
Quito Glacier is a glacier draining the northeast slopes of Mount Plymouth and flowing northeastwards into the sea west of Canto Point in north Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. It was named after the capital of Ecuador, c. 1990, by the Ecuadorian Antarctic Expedition.

Sewing-Machine Needles is a group of three prominent rock needles, the highest 45 m, lying close southeast of Rancho Point, Deception Island, in the South Shetland Islands. The name Sewing-Machine Rock was given by whalers for what was originally a conspicuous natural arch. Needles is now considered the more suitable descriptive term; an earthquake tremor in 1924 caused the arch to collapse.

Sierra Island is a narrow island which is marked by a series of small elevations throughout its length, lying 0.5 miles (0.8 km) northwest of Dee Island and north of Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Surface area 14 hectares.

The Ibar Rocks are two rocks located 0.4 kilometres (0.2 nmi) east of Bonert Rock and 1 kilometre (0.6 nmi) southeast of Canto Point, Greenwich Island, in the South Shetland Islands. The names "Islote Ibar" and "Islote Teniente Ibar" appearing on Chilean hydrographic charts in the 1950s refer to the larger and western rock. The recommended name "Ibar Rocks" includes a submerged outlier to the northeast of the larger rock. Teniente (lieutenant) Mario Ibar P. signed the official act of inauguration of the Chilean Captain Arturo Prat Base on Greenwich Island in 1947.

Express Island is a narrow craggy island, 1.23 kilometres (0.76 mi) long, lying close offshore of northwest Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is situated due north of Greaves Peak, forming most of the east side of Razlog Cove. Surface area 29 hectares.

Astor Island is an island lying between Rugged Island and Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Surface area 12 hectares.

The Asses Ears are a set of three small islands off northwest Robert Island, forming the north part of Potmess Rocks in English Strait, South Shetland Islands. Presumably known to early sealers, the feature was charted and named descriptively by personnel on Discovery II in 1934–35.

Aim Rocks is a group of rocks lying east of Cape Timblón in the middle of Morton Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The name, given by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1961, is descriptive; these rocks in line are a guide for safe passage through the southern entrance of Morton Strait.

Morton Strait is the 9 km (4.9 nmi)-long and 6.2 km (3.3 nmi)-wide strait between Snow Island on the southwest and Rugged Island and Livingston Island on the northeast, in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The Aim Rocks and Long Rock lie in the strait.

Macy Glacier is a 3.7 nautical miles long and 1.4 nautical miles crescent-shaped glacier on the southern slopes of the Tangra Mountains, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The glacier is bounded by Friesland Ridge to the northwest, Levski Ridge to the northeast and Peshev Ridge to the southeast, and flows southwestwards into the head of Brunow Bay.
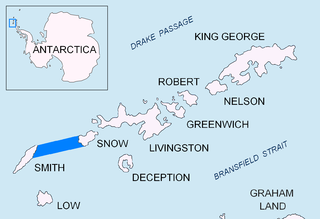
Boyd Strait is the 40-kilometre (25 mi) wide strait lying between Snow Island and Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, and linking Drake Passage and the Bransfield Strait.
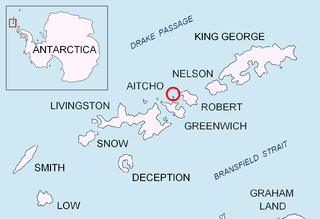
Emeline Island is a conspicuous rocky island rising to over 100 m (328 ft) in the Aitcho group on the west side of English Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The island extends 550 by 320 m with a surface area of 18 hectares. The area was visited by early 19th century seal hunters.

Fuerza Aérea Glacier is a glacier on Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, extending 4.5 kilometres (2.8 mi) in a northeast–southwest direction and 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) in a southeast–northwest direction and draining the northwest slopes of the Breznik Heights to flow northwestwards into Discovery Bay.

Long Rock is a large rock extending 720 m (787 yd) in east-west direction, 180 m (197 yd) wide and rising to 13 m (42.7 ft) in the northeast of Morton Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating on Byers Peninsula.

Withem Island is an island lying off the northwest side of Nelson Island in the South Shetland Islands. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1961 after Nicholas Withem, master of the American sealing vessel Governor Brooks from Salem, MA, who visited the South Shetland Islands in 1820-21. Originally proposed and approved as "Withen Island," the name was amended in 1990 to agree with the correct spelling of the personal name.

Weeks Stack is a sea stack lying off the north tip of Nelson Island in the northern approach to Fildes Strait, in the South Shetland Islands. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1961 for Captain Weeks, Master of the British sealing vessel Horatio from London, who visited the South Shetland Islands in 1820-21.

Pig Rock is a rock, 65 m high, the largest of a group of rocks lying 1.9 kilometres (1 nmi) east of the east end of Nelson Island, in the South Shetland Islands. This rock, known to sealers in the area as early as 1821, was charted and named by DI personnel on the Discovery II in 1935.

Fildes Strait is a strait which extends in a general east-west direction between King George Island and Nelson Island, in the South Shetland Islands. This strait has been known to sealers in the area since about 1822, but at that time it appeared on the charts as "Field's Strait". It was probably named for Robert Fildes, a British sealer of that period, whose vessel Robert was wrecked in Clothier Harbour in 1822.

Folger Rock is a rock lying 2.5 nautical miles (5 km) north of Harmony Point, Nelson Island, in the South Shetland Islands. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1961 for Tristan Folger, the Master of the American sealing vessel William and Nancy from Nantucket, which visited the South Shetland Islands in 1820–21, operating from nearby Harmony Cove.

Sail Rock is the remaining uppermost part of a submerged volcanic edifice lying 7 nautical miles (13 km) southwest of Deception Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is 20 m long in southwest-northeast direction, 12 m wide and 30 m high. From a distance, the rock is reported to resemble a ship under sail, but at close range it is more like a house with a gable roof. The feature's name, which dates back to at least 1822, was probably given by sealers.
















