The British Virgin Islands (BVI) are one of three political divisions of the Virgin Islands archipelago located in the Lesser Antilles, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean. The BVI are the easternmost part of the island chain. The land area totals and comprises 16 inhabited and more than 20 uninhabited islands. The islands of Tortola, Anegada, Virgin Gorda and Jost van Dyke are the largest. Maritime claims include 12 nmi territorial sea and a 200 nmi exclusive fishing zone. In terms of land use, it is 20% arable land, 6.67% permanent crops and 73.33% other as of a 2005 figure. It has strong ties to nearby U.S. Virgin Islands and Puerto Rico.

Geography of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM), a country located in the western Pacific Ocean, and in the Micronesia cultural and ecological sub-region of Oceania. While its total land area is very small at 702 km2 (271 sq mi), it has the 14th largest exclusive economic zone at 2,996,419 km2 (1,156,924 sq mi).

The Republic of Haiti comprises the western three-eighths of the island of Hispaniola, west of the Dominican Republic. Haiti is positioned east of the neighboring island of Cuba, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean.

Indonesia is an archipelagic country located in Southeast Asia and Oceania, lying between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. It is located in a strategic location astride or along major sea lanes connecting East Asia, South Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is the largest archipelago in the world. Indonesia's various regional cultures have been shaped—although not specifically determined—by centuries of complex interactions with its physical environment.

São Tomé and Príncipe is a small island country composed of an archipelago located in the Gulf of Guinea of the equatorial Atlantic Ocean. The nation's main islands are São Tomé Island and Príncipe Island, for which the country is named. These are located about 300 and 250 kilometres, respectively, off the northwest coast of Gabon in Central Africa.

Located in Oceania, Tonga is a small archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, directly south of Samoa and about two-thirds of the way from Hawaii to New Zealand. It has 169 islands, 36 of them inhabited, which are in three main groups – Vavaʻu, Haʻapai, and Tongatapu – and cover an 800-kilometre (500-mile)-long north–south line. The total size is just 747 km2 (288 sq mi). Due to the spread out islands it has the 40th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 659,558 km2 (254,657 sq mi).

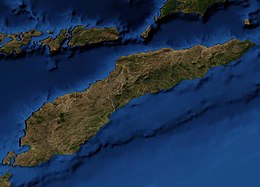
Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is divided between the sovereign states of East Timor in the eastern part and Indonesia in the western part. The Indonesian part, known as West Timor, constitutes part of the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Within West Timor lies an exclave of East Timor called Oecusse District. The island covers an area of 30,777 square kilometres. The name is a variant of timur, Malay for "east"; it is so called because it lies at the eastern end of the Lesser Sunda Islands. Mainland Australia is less than 500 km away, separated by the Timor Sea.

Fiji is a group of volcanic islands in the South Pacific, lying about 4,450 kilometres (2,765 mi) southwest of Honolulu and 1,770 km (1,100 mi) north of New Zealand. Of the 332 islands and 522 smaller islets making up the archipelago, about 106 are permanently inhabited. The total land size is 18,272 km2 (7,055 sq mi). It has the 26th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,282,978 km2 (495,361 sq mi).

Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean Sea. It comprises an archipelago of islands centred upon the geographic coordinates 21°3N, 80°00W. Cuba is the principal island, surrounded by four main archipelagos: the Colorados, the Sabana-Camagüey, the Jardines de la Reina and the Canarreos. Cuba's area is 110,860 km2 (42,800 sq mi) including coastal and territorial waters with a land area of 109,820 km2 (42,400 sq mi), which makes it the eighth-largest island country in the world. The main island (Cuba) has 5,746 km (3,570 mi) of coastline and 28.5 km (17.7 mi) of land borders—all figures including the U.S. Navy's Guantanamo Bay Naval Base. Its official area is 109,884 km2 (42,426 sq mi).

The Cylindrophiidae are a monotypic family of secretive, semifossorial, non-venomous snakes containing the genus Cylindrophis found in southeastern Asia. These are burrowing snakes and most have a banded pattern on the belly. Currently, 13 species are recognized, all with no subspecies. Common names include Asian pipe snakes or Asian cylinder snakes.

Atauro, also known as Kambing Island, is an island and municipality of East Timor. Atauro is a small oceanic island situated north of Dili, on the extinct Wetar segment of the volcanic Inner Banda Arc, between the Indonesian islands of Alor and Wetar. The nearest island is the Indonesian island of Liran, 13.0 km (8.1 mi) to the northeast. At the 2015 census, it had 9,274 inhabitants.

Dili Municipality is one of the 14 municipalities, formerly districts, of Timor-Leste, and includes the national capital Dili. The municipality had a population of 277,279 as of 2015, most of whom live in the capital city.

Ombai Strait is an international strait in Southeast Asia. It separates the Alor Archipelago from the islands of Wetar, Atauro, and Timor in the Lesser Sunda Islands. The strait is also the western portion of a pair of international straits, the other one being Wetar Strait; the two straits combine to link the Pacific Ocean with the Indian Ocean.

Mauremys reevesii, commonly known as the Chinese pond turtle, the Chinese three-keeled pond turtle, or Reeves' turtle, is a species of turtle in the family Geoemydidae, a family which was formerly called Bataguridae. The species is native to East Asia.

The Comoro River is a river in East Timor. It flows north into Ombai Strait, reaching the coast in the north western suburbs of the capital, Dili. In its lower reaches, it is the main and largest of Dili's four major rivers.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to East Timor:

Limnonectes timorensis is a species of frogs in the family Dicroglossidae. It is endemic to the island of Timor at the eastern end of the Lesser Sunda Islands. In Timor-Leste it is an infrequent species associated with rivers in tropical montane forests above 1000 m altitude.

Oecusse, also known as Oecusse-Ambeno and formerly just Ambeno, officially the Special Administrative Region Oecusse-Ambeno, is an exclave, municipality and the only Special Administrative Region (SAR) of East Timor.
Eremiascincus butlerorum is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to the island of Sumba in Indonesia.