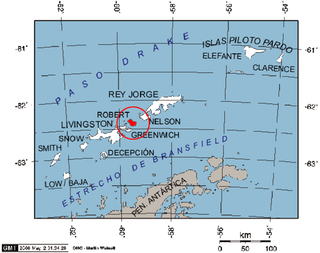
Robert Island or Mitchells Island or Polotsk Island or Roberts Island is an island 11 miles (18 km) long and 8 miles (13 km) wide, situated between Nelson Island and Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Robert Island is located at 62°24′S59°30′W. Surface area 132 km2 (51 sq mi). The name "Robert Island" dates back to around 1821 and is now established in international usage.

Desolation Island is one of the minor islands in the South Shetlands archipelago, Antarctica situated at the entrance to Hero Bay, Livingston Island. The island is V-shaped with its northern coast indented by Kozma Cove. Surface area 3.12 square kilometres (1.20 sq mi).

Voluyak Rocks is a chain of rocks off the north coast of Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated 400 m (440 yd) north of Pavlikeni Point. Extending 1.9 km (1.2 mi) in southeast-northwest direction.

Bistra Glacier is 1 nautical mile long and 0.4 nautical miles wide glacier on the northwest side of Imeon Range on Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is situated southwest of Chuprene Glacier and northwest of Dragoman Glacier, drains the west slopes of Mount Foster and the north slopes of Slaveykov Peak, and flows northwestwards of Zavet Saddle to enter Drake Passage south of Garmen Point.

Barlow Island is a small ice-free island off the north coast of Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica extending 380 by 160 m, surface area 5.28 hectares.

Window Island is a small ice-free island off the north coast of Ray Promontory in the northwest of Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The island has a surface area of 23 hectares and rises to 72 m (236 ft). It was known to the early 19th century sealers operating on Byers Peninsula.

Cecilia Island is the ice-free southernmost island of the Aitcho group on the west side of English Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Extending 910 by 450 m, surface area 36 hectares. The area, visited by American and English sealers in the early 19th century, nowadays has become a popular tourist site frequented by Antarctic cruise ships.
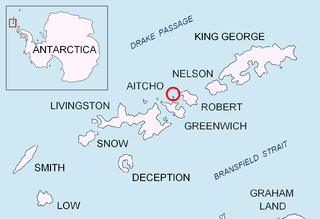
Table Island is a conspicuous flat-topped, rocky island lying north of Greenwich Island and north-northwest of the Aitcho group on the west side of English Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The island is rising to over 150 metres and extending 1.4 by 1 kilometre, with a surface area of 112 hectares. It is separated from Aitcho Islands to the south-southeast by the 1.9-kilometre (1.2-mile) wide Klimash Passage.

Romeo Island is a rocky island lying off the north coast of Greenwich Island and west of Aitcho Islands in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Extending 1.35 km (0.84 mi) in west-northwest direction and 470 m (510 yd) wide, with a surface area of 44 hectares. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers.

Cornwall Island is a low ice-free island off the north coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Surface area 15 hectares. Mónica Rock is lying 1.65 km (1.03 mi) west of the island and 3.4 km (2.1 mi) north of Passage Rock, 2.84 km (1.76 mi) east of Table Island and 2 km (1.2 mi) south of Potmess Rocks. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Clothier Harbour.

Lynx Rocks is a group of rocks in southwestern Hero Bay on the north side of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Blythe Bay.

Eliza Rocks is a chain of rocks lying between Desolation Island and Zed Islands off the north coast of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica and extending 1 km in west-northwest direction. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from Blythe Bay, Desolation Island.

Frederick Rocks is a group of rocks lying in Barclay Bay on the north side of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating on nearby Byers Peninsula.

Eddystone Rocks is a group of two rocks lying to the northwest of Rugged Island off western Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.

Potmess Rocks is a group of large rocks lying northwest of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The group is extending 1.3 by 1 km, featuring the conspicuous rocks named Asses Ears in the north. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Clothier Harbour.

Henfield Rock is an offshore rock lying northwest of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It was known to the early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Clothier Harbour, and sometimes included under the name 'Powels Islands' or 'Heywood Islands'.

Lientur Rocks is a group of prominent adjacent rocks lying off the north coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica and extending 660 m (722 yd) in east-west direction and 320 m (350 yd) in north-south direction. The area was visited by early 19th-century sealers operating from nearby Clothier Harbour.

Skrino Rocks is the chain of rocks off the east coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, extending 570 m (623 yd) in east-west direction.

Alepu Rocks is the group of rocks off the east coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, situated in an area with a diameter of 380 m (416 yd).




















