| Normandien Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Induan | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Unit of | Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone Beaufort Group [1] |
| Sub-units | Harrismith Member |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Sandstone [2] |
| Location | |
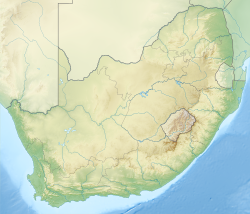
| Coordinates | 28°36′S29°06′E / 28.6°S 29.1°E |
| Approximate paleocoordinates | 66°18′S10°48′W / 66.3°S 10.8°W |
| Region | Free State, KwaZulu-Natal |
| Country | South Africa |
The Normandien Formation is a Triassic-age rock formation located in Free State, South Africa. [2] It is where the fossils of Ericiolacerta, a subtaxa of Ericiolacertidae, [2] were found. [2]