
The Canadian Rockies or Canadian Rocky Mountains, comprising both the Alberta Rockies and the British Columbian Rockies, is the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. It is the easternmost part of the Canadian Cordillera, which is the northern segment of the North American Cordillera, the expansive system of interconnected mountain ranges between the Interior Plains and the Pacific Coast that runs northwest–southeast from central Alaska to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in Mexico.
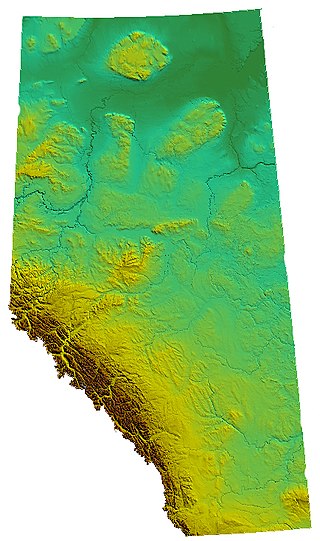
Alberta is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. Located in Western Canada, the province has an area of 661,190 km2 (255,290 sq mi) and is bounded to the south by the United States state of Montana along 49° north for 298 km (185 mi); to the east at 110° west by the province of Saskatchewan for 1,223 km (760 mi); and at 60° north the Northwest Territories for 644 km (400 mi). The southern half of the province borders British Columbia along the Continental Divide of the Americas on the peaks of the Rocky Mountains, while the northern half borders British Columbia along the 120th meridian west. Along with Saskatchewan it is one of only two landlocked provinces or territories.

Mount Ball is a mountain located on the Continental Divide, on the borders of Banff and Kootenay national parks in Western Canada. Mt. Ball is the highest peak of the Ball Range in the Canadian Rockies.

The Highwood River is a tributary of the Bow River in southwestern Alberta, Canada.

Mount Rae is a mountain located on the eastern side of Highway 40 between Elbow Pass and the Ptarmigan Cirque in the Canadian Rockies of Alberta. Mount Rae was named after John Rae, explorer of Northern Canada, in 1859.

The High Rock Range is a mountain range of the Canadian Rockies in southwestern Alberta and southeastern British Columbia, Canada.

Storm Mountain is a mountain in Alberta's Rockies, Canada.

Mount Tyrwhitt is a mountain in British Columbia and Alberta, Canada, located between Highway 40 and Elk Pass in the Elk Range of the Canadian Rockies, west of the Highwood Pass parking lot in Kananaskis Country and south east of Upper Kananaskis Lake. Located on the Continental Divide, it is also therefore on the border between British Columbia and Alberta, which follows the Divide in this area.

Ptarmigan Cirque is the cirque between Mount Arethusa and Mount Rae at the Highwood Pass in Kananaskis Country, Alberta, Canada.

Mount Blakiston is a mountain in the southwestern corner of Alberta, Canada and the highest point within Waterton Lakes National Park. The mountain is situated in the Clark Range, north of Lineham Creek and south of Blakiston Creek. Blakiston's closest neighbours include Mount Hawkins 2,685 m (8,809 ft) directly to the west along a connecting ridge and Mount Lineham 2,728 m (8,950 ft) to the south.

Mount Balfour is a mountain located on the Continental Divide, part of the border between British Columbia and Alberta, in the Waputik Range in the Park Ranges of the Canadian Rockies. It is the 71st highest peak in Alberta and the 113th highest in British Columbia; it is also the 52nd most prominent in Alberta.

Highwood Pass is a mountain pass in Kananaskis Country, Alberta, Canada. It lies west of Mount Rae and Mount Arethusa of the Misty Range, south of Elbow Pass. It lies within the Peter Lougheed Provincial Park on Alberta Highway 40. The Highwood River originates in the pass.

The Livingstone Range is a sub-range of the Canadian Rockies in Alberta, Canada. It forms the eastern boundary of the Rockies in the south of the province. Its northern boundary is the Highwood River and it extends to Crowsnest Pass in the south. The Livingstone and Oldman Rivers bound it to the west.

Castleguard Mountain, also known as Mount Castleguard, is an isolated mountain located near the southern edge of the Columbia Icefield at the northern edge of Banff National Park in Alberta, Canada. In 1918, Irish land surveyor Arthur Oliver Wheeler named the mountain because of its castle-like appearance, which seemed to stand guard over the southern portion of the Columbia Icefield. Castleguard was first ascended in 1919 by the Interprovincial Boundary Commission, which determined the exact location of the boundary between British Columbia and Alberta along the continental divide.

Gap Mountain is a 2,675-metre (8,776-foot) mountain summit located at the southern end of the Opal Range in the Canadian Rockies of Alberta, Canada. The nearest higher neighbor is Elpoca Mountain, 2 km (1.2 mi) to the east. Gap Mountain is situated 5 km (3.1 mi) south of Mount Wintour, within Peter Lougheed Provincial Park. Gap Mountain is a conspicuous peak seen from Alberta Highway 40 at Highwood Pass. It is a popular climbing destination because it offers exposed scrambling on its eastern flanks with excellent summit views of Kananaskis Country.

The Flathead Range is a mountain range of the Canadian Rockies in Alberta and British Columbia, Canada. It is located on the Continental Divide, east of Fernie, in the Kootenay Land District. It stretches 27 km (17 mi) lengthwise north–south from Crowsnest Pass to North Kootenay Pass. The range's toponym was officially adopted on 30 June 1912 by the Geographic Board of Canada, and was named in association with the Flathead River.

Mount Head is a 2,782-metre (9,127-foot) mountain summit located in Alberta, Canada.

Holy Cross Mountain is a 2,650-metre (8,694-foot) mountain summit located in Alberta, Canada.

Pyriform Mountain is a 2,739-metre (8,986-foot) mountain summit located 74 km (46 mi) southwest of Calgary in Kananaskis Country of Alberta, Canada. Pyriform Mountain is the third-highest officially named peak in the Highwood Range which is a subrange of the Canadian Rockies. Precipitation runoff from the mountain's west slope drains into headwaters of Junction Creek which is a tributary of the Sheep River; and the east slope drains to Trap Creek which is a tributary of the Highwood River. Topographic relief is modest as the summit rises approximately 740 m (2,430 ft) above Junction Creek in 2 km (1.2 mi).



















