
Brunei, officially Brunei Darussalam, is a country in Southeast Asia, situated on the northern coast of the island of Borneo. Apart from its coastline on the South China Sea, it is completely surrounded by the Malaysian state of Sarawak, with its territory bifurcated by the Sarawak district of Limbang. Brunei is the only sovereign state entirely on Borneo; the remainder of the island is divided between its multi-landmass neighbours of Malaysia and Indonesia. As of 2023, the country had a population of 455,858, of whom approximately 180,000 resided in the capital and largest city of Bandar Seri Begawan. Its official language is Malay and Islam is the state religion of the country, although other religions are nominally tolerated. The government of Brunei is a constitutional absolute monarchy ruled by the Sultan, and it implements a fusion of English common law and jurisprudence inspired by Islam, including sharia.

Ivory Coast is a sub-Saharan nation in southern West Africa located at 8° N, 5° W. The country is approximately square in shape.

The Cook Islands can be divided into two groups: the Southern Cook Islands and the Northern Cook Islands. The country is located in Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand.

Indonesia is an archipelagic country located in Southeast Asia and Oceania, lying between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. It is located in a strategic location astride or along major sea lanes connecting East Asia, South Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is the largest archipelago in the world. Indonesia's various regional cultures have been shaped—although not specifically determined—by centuries of complex interactions with its physical environment.

Nigeria is a country in West Africa. It shares land borders with the Republic of Benin to the west, Chad and Cameroon to the east, and Niger to the north. Its coast lies on the Gulf of Guinea in the south and it borders Lake Chad to the northeast. Notable geographical features in Nigeria include the Adamawa Plateau, Mambilla Plateau, Jos Plateau, Obudu Plateau, the Niger River, Benue River, and Niger Delta.
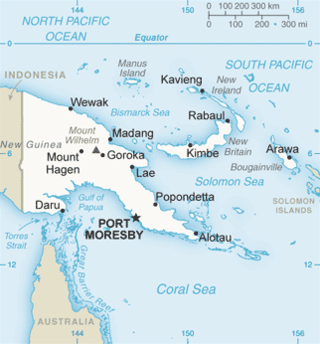
The geography of Papua New Guinea describes the eastern half of the island of New Guinea, the islands of New Ireland, New Britain and Bougainville, and smaller nearby islands. Together these make up the nation of Papua New Guinea in tropical Oceania, located in the western edge of the Pacific Ocean.

Sierra Leone is a country in West Africa with a North Atlantic Ocean coastline to the west. It lies on the African Plate. The country's main geographical features include wooded hill country, an upland plateau, and mountains in the east. The highest peak is Mount Bintumani, which is 1,948 meters (6,391 ft) above sea level. The coastline has a belt of mangrove swamps. Freetown, the nation's capital city, has one of the world's largest natural harbours. The Rokel River is the largest river in Sierra Leone. It is 400 kilometres (250 mi) long and has a basin with a total area of 10,622 square kilometres (4,101 sq mi).

Solomon Islands is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean, that lies east of Papua New Guinea.

Thailand is in the middle of mainland Southeast Asia. It has a total size of 513,120 km2 (198,120 sq mi) which is the 50th largest in the world. The land border is 4,863 km (3,022 mi) long with Myanmar, Cambodia, Laos and Malaysia. The nation's axial position influenced many aspects of Thailand's society and culture. It controls the only land route from Asia to Malaysia and Singapore. It has an exclusive economic zone of 299,397 km2 (115,598 sq mi).
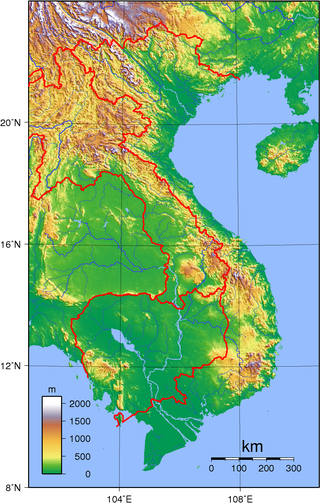
Vietnam is located on the eastern margin of the Indochinese peninsula and occupies about 331,211.6 square kilometres (127,881.5 sq mi), of which about 25% was under cultivation in 1987. It borders the Gulf of Tonkin, Gulf of Thailand, and Pacific Ocean, along with China, Laos, and Cambodia. The elongated roughly S shaped country has a north-to-south distance of 1,650 km (1,030 mi) and is about 50 km (31 mi) wide at the narrowest point. With a coastline of 3,260 km (2,030 mi), excluding islands, Vietnam claims 12 nautical miles as the limit of its territorial waters, an additional 12 nautical miles as a contiguous customs and security zone. It has an exclusive economic zone of 417,663 km2 (161,261 sq mi) with 200 nautical miles.

