
Tundzha Glacier is a glacier on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated east-southeast of Berkovitsa Glacier, west of Saedinenie Snowfield, northwest of Pimpirev Glacier, north of Kamchiya Glacier and east-northeast of Verila Glacier. It is bounded by Snow Peak to the west, Teres Ridge to the east and the glacial divide between the Drake Passage and Bransfield Strait to the south. The glacier extends 7.5 nautical miles in east-west direction and 2.4 nautical miles in the north-south direction, and drains northwards into Hero Bay between Avitohol Point and Siddins Point.

Desolation Island is one of the minor islands in the South Shetlands archipelago, Antarctica situated at the entrance to Hero Bay, Livingston Island. The island is V-shaped with its northern coast indented by Kozma Cove. Surface area 3.12 square kilometres (1.20 sq mi).

Belchin Rock is a rock off the north coast of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated in Hero Bay 2.2 km (1.4 mi) northeast of Siddins Point and 2 km (1.2 mi) north of Melta Point.

Koynare Rocks are a small group of rocks in Hero Bay off the north coast Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated 7.5 km (4.66 mi) northeast of Siddins Point, 5.3 km (3.29 mi) northwest of Bezmer Point, and 1.4 km (0.87 mi) south of Miladinovi Islets. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers.

Cape Conway is the rounded low and ice-free tipped cape forming the south extremity of Snow Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is a south entrance point for Boyd Strait. Tooth Rock rising to 85 m (279 ft) and lying 1.94 km (1.21 mi) to the south is the largest in a group of rocks extending 2.7 km (1.7 mi) from the cape. The area was visited by 19th century sealers.

The Meade Islands are a group of two large islands, Zverino Island and Cave Island, the minor Pisanitsa Island, and several rocks lying in the north entrance to McFarlane Strait, off Archar Peninsula, Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The surface areas of the first two islands are 48 hectares and 18 hectares. respectively. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers.
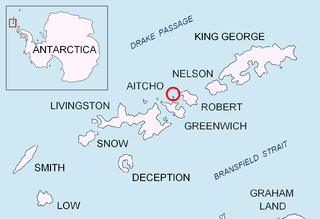
Table Island is a conspicuous flat-topped, rocky island lying north of Greenwich Island and north-northwest of the Aitcho group on the west side of English Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The island is rising to over 150 metres and extending 1.4 by 1 kilometre, with a surface area of 112 hectares. It is separated from Aitcho Islands to the south-southeast by the 1.9-kilometre (1.2-mile) wide Klimash Passage.

Cornwall Island is a low ice-free island off the north coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Surface area 15 hectares. Mónica Rock is lying 1.65 km (1.03 mi) west of the island and 3.4 km (2.1 mi) north of Passage Rock, 2.84 km (1.76 mi) east of Table Island and 2 km (1.2 mi) south of Potmess Rocks. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Clothier Harbour.

Wood Island is a conspicuous rocky island in Hero Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica lying southeast of Desolation Island and Miladinovi Islets and forming the south side of Blythe Bay. Surface area 14 hectares .) The area was frequented by early nineteenth century English and American sealers operating from Blythe Bay.

Craggy Island is a narrow island marked by crags, lying in Hero Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica and forming the northeast side of Blythe Bay. Its surface area is 9 hectares .) The area was frequented by early nineteenth century English and American sealers operating from Blythe Bay.

Cape Danger is the rocky point forming the northwest extremity of the ice-free Desolation Island situated in the entrance to Hero Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The cape forms the west side of the entrance to Kozma Cove. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Blythe Bay.

Chapman Rocks is a group of rocks in central Hero Bay on the north side of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Blythe Bay.

Eliza Rocks is a chain of rocks lying between Desolation Island and Zed Islands off the north coast of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica and extending 1 km in west-northwest direction. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from Blythe Bay, Desolation Island.

Frederick Rocks is a group of rocks lying in Barclay Bay on the north side of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating on nearby Byers Peninsula.

Hetty Rock is the largest of several rocks in Walker Bay off John Beach in western Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers.

Eddystone Rocks is a group of two rocks lying to the northwest of Rugged Island off western Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.

Mellona Rocks is a group of scattered rocks lying at the north entrance to Nelson Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica and extending 1.7 by 0.9 km. The area was known to the early 19th-century sealers and sometimes included under the names 'Heywood Islands' or 'Powels Islands'.

Liberty Rocks is a group of four prominent adjacent rocks lying at the north entrance to Nelson Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica and extending 430 by 120 m. The area was visited by early 19th-century sealers.

Vodoley Rock is the rock extending 220 m in northwest-southeast direction and 110 m wide in Barclay Bay on the west side of Ioannes Paulus II Peninsula on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating on nearby Byers Peninsula and Cape Shirreff.






















