
Athlon is the brand name applied to a series of x86-compatible microprocessors designed and manufactured by AMD. The original Athlon was the first seventh-generation x86 processor and the first desktop processor to reach speeds of one gigahertz (GHz). It made its debut as AMD's high-end processor brand on June 23, 1999. Over the years AMD has used the Athlon name with the 64-bit Athlon 64 architecture, the Athlon II, and Accelerated Processing Unit (APU) chips targeting the Socket AM1 desktop SoC architecture, and Socket AM4 Zen microarchitecture. The modern Zen-based Athlon with a Radeon Graphics processor was introduced in 2019 as AMD's highest-performance entry-level processor.

Celeron is a discontinued series of low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers, manufactured by Intel. The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, 1998, and was based on the Pentium II.

The Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture ("P6") and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million transistors. However, its L2 cache subsystem was a downgrade when compared to the Pentium Pros. It is a single-core microprocessor.

The Pentium III brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile CPUs based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 28, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded processors. The most notable differences were the addition of the Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) instruction set, and the introduction of a controversial serial number embedded in the chip during manufacturing. The Pentium III is also a single-core processor.

The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel and introduced on November 1, 1995. It introduced the P6 microarchitecture and was originally intended to replace the original Pentium in a full range of applications. Later, it was reduced to a more narrow role as a server and high-end desktop processor. The Pentium Pro was also used in supercomputers, most notably ASCI Red, which used two Pentium Pro CPUs on each computing nodes and was the first computer to reach over one teraFLOPS in 1996, topping the number one spot in the TOP500 list from 1997 to 2000.
The Pentium OverDrive was a microprocessor marketing brand name used by Intel, to cover a variety of consumer upgrade products sold in the mid-1990s. It was originally released for 486 motherboards, and later some Pentium sockets. Intel dropped the brand, as it failed to appeal to corporate buyers, and discouraged new system sales.

The Athlon 64 is a ninth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name Athlon, and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP. The Athlon 64 was the second processor to implement the AMD64 architecture and the first 64-bit processor targeted at the average consumer. Variants of the Athlon 64 have been produced for Socket 754, Socket 939, Socket 940, and Socket AM2. It was AMD's primary consumer CPU, and primarily competed with Intel's Pentium 4, especially the Prescott and Cedar Mill core revisions.

The Pentium M is a family of mobile 32-bit single-core x86 microprocessors introduced in March 2003 and forming a part of the Intel Carmel notebook platform under the then new Centrino brand. The Pentium M processors had a maximum thermal design power (TDP) of 5–27 W depending on the model, and were intended for use in laptops. They evolved from the core of the last Pentium III–branded CPU by adding the front-side bus (FSB) interface of Pentium 4, an improved instruction decoding and issuing front end, improved branch prediction, SSE2 support, and a much larger cache.

Xeon is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for error correction code (ECC) memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and extra provision for enterprise-grade reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) features responsible for handling hardware exceptions through the Machine Check Architecture (MCA). They are often capable of safely continuing execution where a normal processor cannot due to these extra RAS features, depending on the type and severity of the machine-check exception (MCE). Some also support multi-socket systems with two, four, or eight sockets through use of the Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) bus, which replaced the older QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) bus.

The K6-III was an x86 microprocessor line manufactured by AMD that launched on February 22, 1999. The launch consisted of both 400 and 450 MHz models and was based on the preceding K6-2 architecture. Its improved 256 KB on-chip L2 cache gave it significant improvements in system performance over its predecessor the K6-2. The K6-III was the last processor officially released for desktop Socket 7 systems, however later mobile K6-III+ and K6-2+ processors could be run unofficially in certain socket 7 motherboards if an updated BIOS was made available for a given board. The Pentium III processor from Intel launched 6 days later.
Slot 2 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the 330-lead Single Edge Contact Cartridge used by Intel's Pentium II Xeon and Pentium III Xeon.

The Athlon 64 X2 is the first native dual-core desktop central processing unit (CPU) designed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It was designed from scratch as native dual-core by using an already multi-CPU enabled Athlon 64, joining it with another functional core on one die, and connecting both via a shared dual-channel memory controller/north bridge and additional control logic. The initial versions are based on the E stepping model of the Athlon 64 and, depending on the model, have either 512 or 1024 KB of L2 cache per core. The Athlon 64 X2 can decode instructions for Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSE3), except those few specific to Intel's architecture. The first Athlon 64 X2 CPUs were released in May 2005, in the same month as Intel's first dual-core processor, the Pentium D.
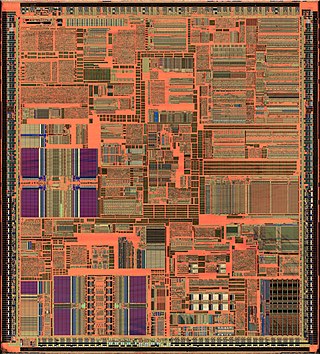
The P6 microarchitecture is the sixth-generation Intel x86 microarchitecture, implemented by the Pentium Pro microprocessor that was introduced in November 1995. It is frequently referred to as i686. It was planned to be succeeded by the NetBurst microarchitecture used by the Pentium 4 in 2000, but was revived for the Pentium M line of microprocessors. The successor to the Pentium M variant of the P6 microarchitecture is the Core microarchitecture which in turn is also derived from P6.
The Intel Core microarchitecture is a multi-core processor microarchitecture launched by Intel in mid-2006. It is a major evolution over the Yonah, the previous iteration of the P6 microarchitecture series which started in 1995 with Pentium Pro. It also replaced the NetBurst microarchitecture, which suffered from high power consumption and heat intensity due to an inefficient pipeline designed for high clock rate. In early 2004 the new version of NetBurst (Prescott) needed very high power to reach the clocks it needed for competitive performance, making it unsuitable for the shift to dual/multi-core CPUs. On May 7, 2004 Intel confirmed the cancellation of the next NetBurst, Tejas and Jayhawk. Intel had been developing Merom, the 64-bit evolution of the Pentium M, since 2001, and decided to expand it to all market segments, replacing NetBurst in desktop computers and servers. It inherited from Pentium M the choice of a short and efficient pipeline, delivering superior performance despite not reaching the high clocks of NetBurst.
AMD Turion is the brand name AMD applies to its x86-64 low-power consumption (mobile) processors codenamed K8L. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2/Ultra processors compete with Intel's mobile processors, initially the Pentium M and the Intel Core and Intel Core 2 processors.
Apollo VP3 is a x86 based Socket 7 chipset which was manufactured by VIA Technologies and was launched in 1997. On its time Apollo VP3 was a high performance, cost effective, and energy efficient chipset. It offered AGP support for Socket 7 processors which was not supported at that moment by Intel, SiS and ALi chipsets. In November 1997 FIC released motherboard PA-2012, which uses Apollo VP3 and has AGP bus. This was the first Socket 7 motherboard supporting AGP.









