Eastern Wu. Nevertheless,writers such as Kang Youwei consider it to be a "fourth country".
Ijinasi or Naejinjuji (內珍朱智) was the founder and first king of Daegaya.
Grand Prince Wolsan was a Korean Royal Prince as the oldest son of Deokjong of Joseon and Queen Sohye. His personal name was Yi Jeong.