Vanuatu is a nation and group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean. It is composed of over 80 islands with 2,528 kilometres (1,571 mi) of coastline and a total surface area of 12,189 square kilometres (4,706 sq mi). It's a small country with a total size of 12,189 km2 (4,706 sq mi). Due to the spread out islands it has the 39th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 663,251 km2 (256,083 sq mi).

Bandar Seri Begawan, and colloquially referred to as BSB, is the capital and largest city of Brunei. It is officially a municipal area with an area of 100.36 square kilometres (38.75 sq mi) and an estimated population of 100,700 as of 2007. It is part of Brunei-Muara District, the smallest yet most populous district which is home to over 70 per cent of the country's population. It is the country's largest urban centre and nominally the country's only city. The capital is home to Brunei's seat of government, as well as a commercial and cultural centre. It was formerly known as Brunei Town until it was renamed in 1970 in honour of Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III, the 28th Sultan of Brunei and the father of the current Sultan, Hassanal Bolkiah.

The geography of Malaysia includes both the physical and the human geography of Malaysia, a Southeast Asian country made up of two major landmasses separated by water—Peninsular Malaysia to the west and East Malaysia to the east—and numerous smaller islands that surround those landmasses. Peninsular Malaysia is on the southernmost part of the Malay Peninsula, south of Thailand, north of Singapore and east of the Indonesian island of Sumatra; East Malaysia comprises most of the northern part of Borneo, and shares land borders with Brunei to the north and Indonesian Borneo to the south.

Somalia is a country located in the Horn of Africa which officially consists of the intra-46th meridian east territory, the seven federal member states, namely Galmudug, Hirshabelle, Jubaland, South West, Puntland, and the municipality of Benadir. It is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, the Gulf of Aden to the north, the Somali Sea and Guardafui Channel to the east, and Kenya to the southwest. With a land area of 637,657 square kilometers, Somalia's terrain consists mainly of plateaus, plains and highlands. Its coastline is more than 3,333 kilometers in length, the longest of mainland Africa. It has been described as being roughly shaped "like a tilted number seven".

Bangladesh is a densely populated, low-lying, mainly riverine country located in South Asia with a coastline of 580 km (360 mi) on the northern littoral of the Bay of Bengal. The delta plain of the Ganges (Padma), Brahmaputra (Jamuna), and Meghna Rivers and their tributaries occupy 79 percent of the country. Four uplifted blocks occupy 9 percent and steep hill ranges up to approximately 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) high occupy 12 percent in the southeast and in the northeast. Straddling the Tropic of Cancer, Bangladesh has a tropical monsoon climate characterised by heavy seasonal rainfall, high temperatures, and high humidity. Natural disasters such as floods and cyclones accompanied by storm surges periodically affect the country. Most of the country is intensively farmed, with rice the main crop, grown in three seasons. Rapid urbanisation is taking place with associated industrial and commercial development. Exports of garments and shrimp plus remittances from Bangladeshis working abroad provide the country's three main sources of foreign exchange income.
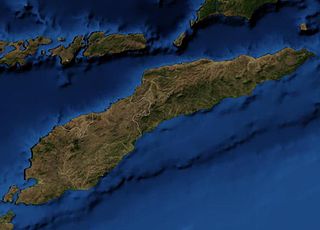
East Timor includes the mountainous eastern half of Timor, the Ocussi-Ambeno region on the northwest portion of the island of Timor, and the islands of Atauro and Jaco. The country is located northwest of Australia in the Lesser Sunda Islands at the eastern end of the Indonesian Archipelago. 'Timor' is a Portuguese derivation of 'Timor', the Malay word for "Orient"; the island of Timor is part of the Malay Archipelago and is the largest and easternmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East Timor is the only Asian nation to lie entirely within the Southern Hemisphere. The Loes River is the longest with a length of 80 km (50 mi). This river system covers an area of 2,184 km2 (843 sq mi). It is a small country with a land size of 14,919 km2 (5,760 sq mi). The exclusive economic zone is 70,326 km2 (27,153 sq mi).

The Intertropical Convergence Zone, known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal equator though its specific position varies seasonally. When it lies near the geographic Equator, it is called the near-equatorial trough. Where the ITCZ is drawn into and merges with a monsoonal circulation, it is sometimes referred to as a monsoon trough.

The geography of South America contains many diverse regions and climates. Geographically, South America is generally considered a continent forming the southern portion of the landmass of the Americas, south and east of the Colombia–Panama border by most authorities, or south and east of the Panama Canal by some. South and North America are sometimes considered a single continent or supercontinent, while constituent regions are infrequently considered subcontinents.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and a topical guide to Brunei:

A tropical rainforest climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southeast Florida, United States, and Okinawa, Japan that fall into the tropical rainforest climate category. They experience high mean annual temperatures, small temperature ranges, and rain that falls throughout the year. Regions with this climate are typically designated Af by the Köppen climate classification. A tropical rainforest climate is typically hot, very humid, and wet with no dry season.




















